Can Ovarian Cancer be Cured?
Sometimes
Outcomes depend on the stage at diagnosis, response to treatment, and whether the cancer has spread; early detection and treatment improve the chances of successful outcomes
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer is cancer that begins in the ovaries. Treatment typically involves surgery, chemotherapy, and sometimes radiation therapy. Early detection is challenging, so awareness of symptoms and regular gynecological check-ups are crucial. Prognosis varies based on factors such as the stage and type of ovarian cancer. Ongoing monitoring is important for assessing treatment response and detecting potential recurrence.
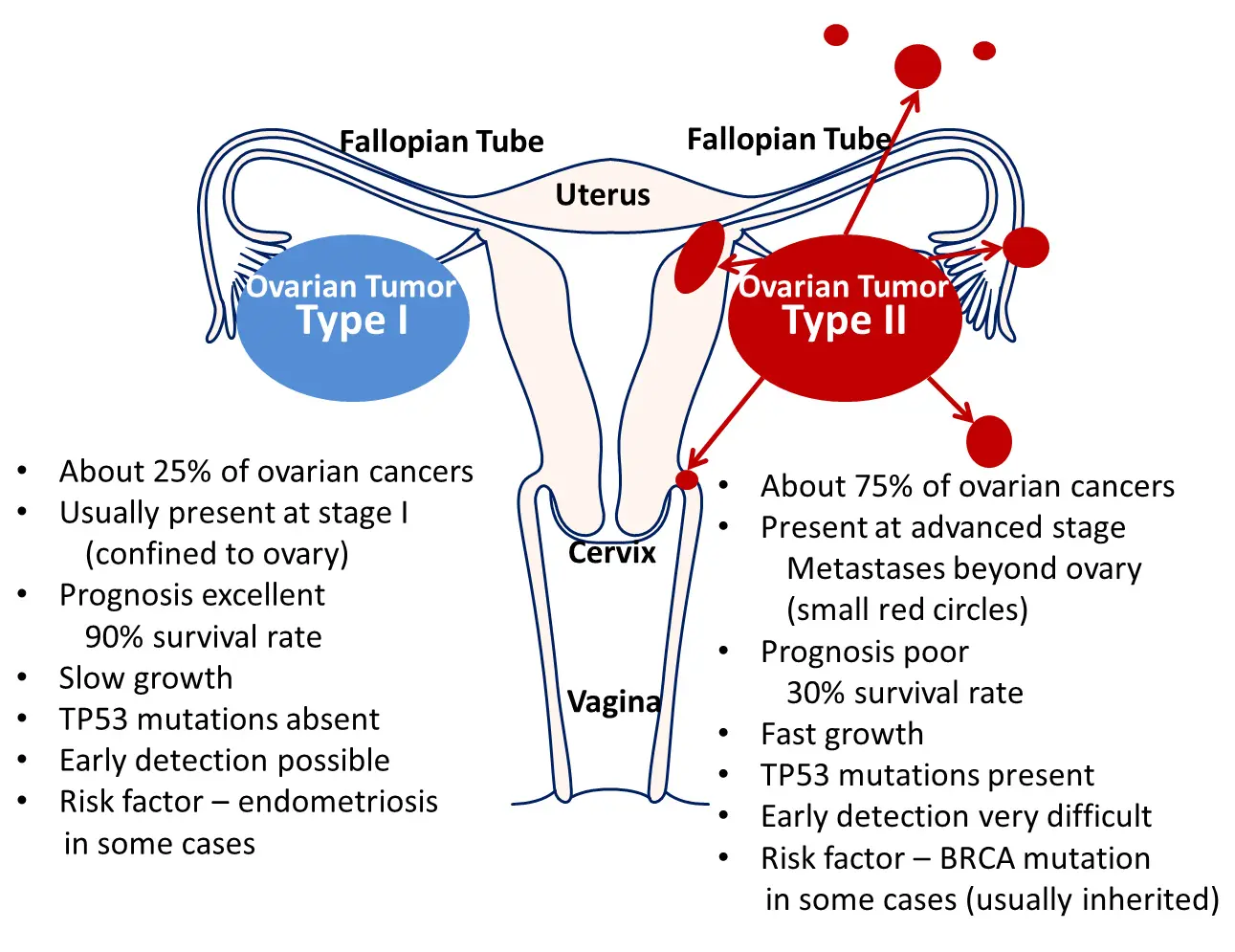
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Cancer that forms in the ovaries

Symptoms
Abdominal pain or swelling, bloating, changes in bowel or urinary habits, fatigue

Diagnosis
Imaging studies, sometimes biopsy

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the stage and response to treatment

Complications
Metastasis, complications of untreated cancer
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic mutations (BRCA1, BRCA2), family history, aging, hormonal factors, endometriosis

Treatments
Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, hormone therapy

Prevention
Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, hormone therapy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Cancer affecting the ovaries

Patient Perspectives
Prognosis varies based on the stage and response to treatment
This information is for general understanding and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with healthcare providers for accurate and personalized information related to your health.
Share: