Can Systemic Sclerosis be Cured?
No (manageable)
No cure; management aims to control symptoms, prevent complications
What is Systemic Sclerosis?
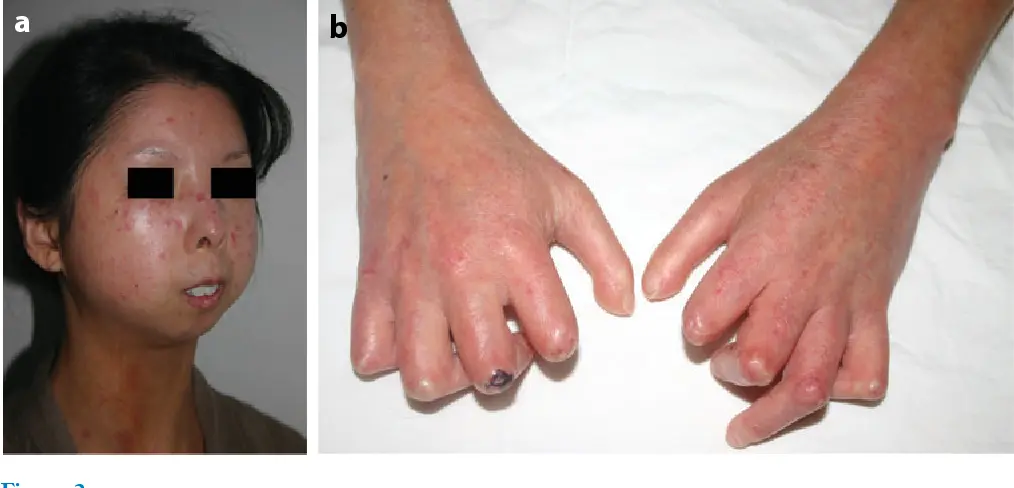
Systemic sclerosis, or scleroderma, is a rare autoimmune disease that leads to hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues. Treatment involves managing symptoms and may include medications.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
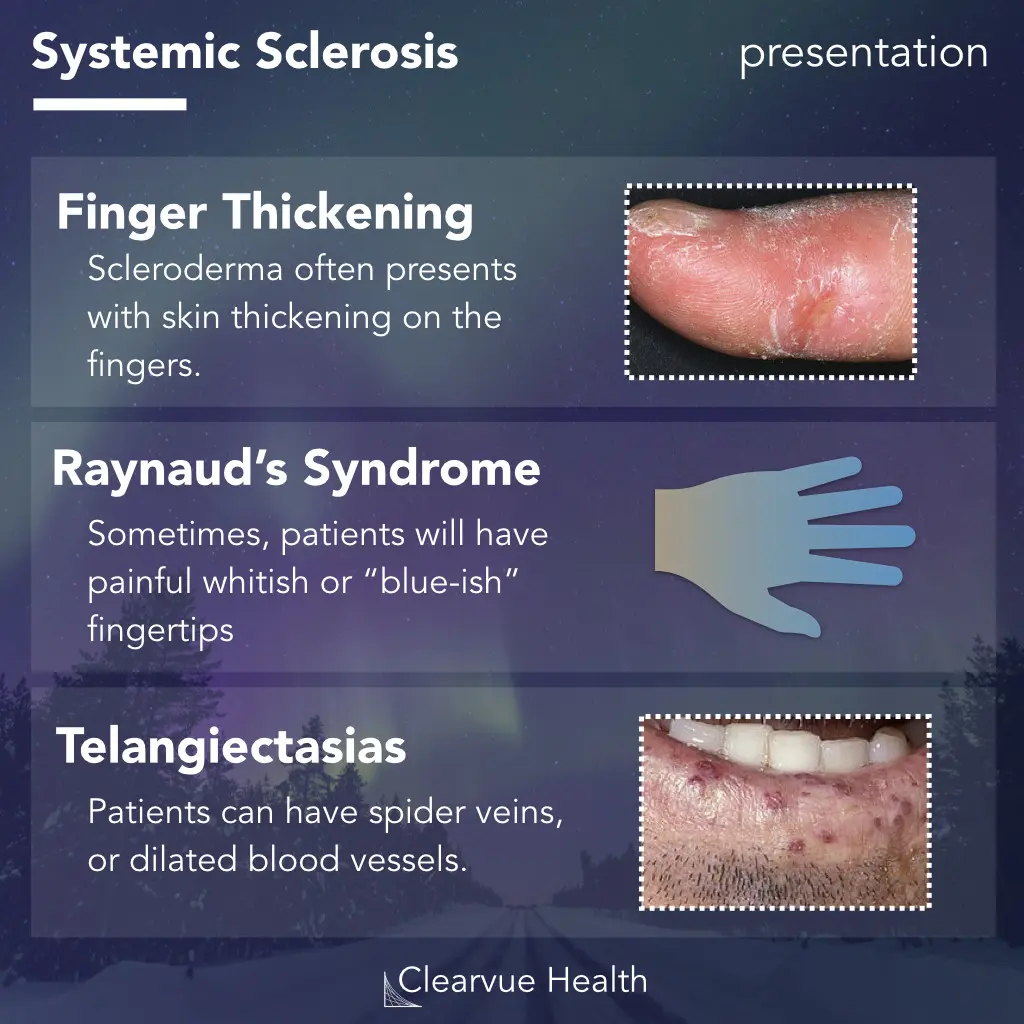
Connective tissue disorder causing fibrosis and vascular abnormalities

Symptoms
Skin thickening, Raynaud’s phenomenon, internal organ involvement

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the progression and response to treatment

Complications
Organ damage, complications of untreated systemic sclerosis
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Unknown (likely autoimmune)

Treatments
Medications (immunosuppressants), symptom management, physical therapy, lifestyle adjustments

Prevention
Medications (immunosuppressants), symptom management, physical therapy, lifestyle adjustments
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Autoimmune disease causing thickening and scarring of connective tissue

Patient Perspectives
Management focuses on symptom relief and preventing complications
While the information presented here reflects the current knowledge about these conditions and treatments, it’s important to understand that individual cases may differ. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Share: