Can Thyroiditis be Cured?
Sometimes
Management is possible with medication, but some cases may progress to chronic thyroid dysfunction

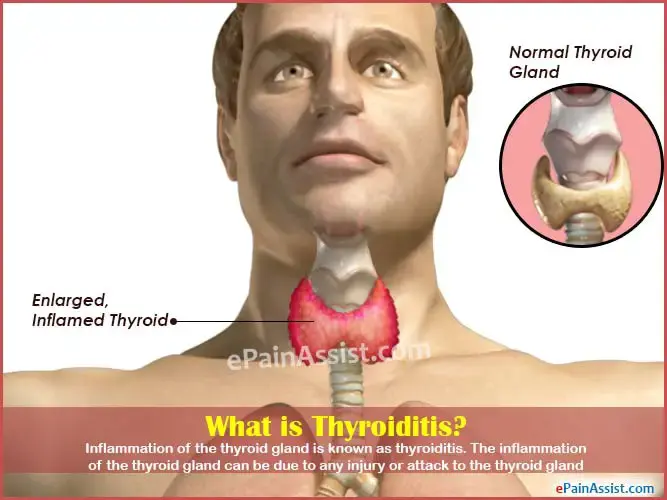
What is Thyroiditis?
Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid gland. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include medications. Regular monitoring is important for assessing thyroid function, managing symptoms, and preventing complications.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Inflammation of the thyroid gland

Symptoms
Fatigue, weight gain, joint and muscle pain (Hashimoto’s); or weight loss, anxiety, heat intolerance (Graves’ disease)

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, blood tests, sometimes imaging

Prognosis
Variable, depends on type and treatment

Complications
Inflammation of the thyroid, potential for hormonal imbalances
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Autoimmune factors (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis), viral infections, medications

Treatments
Medications (thyroid hormone replacement, anti-inflammatory drugs), beta-blockers (for symptom relief)

Prevention
Medications (thyroid hormone replacement, anti-inflammatory drugs), beta-blockers (for symptom relief)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common, can occur in individuals of any age

Patient Perspectives
Lifelong management tailored to type and severity
This information serves as a general overview and does not constitute professional medical advice. Always consult with healthcare providers for accurate and personalized insights regarding your health.
Share: