Can Lupus be Cured?
No
Lifelong management involves controlling symptoms and preventing flare-ups; outcomes vary, and there is no cure for lupus
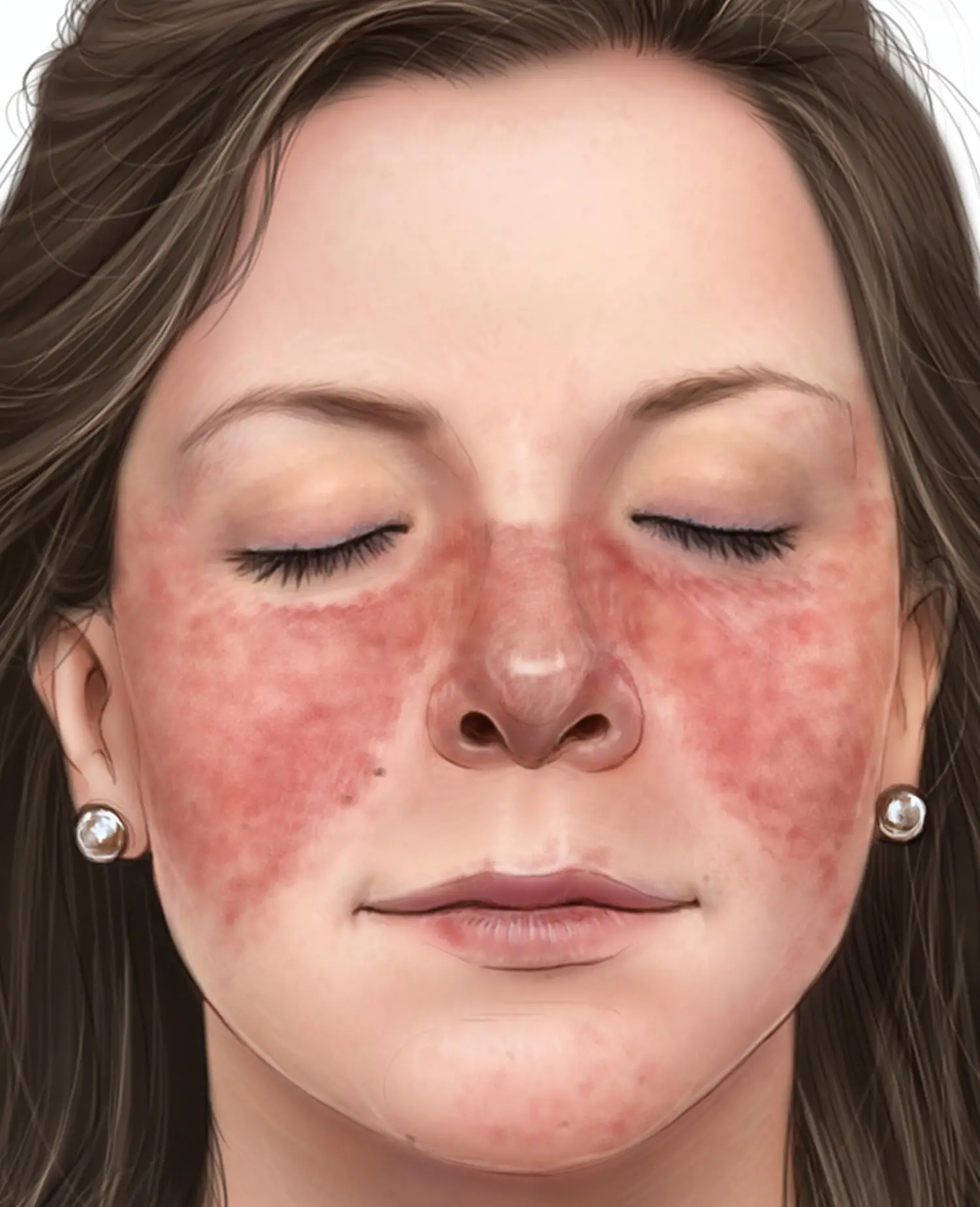
What is Lupus?
Lupus, or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease that can affect various organs. Treatment involves managing symptoms and may include medications like corticosteroids and immunosuppressants.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Systemic autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks healthy tissues and organs

Symptoms
Joint pain, skin rash (butterfly rash), fatigue, fever, organ involvement (kidneys, heart, lungs)

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, blood tests, sometimes biopsy

Prognosis
Variable, depends on disease activity

Complications
Organ involvement, potential for complications
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors; often triggered by infections, sunlight, medications

Treatments
Medications (anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants), lifestyle changes, managing specific symptoms

Prevention
Medications (anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants), lifestyle changes, managing specific symptoms
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common, more prevalent in females

Patient Perspectives
Lifelong management tailored to disease activity
This information is for general understanding and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with healthcare providers for accurate and personalized information related to your health.
Share: