Can Neuropathic Pain be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment can manage symptoms, but a complete cure may not always be achievable; outcomes depend on the underlying cause, response to treatment, and the management of contributing factors
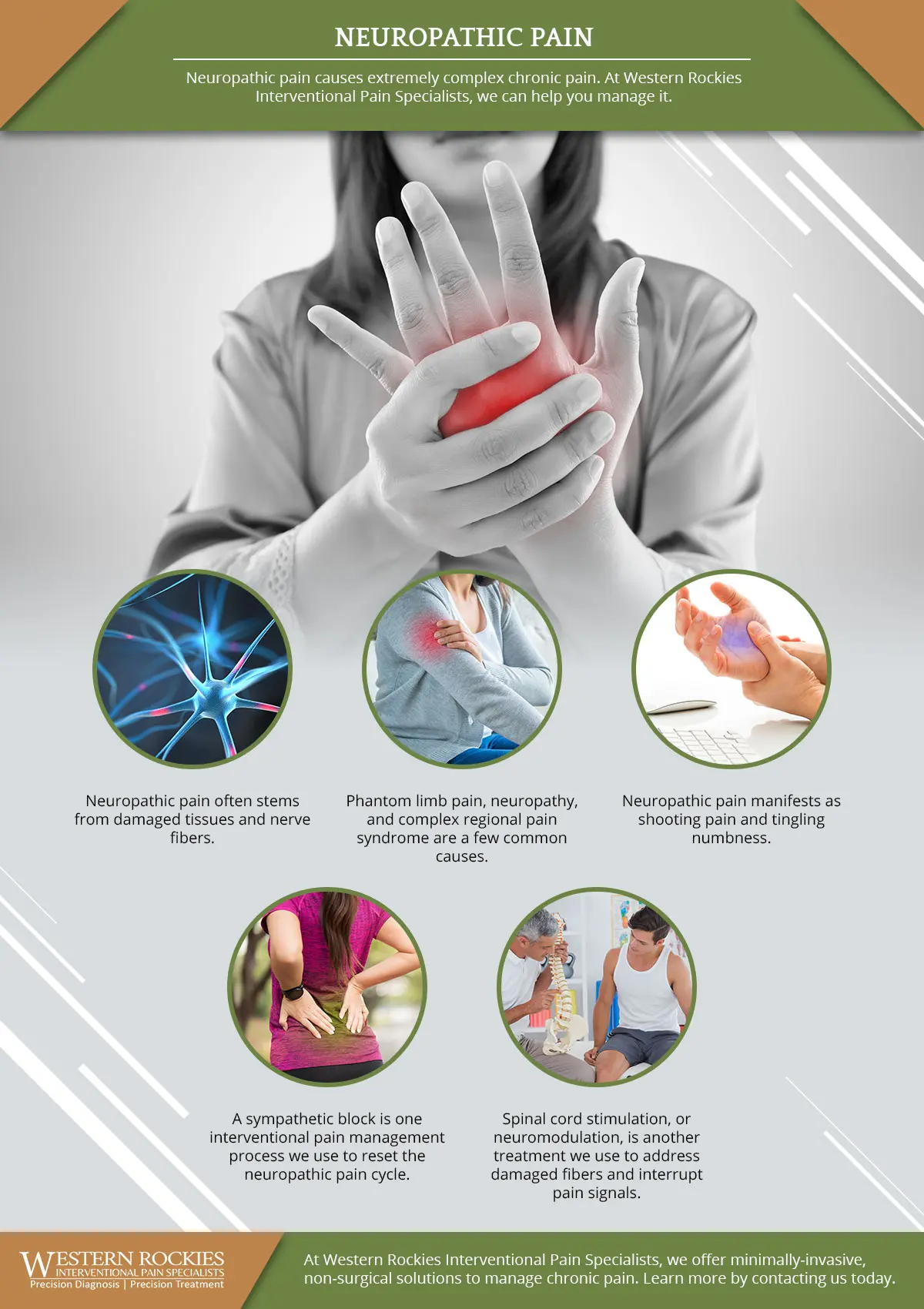
What is Neuropathic Pain?
Neuropathic pain is pain caused by damage or dysfunction of the nervous system. It can result from conditions such as diabetes or nerve injuries. Treatment involves medications to manage pain, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. A multidisciplinary approach may be used to address the diverse aspects of neuropathic pain. Regular follow-up is important to assess treatment efficacy and adjust interventions as needed.
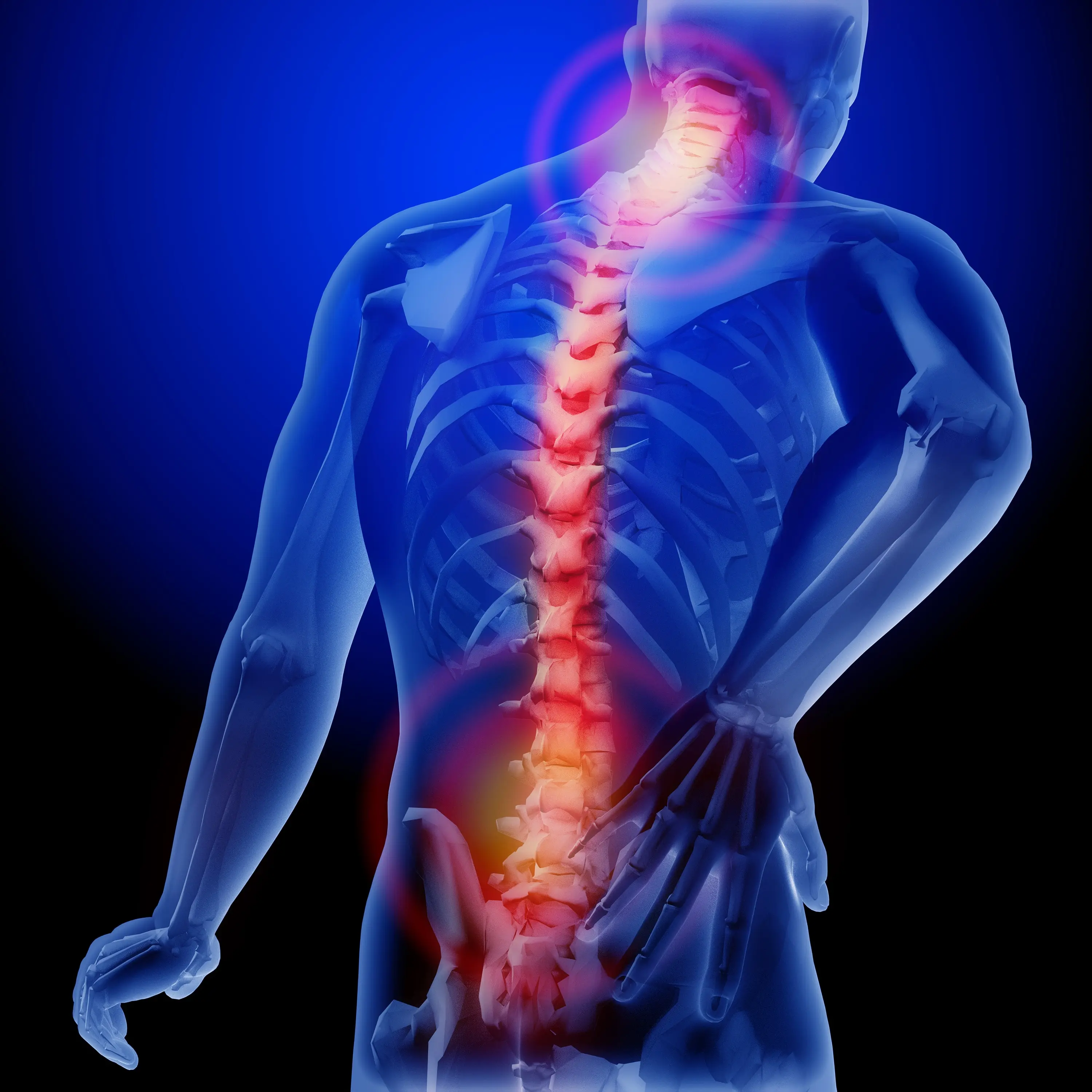
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Chronic pain caused by nerve damage or dysfunction

Symptoms
Burning, shooting pain, tingling, numbness

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, sometimes imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the underlying cause and response to treatment

Complications
Impaired quality of life, complications affecting daily activities
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Diabetes, nerve compression, autoimmune diseases, infections, trauma, certain medications

Treatments
Medications (antidepressants, anticonvulsants, pain relievers), physical therapy, nerve blocks, spinal cord stimulation

Prevention
Medications (antidepressants, anticonvulsants, pain relievers), physical therapy, nerve blocks, spinal cord stimulation
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Chronic pain due to nerve dysfunction

Patient Perspectives
Medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications
This information aims to provide a general understanding of the subject matter, but individual circumstances can vary significantly. Please remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Share: