Can Horner’s Syndrome be Cured?
Depends on cause
Management focuses on addressing the underlying cause; may be reversible in some cases
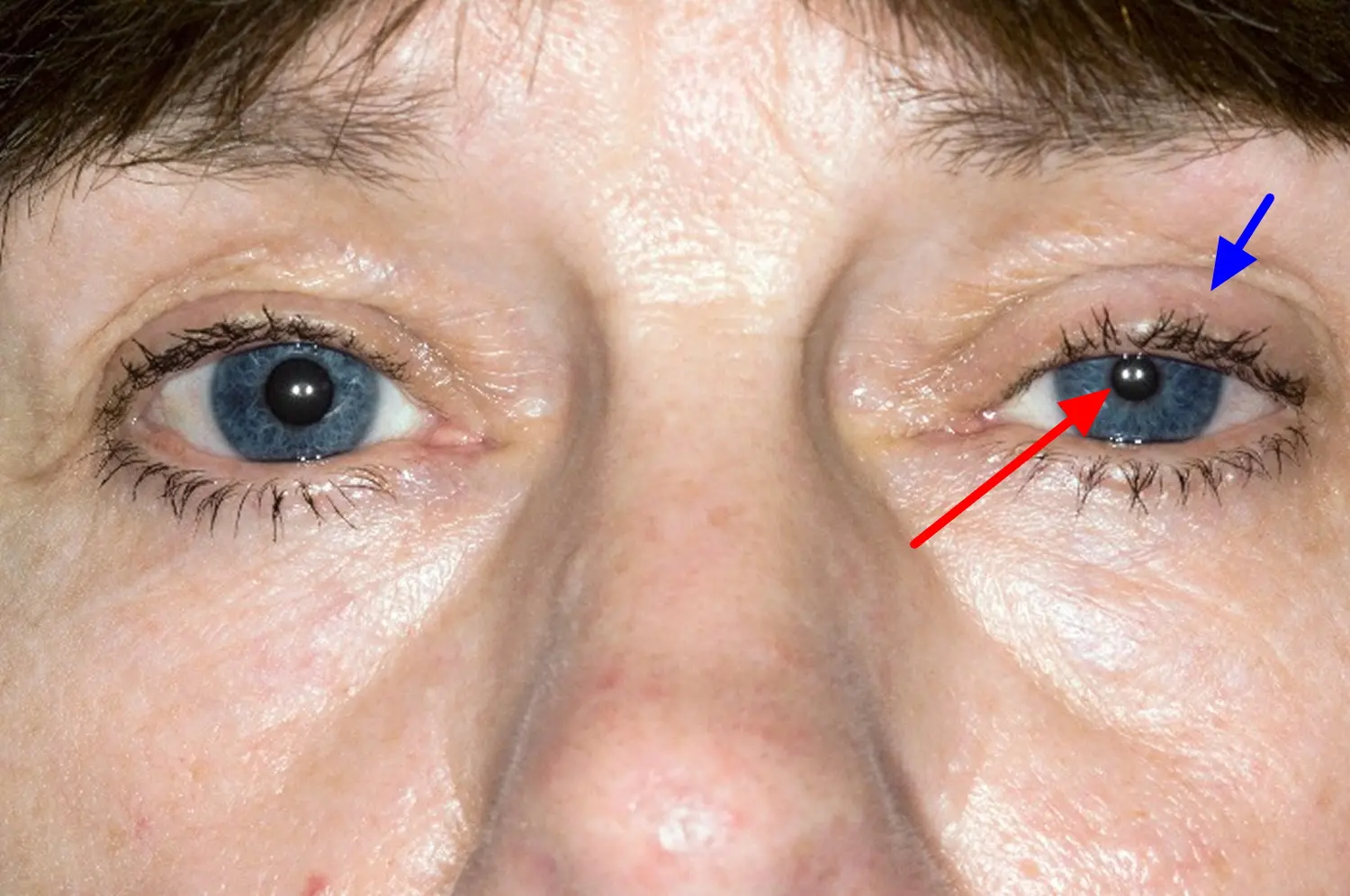
What is Horner’s Syndrome?
Horner’s syndrome is a neurological condition characterized by a group of signs, including ptosis (drooping of the upper eyelid) and miosis (constricted pupil). The underlying cause determines the treatment approach.
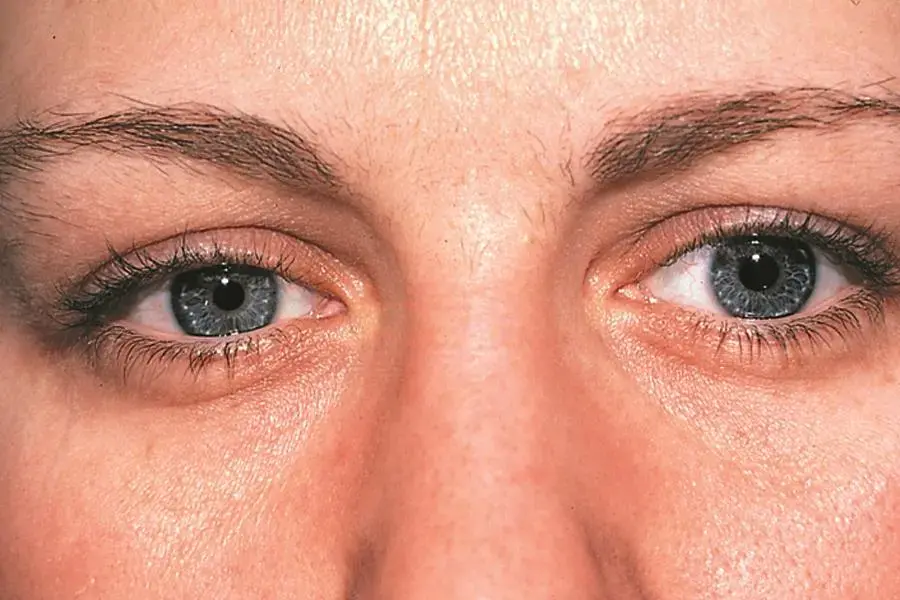
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Neurological syndrome affecting the eye and facial muscles

Symptoms
Ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis

Diagnosis
Clinical examination, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the underlying cause and response to treatment

Complications
Ptosis, complications of untreated syndrome
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Nerve pathway disruption

Treatments
Addressing underlying cause, supportive care

Prevention
Addressing underlying cause, supportive care
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Disruption of sympathetic nerve pathway

Patient Perspectives
Management focuses on addressing the underlying cause
Remember, the information provided here is intended for general knowledge purposes and may not apply to every individual case. To ensure you have accurate information relevant to your specific situation, always consult with a healthcare professional.
Share: