Can Thalassemia be Cured?
No
Treatment aims to manage symptoms, but there is no cure for thalassemia; lifelong care is often necessary
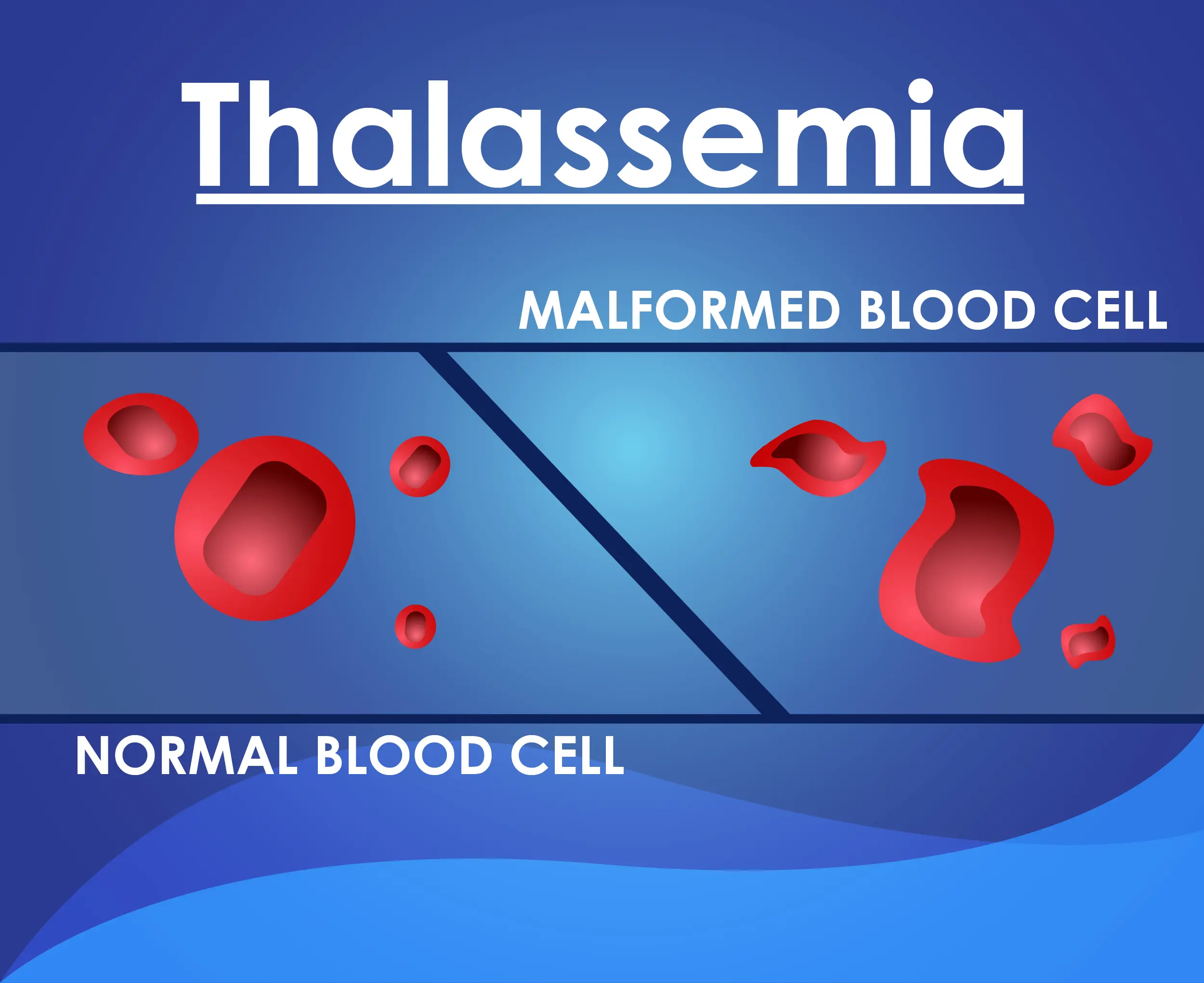
What is Thalassemia?
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder affecting hemoglobin production. Treatment may include blood transfusions and iron chelation therapy. Regular monitoring is important for assessing blood counts, managing iron levels, and preventing complications.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Inherited blood disorder affecting hemoglobin production, leading to anemia

Symptoms
Fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath

Diagnosis
Blood tests, genetic testing

Prognosis
Variable, depends on type and treatment

Complications
Anemia, potential for complications
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic mutations affecting the production of hemoglobin

Treatments
Blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy, bone marrow transplantation

Prevention
Blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy, bone marrow transplantation
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common in individuals of Mediterranean, Asian, and African descent

Patient Perspectives
Lifelong management tailored to type and severity
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: