Can Scleroderma be Cured?
No (manageable)
No cure; management focuses on controlling symptoms, preventing complications
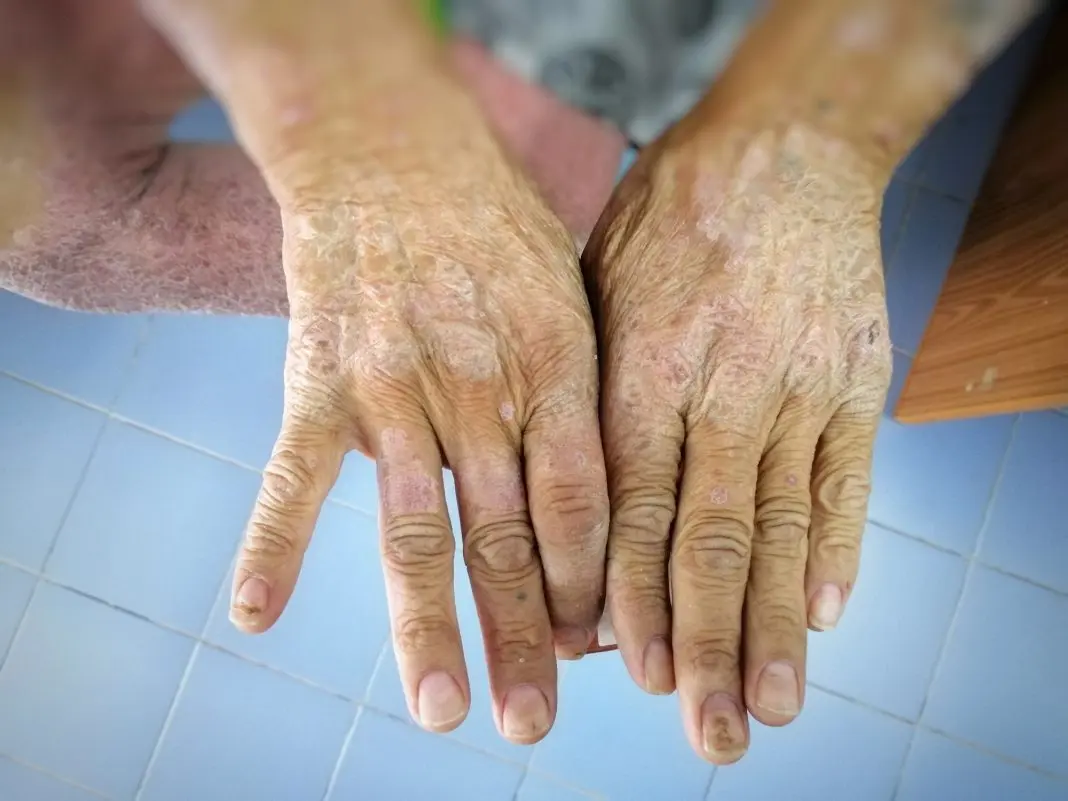
What is Scleroderma?
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that result in skin thickening and connective tissue damage. Treatment varies and may include medications to manage symptoms.
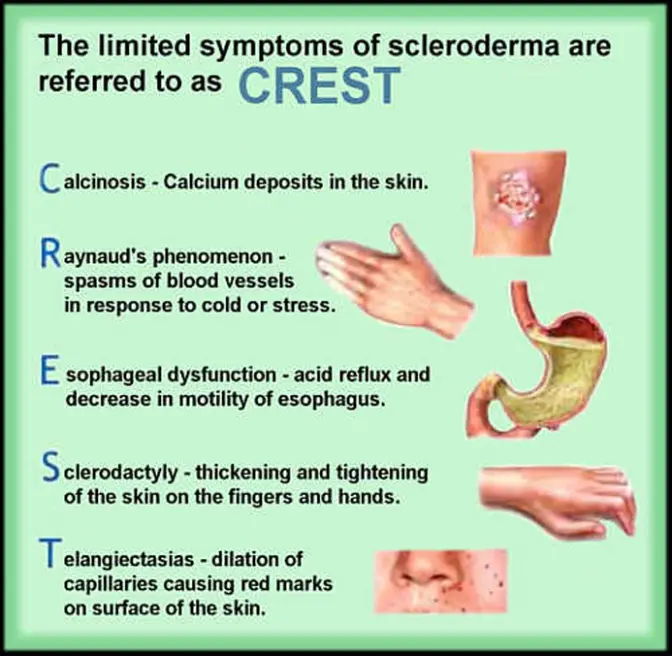
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Chronic autoimmune disease affecting the skin and internal organs

Symptoms
Skin thickening, Raynaud’s phenomenon, internal organ involvement

Diagnosis
Clinical examination, sometimes blood tests

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the progression and response to treatment

Complications
Organ damage, complications of untreated scleroderma
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Unknown (immune system dysfunction)

Treatments
Medications (immunosuppressants), physical therapy, supportive care

Prevention
Medications (immunosuppressants), physical therapy, supportive care
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Autoimmune disease causing skin and connective tissue problems

Patient Perspectives
Management focuses on symptom relief and preventing complications
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: