Can Neuromyelitis Optica be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment can manage symptoms and prevent relapses, but a complete cure may not be possible; outcomes vary, and long-term management is often necessary
What is Neuromyelitis Optica?
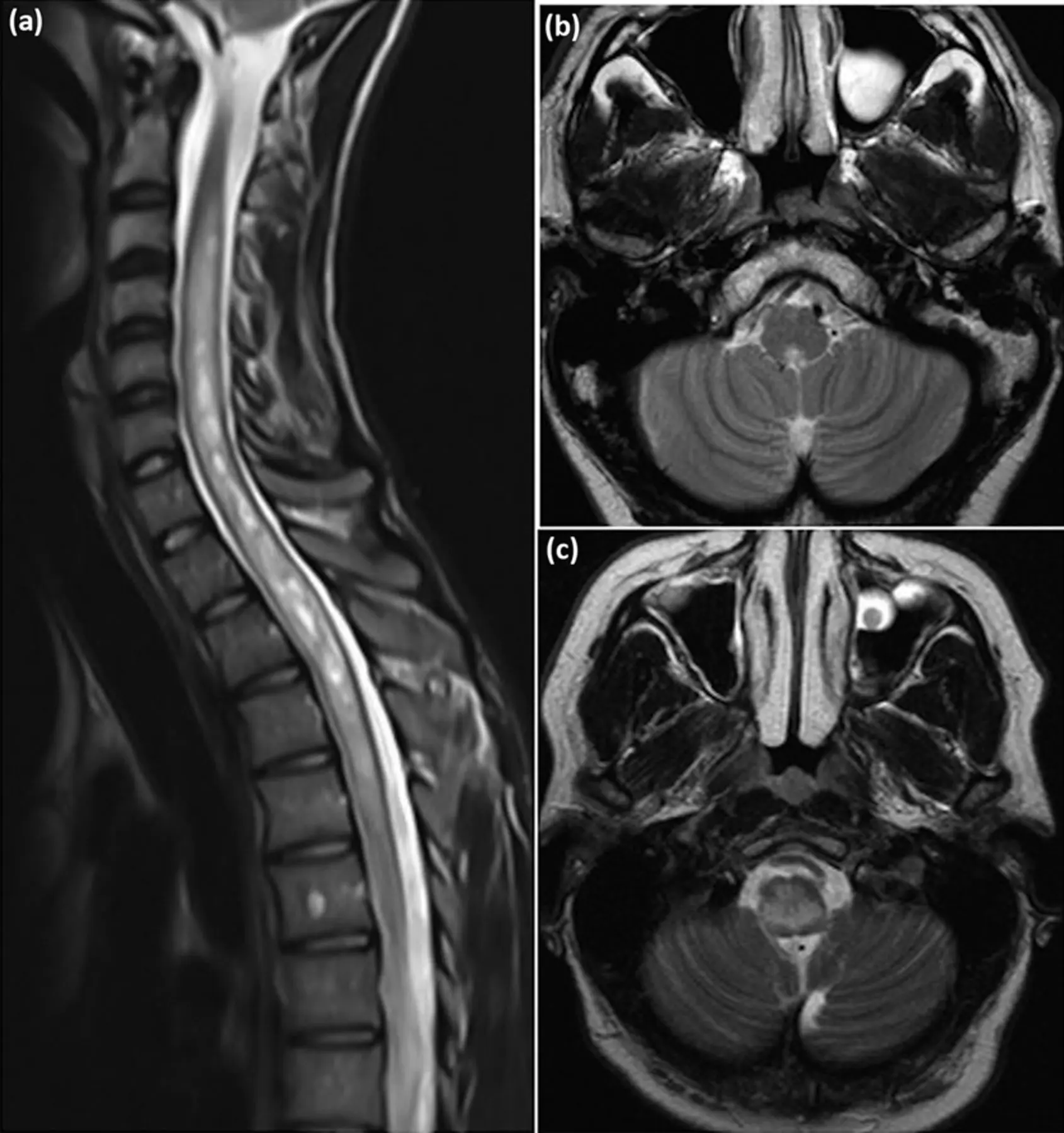
Neuromyelitis optica is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the optic nerves and spinal cord. Treatment involves immunosuppressive medications to reduce the risk of relapses. Ongoing monitoring is crucial to manage symptoms and adjust treatment as needed. Neuromyelitis optica can have varying courses, and a multidisciplinary approach may be used to address the diverse aspects of the condition.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Autoimmune disorder affecting the central nervous system, particularly the optic nerves and spinal cord

Symptoms
Optic neuritis (vision loss), transverse myelitis (spinal cord inflammation), neurological symptoms

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the severity and response to treatment

Complications
Neurological deficits, complications affecting daily life
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Autoimmune response targeting aquaporin-4, genetic and environmental factors

Treatments
Immunosuppressive medications (corticosteroids, immunosuppressants), plasma exchange, symptomatic treatment

Prevention
Immunosuppressive medications (corticosteroids, immunosuppressants), plasma exchange, symptomatic treatment
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Autoimmune disorder affecting the optic nerves and spinal cord

Patient Perspectives
Immunotherapy, corticosteroids, management of symptoms
This information is for general understanding and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with healthcare providers for accurate and personalized information related to your health.
Share: