Can Thyroid Eye Disease be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment can manage symptoms, but outcomes depend on the severity and progression of the eye disease
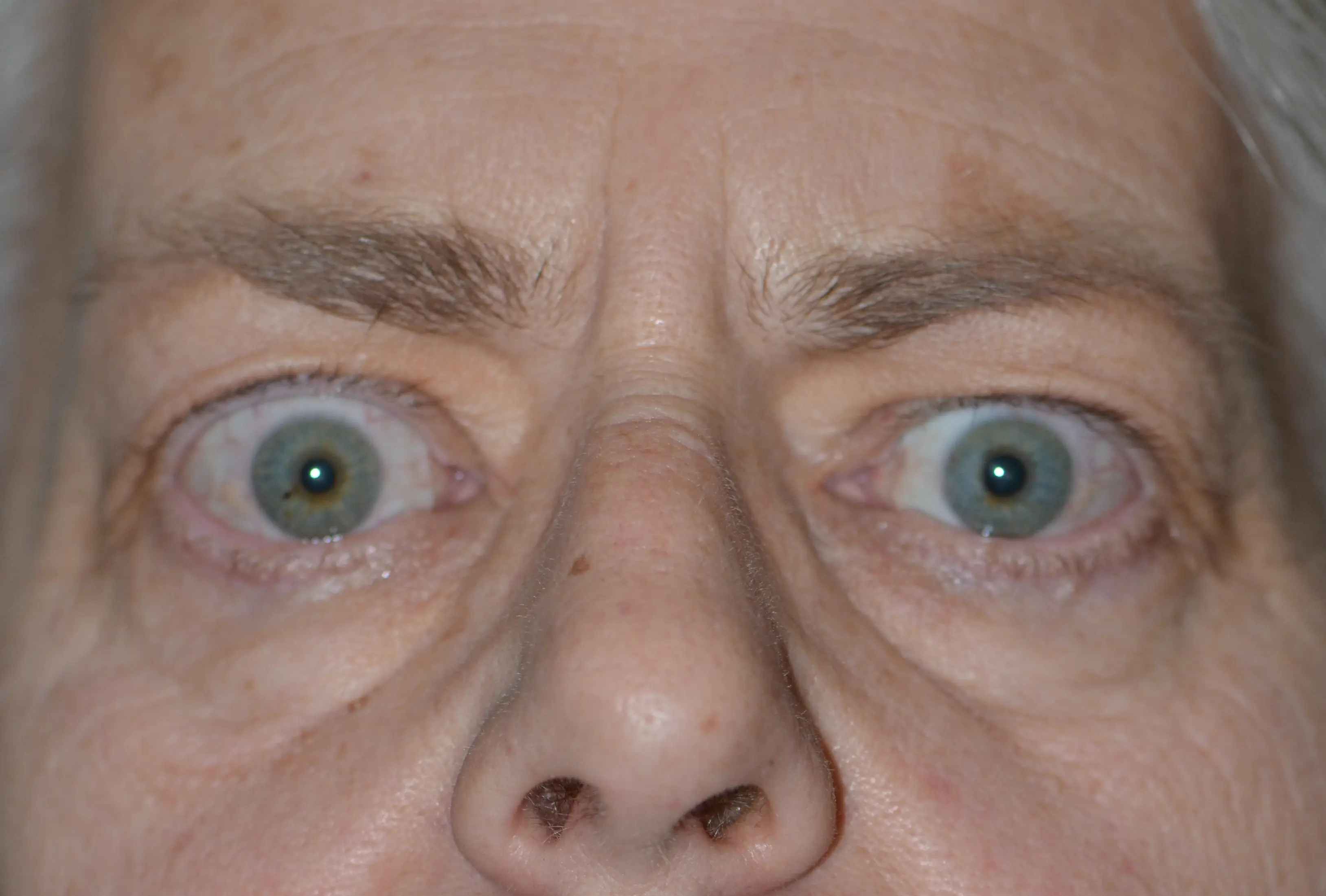
What is Thyroid Eye Disease?
Thyroid eye disease, or Graves’ ophthalmopathy, is an autoimmune condition affecting the eyes in individuals with hyperthyroidism. Treatment may include medications, surgery, or other interventions. Regular monitoring is crucial for assessing eye function, managing symptoms, and providing ongoing care.
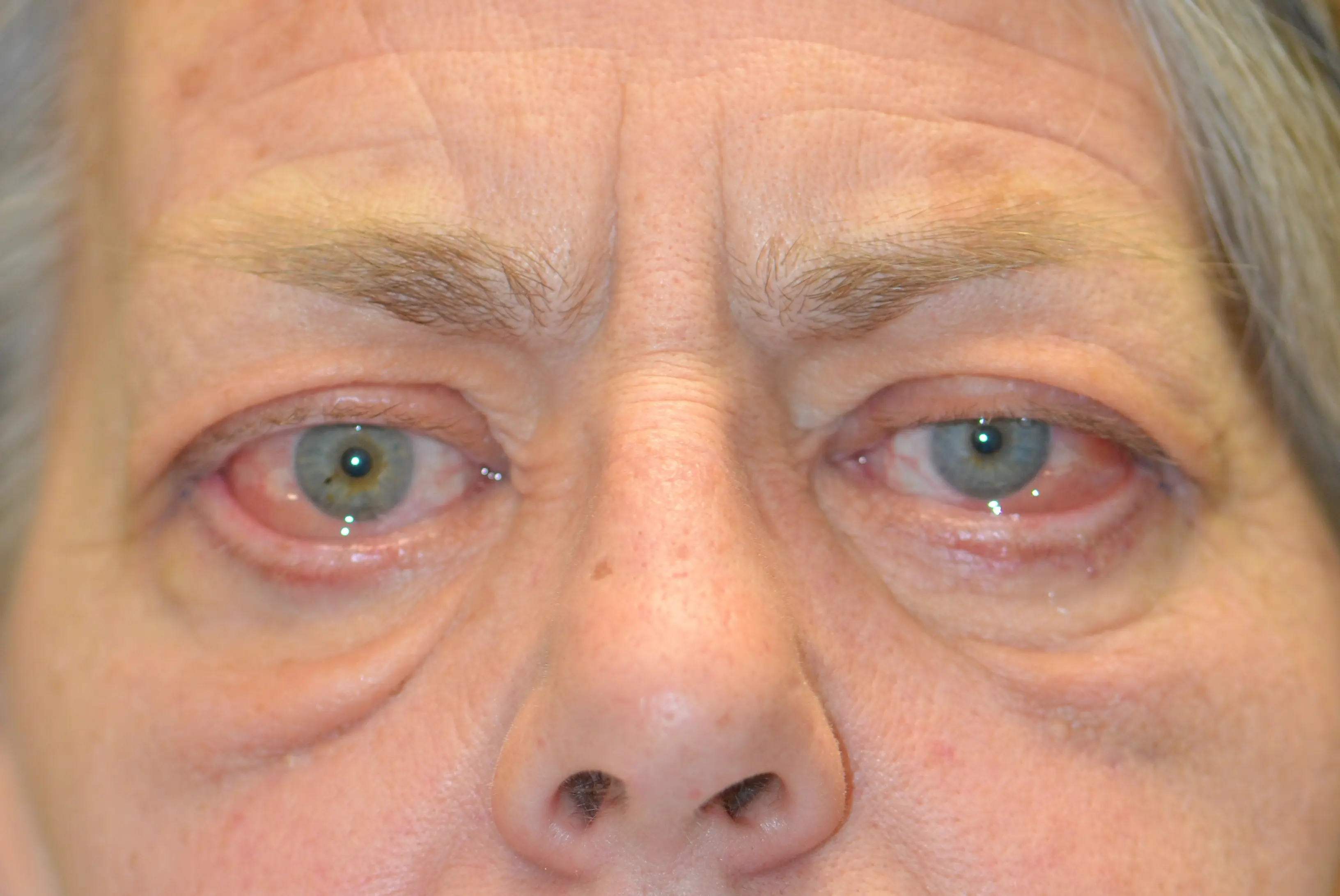
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Autoimmune condition affecting the tissues around the eyes in individuals with thyroid disorders

Symptoms
Eye bulging, double vision, dry eyes

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable, depends on severity and treatment

Complications
Eye discomfort, potential for vision issues
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Autoimmune factors, often associated with Graves’ disease

Treatments
Management of thyroid disorder, eye lubrication, medications, surgery (in some cases)

Prevention
Management of thyroid disorder, eye lubrication, medications, surgery (in some cases)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common in individuals with autoimmune thyroid disease

Patient Perspectives
Lifelong management tailored to symptoms
This information aims to provide a general understanding of the subject matter, but individual circumstances can vary significantly. Please remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Share: