Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a serious infectious disease caused by the Clostridium tetani bacterium. This bacteria releases a toxin that affects the nervous system, leading to painful muscle contractions, particularly in the jaw and facial muscles. While tetanus cannot be cured once symptoms develop, effective treatment can manage symptoms, improve recovery, and significantly increase the chances of survival.
Understanding Tetanus and its Treatment:
- Tetanus infection enters the body through wounds, often from puncture wounds, burns, or chronic ulcers. Spores of the bacteria can lie dormant for years and become active when they encounter suitable conditions.
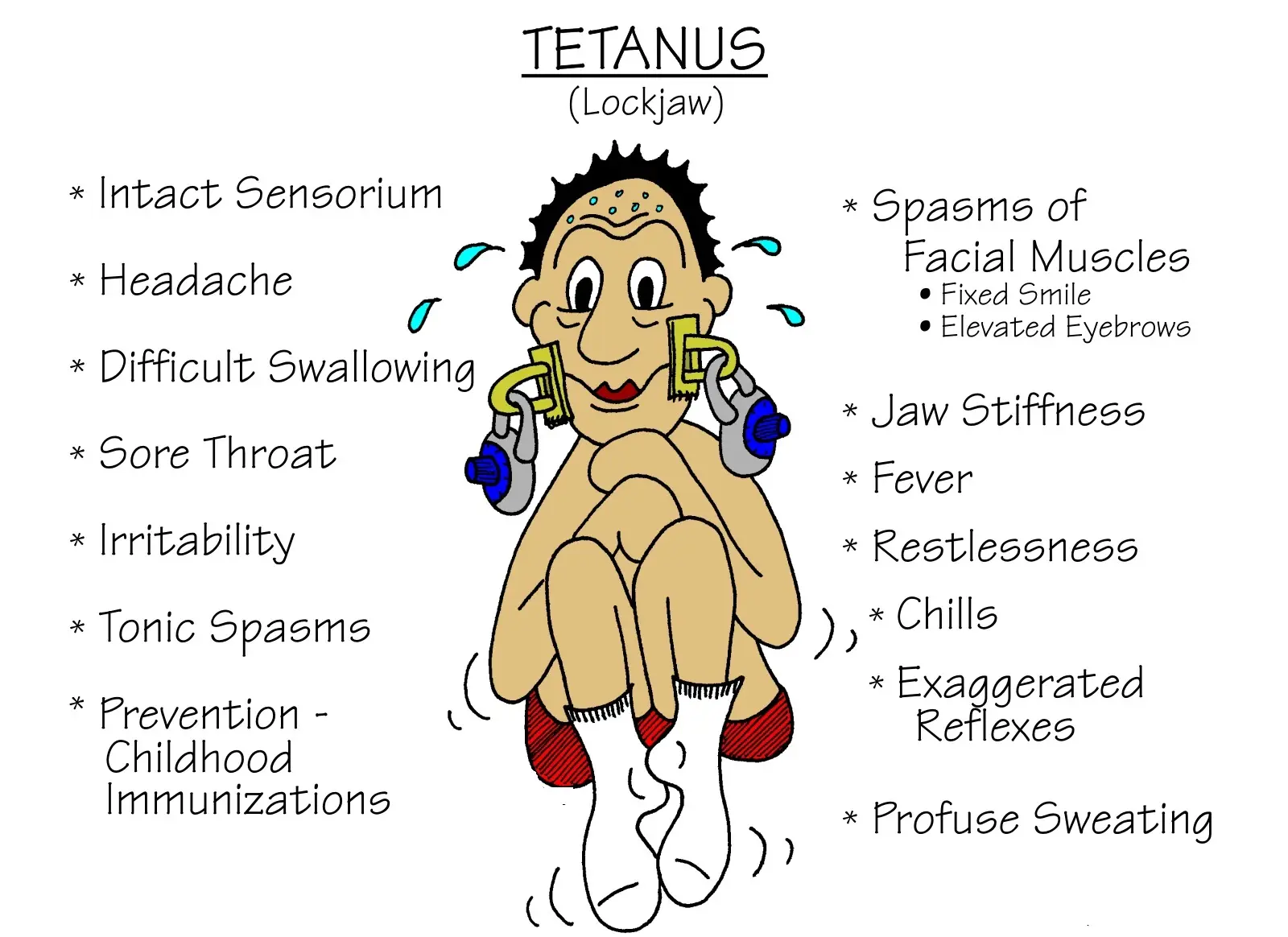
- The toxin produced by the bacteria disrupts nerve signals, causing muscle stiffness and spasms, starting in the jaw and neck and progressing to other parts of the body. Difficulty swallowing and breathing can become life-threatening complications.
- Treatment for tetanus focuses on managing symptoms and preventing further complications. This includes:
- Tetanus antitoxin: This medication neutralizes the toxin circulating in the bloodstream, preventing further damage to the nervous system.
- Wound care: Thorough cleaning and debridement of the wound are crucial to remove bacteria and prevent further infection.
- Medications: Medications like muscle relaxants and sedatives help control muscle spasms and ease pain.
- Respiratory support: In severe cases, patients may require ventilator support to assist with breathing.
Importance of Prevention:
While there is no cure for tetanus, vaccination offers protection against tetanus. The tetanus toxoid vaccine stimulates the body’s immune system to develop antibodies against the tetanus toxin. This vaccine is usually administered as part of a combined vaccine, such as tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis (Tdap).
Maintaining Protection:
- The tetanus shot provides long-term protection, but booster shots are recommended every 10 years to maintain adequate immunity.
- Seek medical care immediately if you experience any symptoms of tetanus, especially after a wound, even if it seems minor. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of recovery.
Key Takeaways:
- Tetanus is a serious but preventable disease.
- There is no cure for tetanus, but effective treatment can manage symptoms and improve recovery.
- Vaccination with Tdap or tetanus-containing vaccines is essential for protection.
- Regular booster shots are crucial to maintain immunity.
- If you experience any symptoms of tetanus, seek medical care immediately.