Can Acoustic Neuroma be Cured?
Maybe
Treatment can control symptoms and halt tumor growth, but complete removal may not always be possible; outcomes depend on factors like tumor size and location

What is Acoustic Neuroma?
Acoustic neuroma is a noncancerous tumor on the vestibular nerve in the inner ear. Treatment options include observation, radiation therapy, or surgery. Regular monitoring is crucial for assessing tumor growth and managing symptoms.
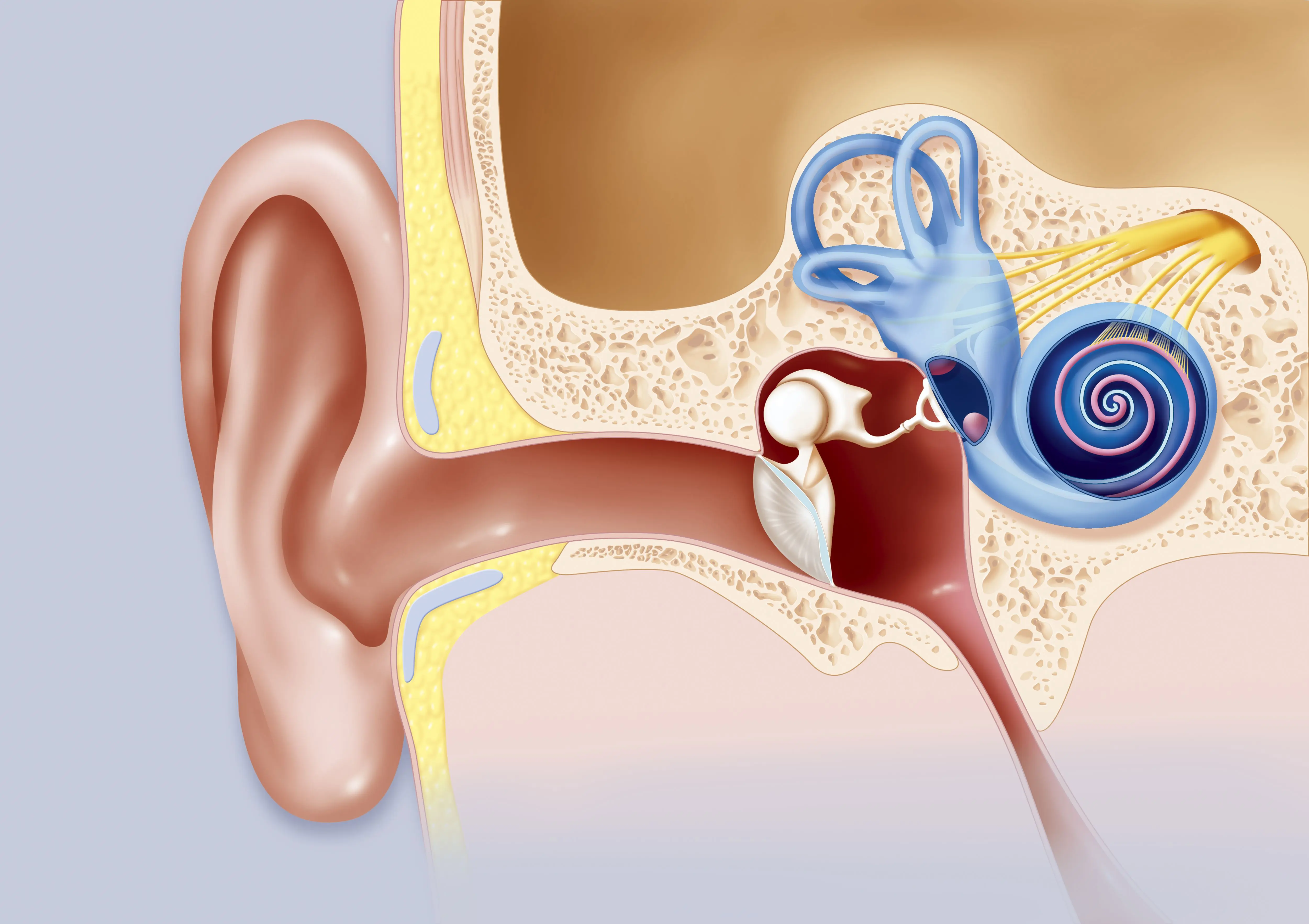
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Benign tumor on the vestibular nerve affecting hearing and balance

Symptoms
Gradual hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), imbalance, facial numbness

Diagnosis
MRI, audiometry, electronystagmography

Prognosis
Generally slow-growing; outcomes vary depending on size and location

Complications
Hearing loss, tinnitus, imbalance
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Usually caused by a malfunctioning gene (NF2), often arises spontaneously

Treatments
Observation, surgery, radiation therapy depending on size and symptoms

Prevention
Observation, surgery, radiation therapy depending on size and symptoms
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Relatively rare; most commonly diagnosed in adults aged 30-60

Patient Perspectives
Early diagnosis and monitoring are crucial for better outcomes
This information aims to provide a general understanding of the subject matter, but individual circumstances can vary significantly. Please remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Share: