Can Vulval Cancer be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment success depends on the stage at diagnosis and the extent of the cancer; outcomes improve with early detection and intervention

What is Vulval Cancer?
Vulval cancer is cancer that develops in the vulva. Treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination. Regular monitoring is crucial for assessing the response to treatment, detecting recurrences, and managing potential complications.
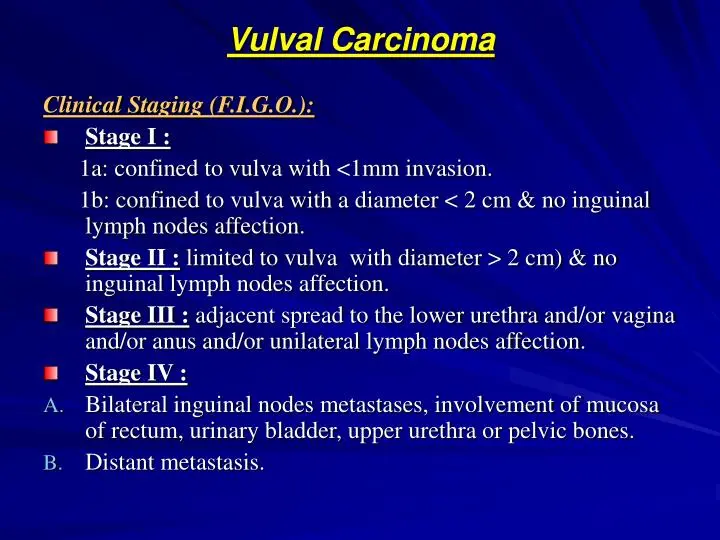
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Cancer that begins in the vulva, the external female genitalia

Symptoms
Itching, pain, changes in skin color or texture, lumps or sores

Diagnosis
Clinical examination, sometimes biopsy

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the stage and response to treatment

Complications
Spread of cancer, complications of untreated vulval cancer
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, age, smoking, immune system suppression

Treatments
Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy

Prevention
Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Cancer affecting the external female genitalia

Patient Perspectives
Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes
This information serves as a general overview and does not constitute professional medical advice. Always consult with healthcare providers for accurate and personalized insights regarding your health.
Share: