Can Nerve Palsy be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment aims to improve function and manage symptoms; outcomes depend on the cause and extent of nerve damage
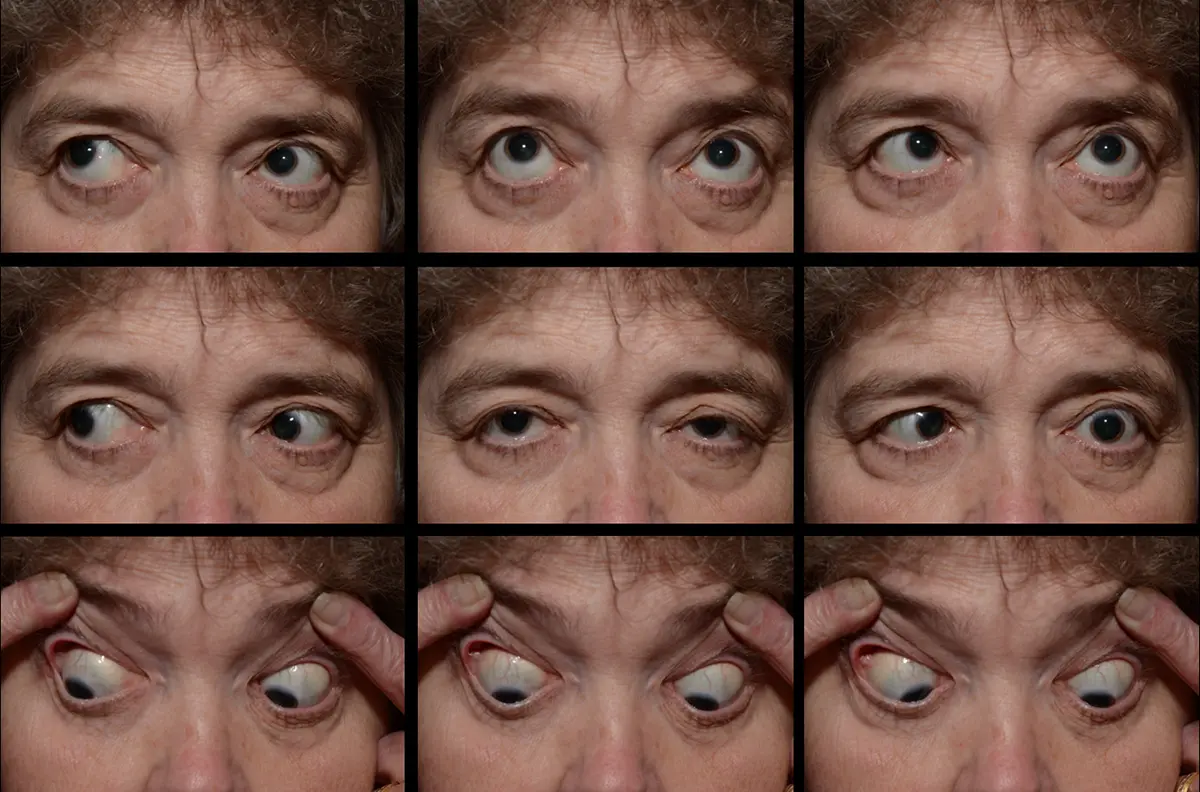
What is Nerve Palsy?
Nerve palsy refers to the loss of voluntary muscle control due to damage or impairment of a nerve. Causes may include trauma, infection, or compression. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve physical therapy, medications, or surgical interventions. Prognosis varies based on the severity of nerve damage and the success of treatment.
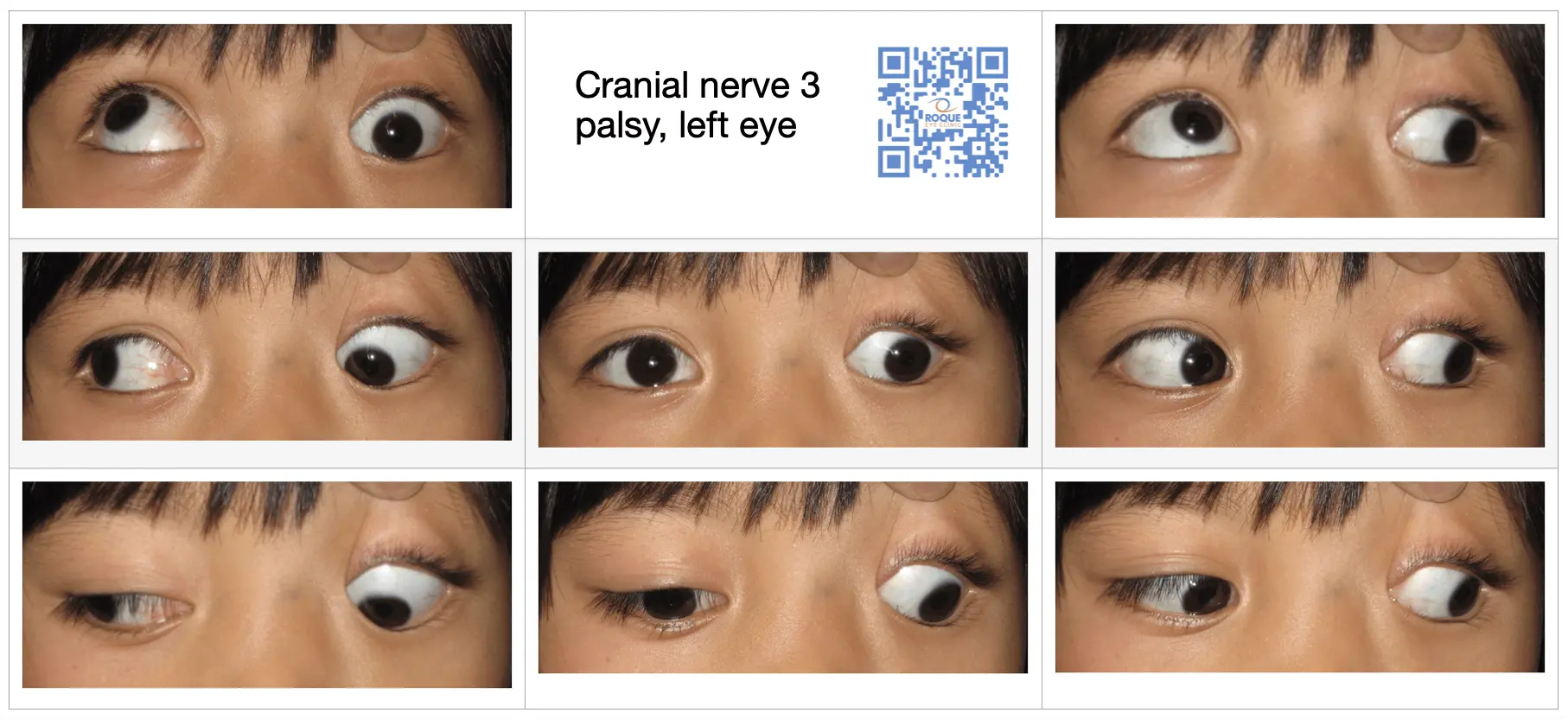
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Partial or complete loss of movement or sensation in a specific area due to nerve damage

Symptoms
Muscle weakness, loss of sensation, pain, tingling

Diagnosis
Prenatal screening, imaging

Prognosis
Variable, depends on severity

Complications
Neurological issues, potential for complications
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Trauma, infections (such as Bell’s palsy), inflammation, tumors, vascular disorders, nerve compression

Treatments
Physical therapy, pain management, medications, surgery (in some cases)

Prevention
Physical therapy, pain management, medications, surgery (in some cases)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common, often related to inadequate folic acid

Patient Perspectives
Lifelong management tailored to specific defects
As always, consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and care.
Share: