Can Uterine Cancer be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment success depends on the stage at diagnosis and the extent of the cancer; outcomes improve with early detection and intervention
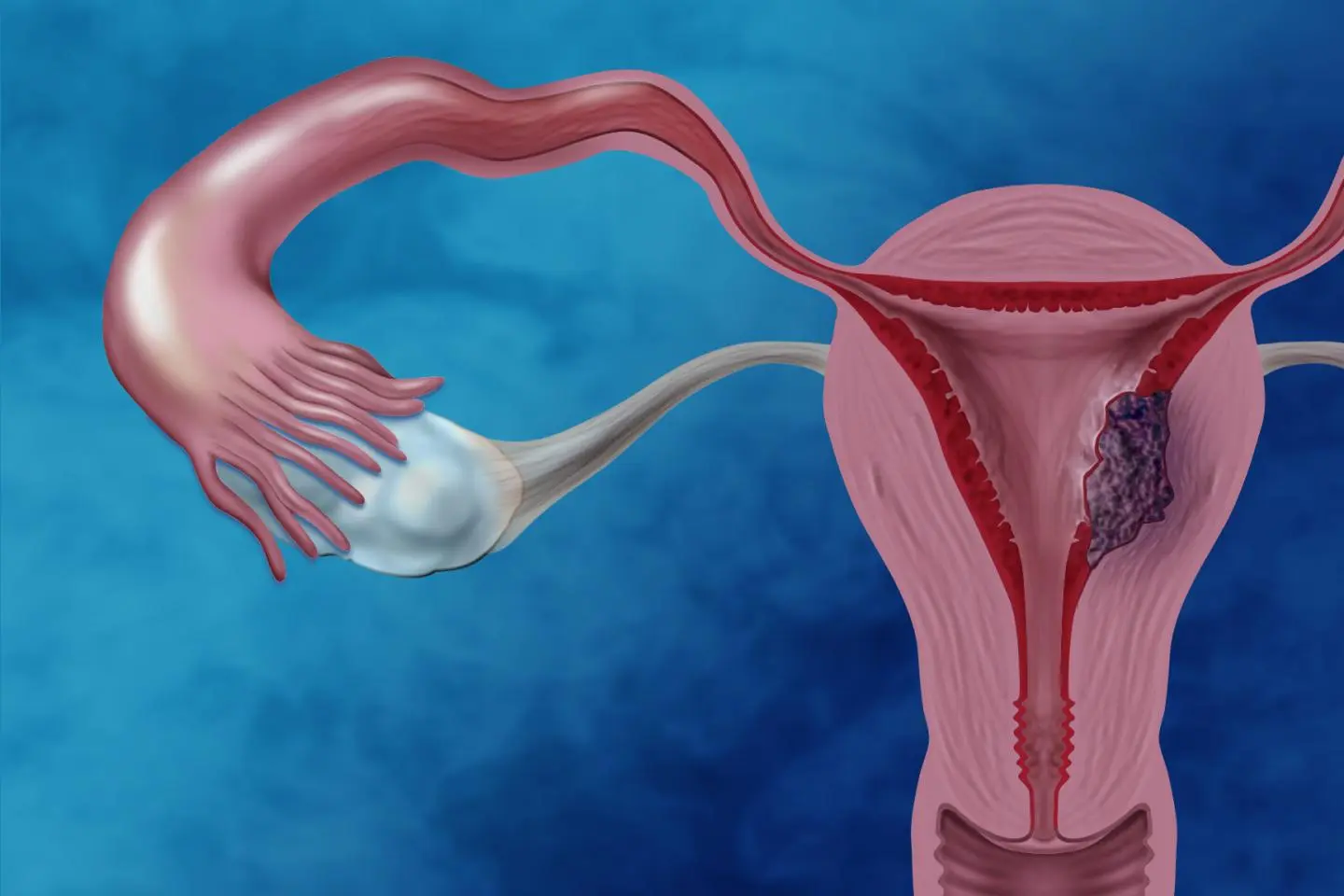
What is Uterine Cancer?
Uterine cancer is cancer that develops in the uterus. Treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or hormone therapy. Regular monitoring is crucial for assessing the response to treatment, detecting recurrences, and managing potential complications.
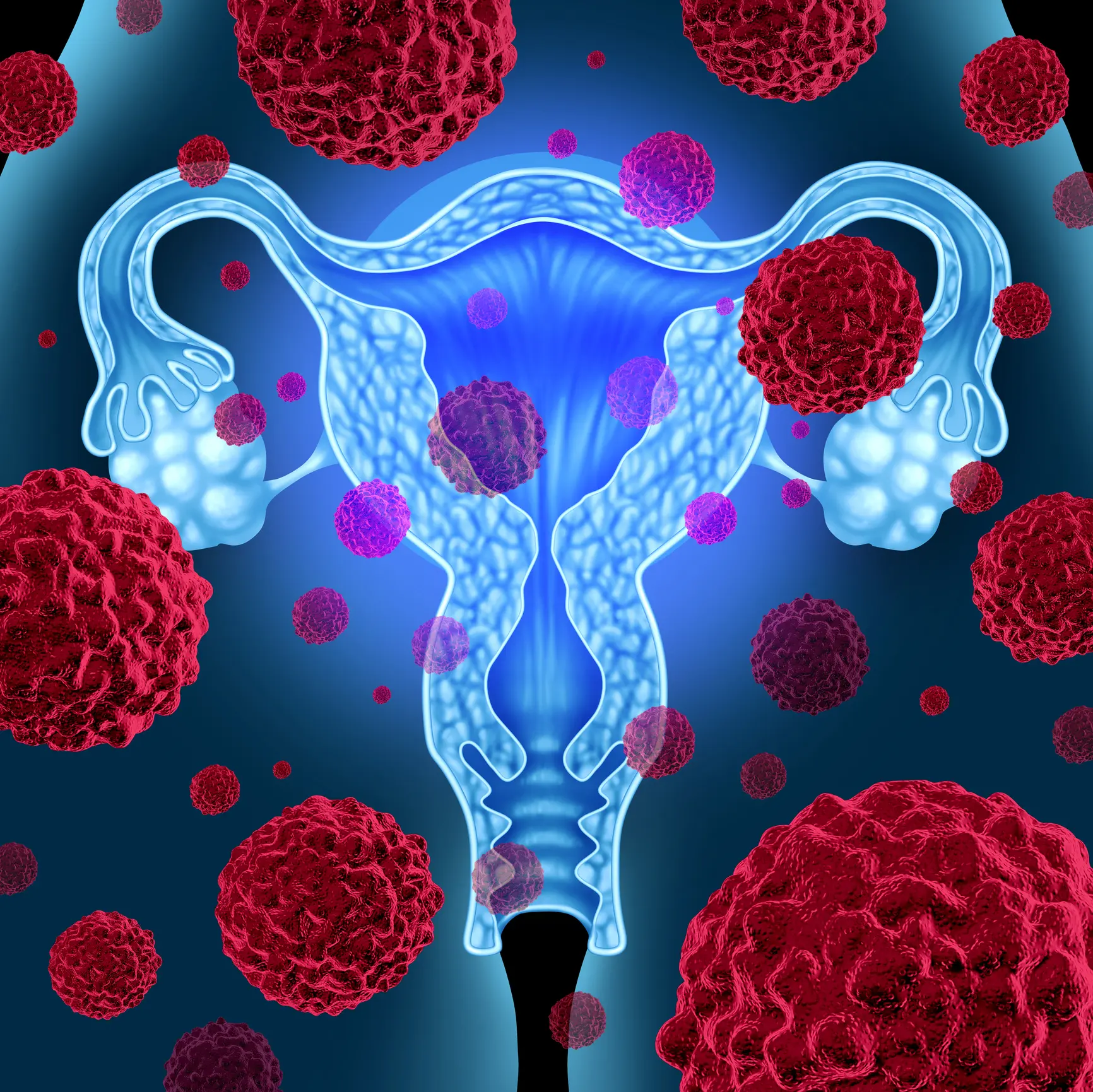
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Cancer that begins in the lining of the uterus

Symptoms
Abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, pain during intercourse

Diagnosis
Biopsy, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the stage and interventions

Complications
Cancer spread, complications affecting adjacent structures
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Hormonal factors, genetic mutations, obesity, age

Treatments
Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy

Prevention
Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Cancer of the uterus

Patient Perspectives
Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, supportive care
Remember, the information provided here is intended for general knowledge purposes and may not apply to every individual case. To ensure you have accurate information relevant to your specific situation, always consult with a healthcare professional.
Share: