Can Hepatocellular Carcinoma be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment options depend on factors such as tumor size, location, and overall health; outcomes vary, and early detection and intervention are crucial; prevention and management of underlying liver conditions can reduce the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma
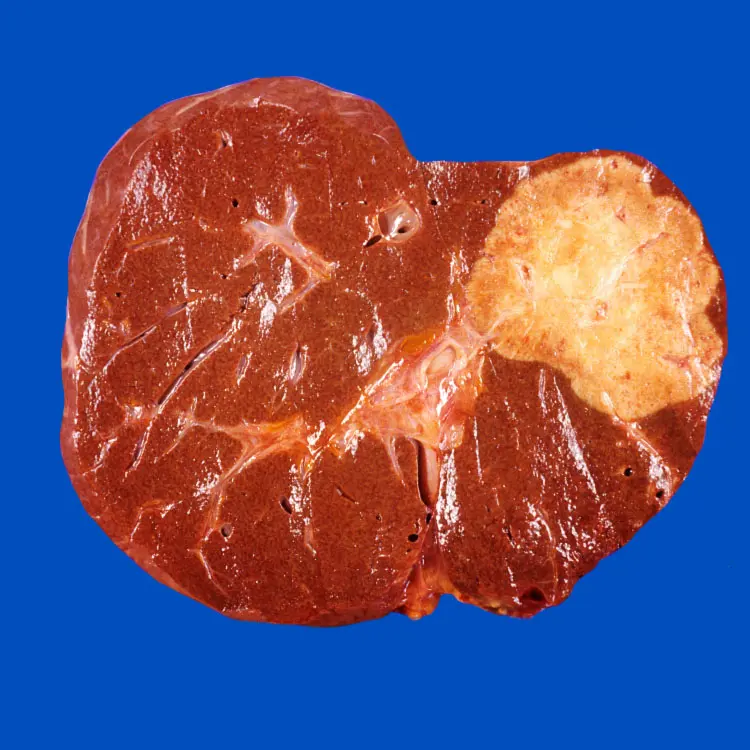

What is Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a type of liver cancer that often develops in individuals with chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis. Symptoms may include abdominal pain and weight loss. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Primary liver cancer originating in the hepatocytes

Symptoms
Abdominal pain, weight loss, jaundice, swelling in the abdomen

Diagnosis
Imaging studies, sometimes biopsy

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the stage and interventions

Complications
Cancer spread, complications affecting liver function
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis B or C infection, alcohol-related liver disease, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease

Treatments
Surgery, liver transplant, chemotherapy, targeted therapy

Prevention
Surgery, liver transplant, chemotherapy, targeted therapy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Primary cancer of the liver

Patient Perspectives
Surgery, liver transplant, chemotherapy
Please remember that this information is provided for general understanding, and individual cases may vary. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and information.
Share: