Can Rheumatoid Arthritis be Cured?
No
While there is no cure, treatment can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression; outcomes vary, and early intervention is important for better results
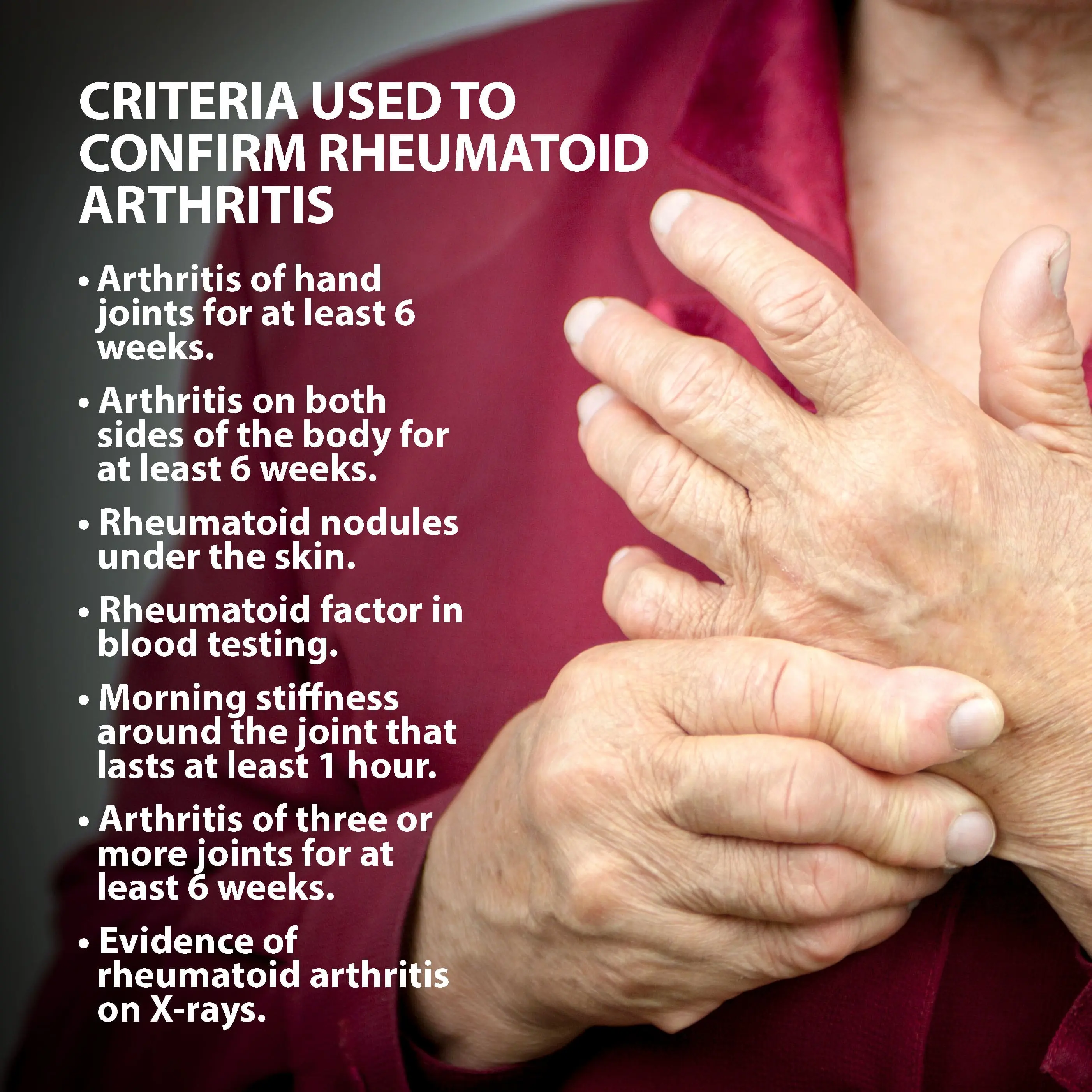
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory joint disorder. Treatment includes medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Regular monitoring is important for assessing disease activity, managing symptoms, and adjusting treatment as needed.
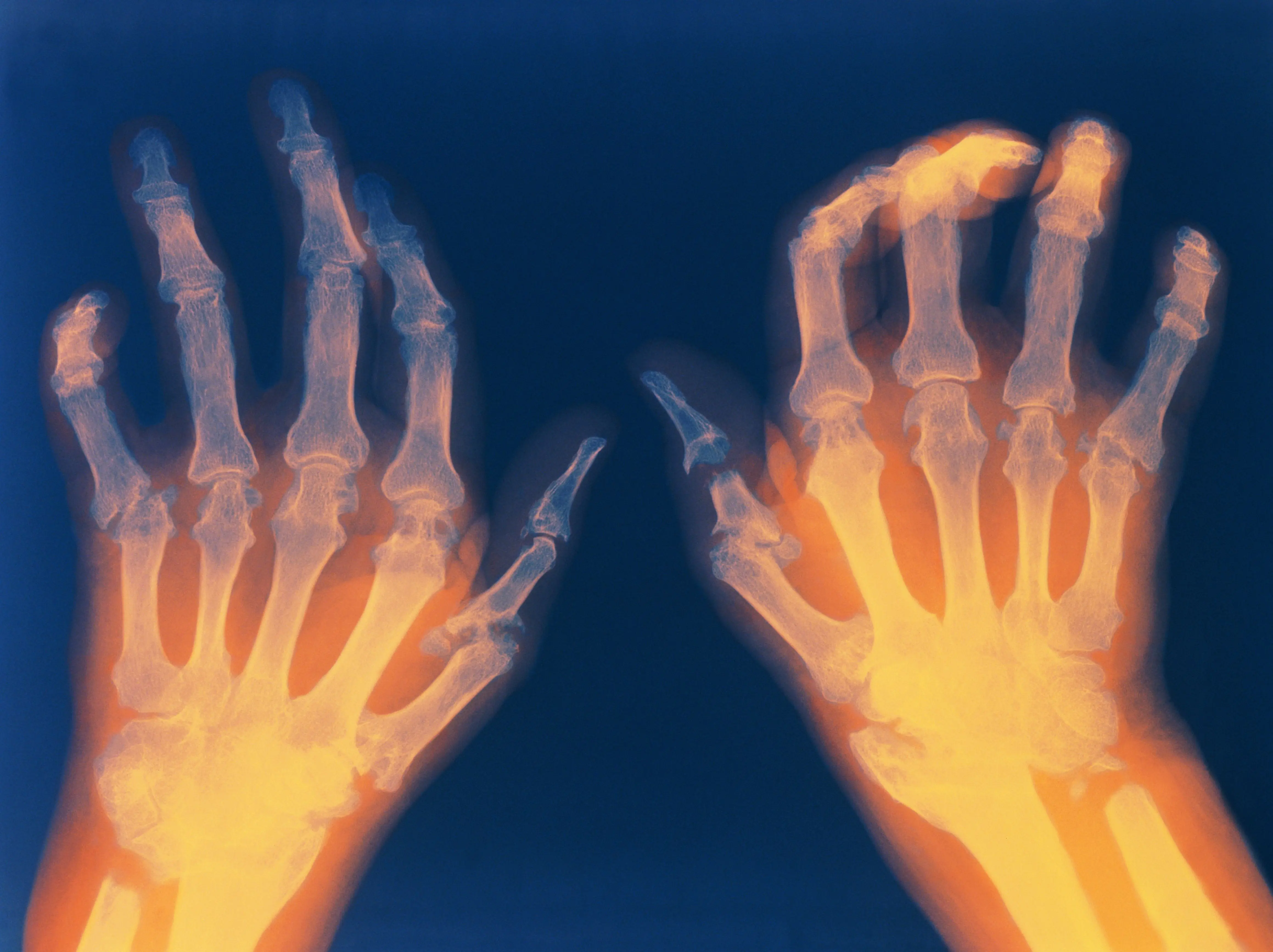
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Autoimmune disorder causing inflammation in the joints

Symptoms
Joint pain, swelling, stiffness, fatigue

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the progression of the disease

Complications
Joint damage, complications affecting multiple organs
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Autoimmune factors, genetic predisposition

Treatments
Medications (DMARDs, NSAIDs), physical therapy, lifestyle modifications

Prevention
Medications (DMARDs, NSAIDs), physical therapy, lifestyle modifications
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Chronic inflammatory joint disease

Patient Perspectives
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, supportive care
This information serves as a general overview and does not constitute professional medical advice. Always consult with healthcare providers for accurate and personalized insights regarding your health.
Share: