Can Mouth Cancer be Cured?
Sometimes
Outcomes depend on the stage, type of cancer, and response to treatment; early detection and intervention improve the chances of successful treatment
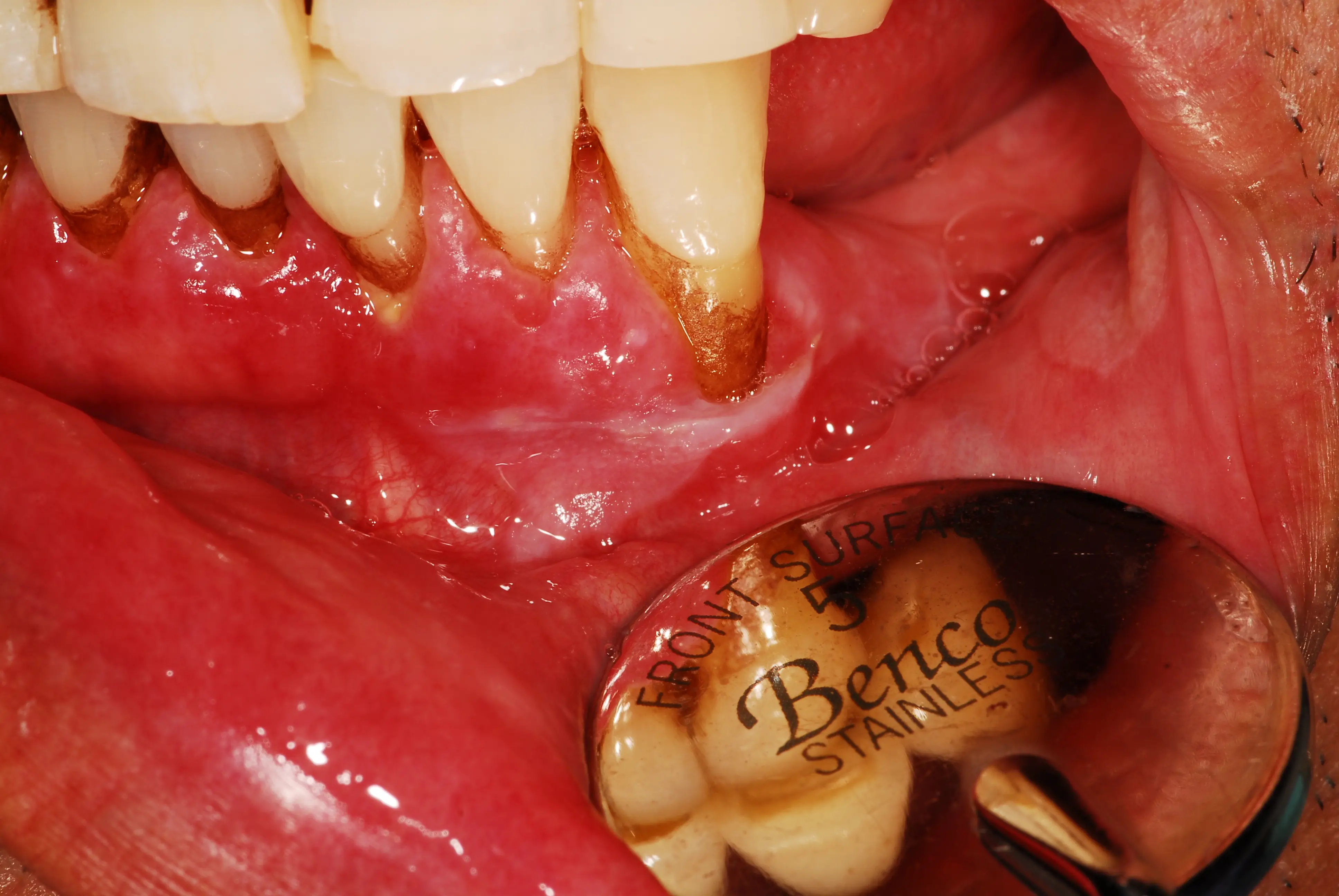
What is Mouth Cancer?
Mouth cancer refers to cancer that occurs in any part of the oral cavity, including the lips, tongue, gums, and palate. Treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the type and stage of the cancer. Early detection through regular dental check-ups and lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking, is crucial for improving outcomes.
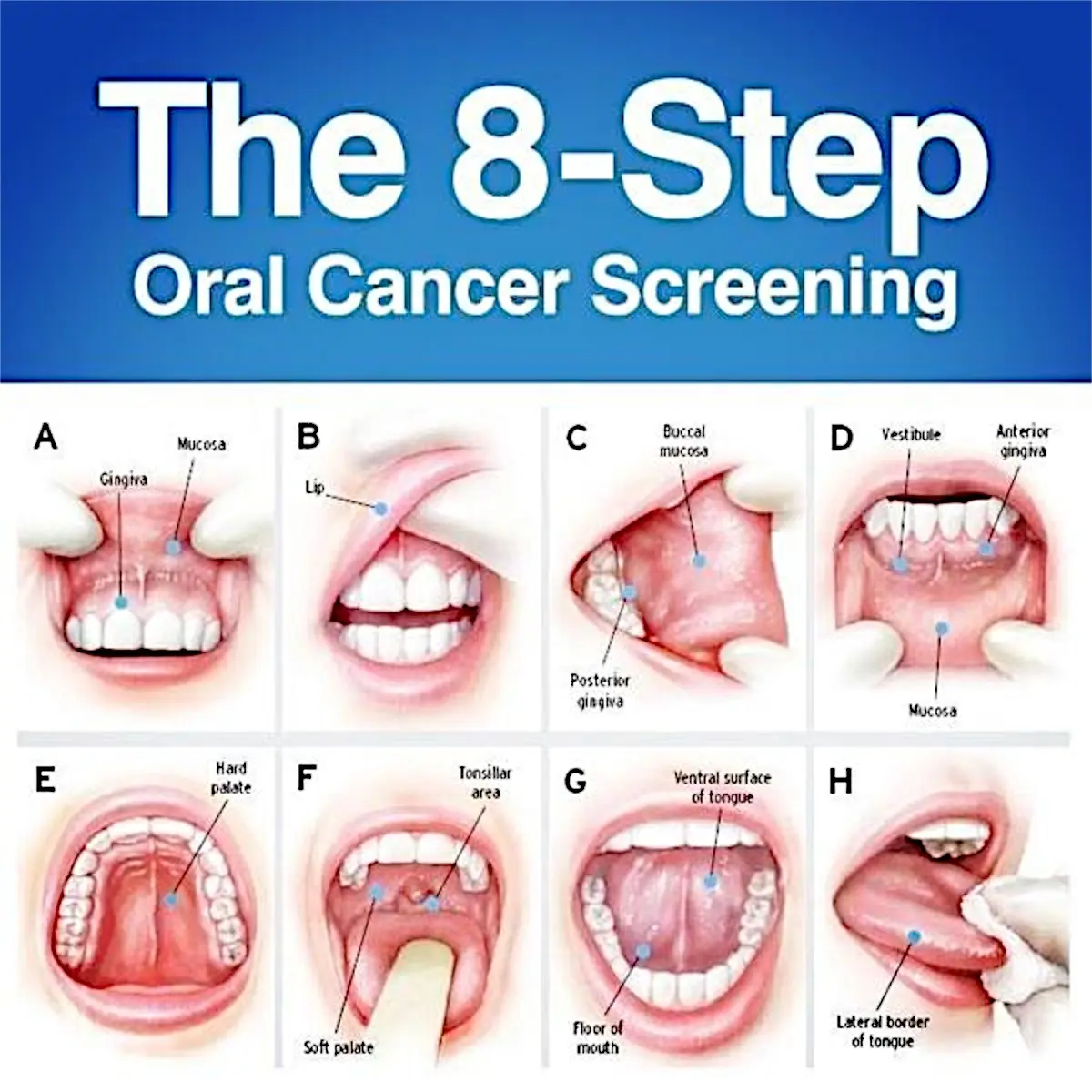
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Cancer that forms in the tissues of the mouth, including the lips, tongue, cheeks, and throat

Symptoms
Persistent mouth sores, pain, difficulty swallowing, changes in voice

Diagnosis
Biopsy, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the stage and response to treatment

Complications
Metastasis, complications of treatment
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, sun exposure

Treatments
Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy

Prevention
Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Cancer affecting the mouth and oral cavity

Patient Perspectives
Prognosis varies based on the stage and response to treatment
While the information presented here reflects the current knowledge about these conditions and treatments, it’s important to understand that individual cases may differ. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Share: