Can Spina Bifida be Cured?
No (manageable)
No cure; management focuses on preventing complications, supportive care
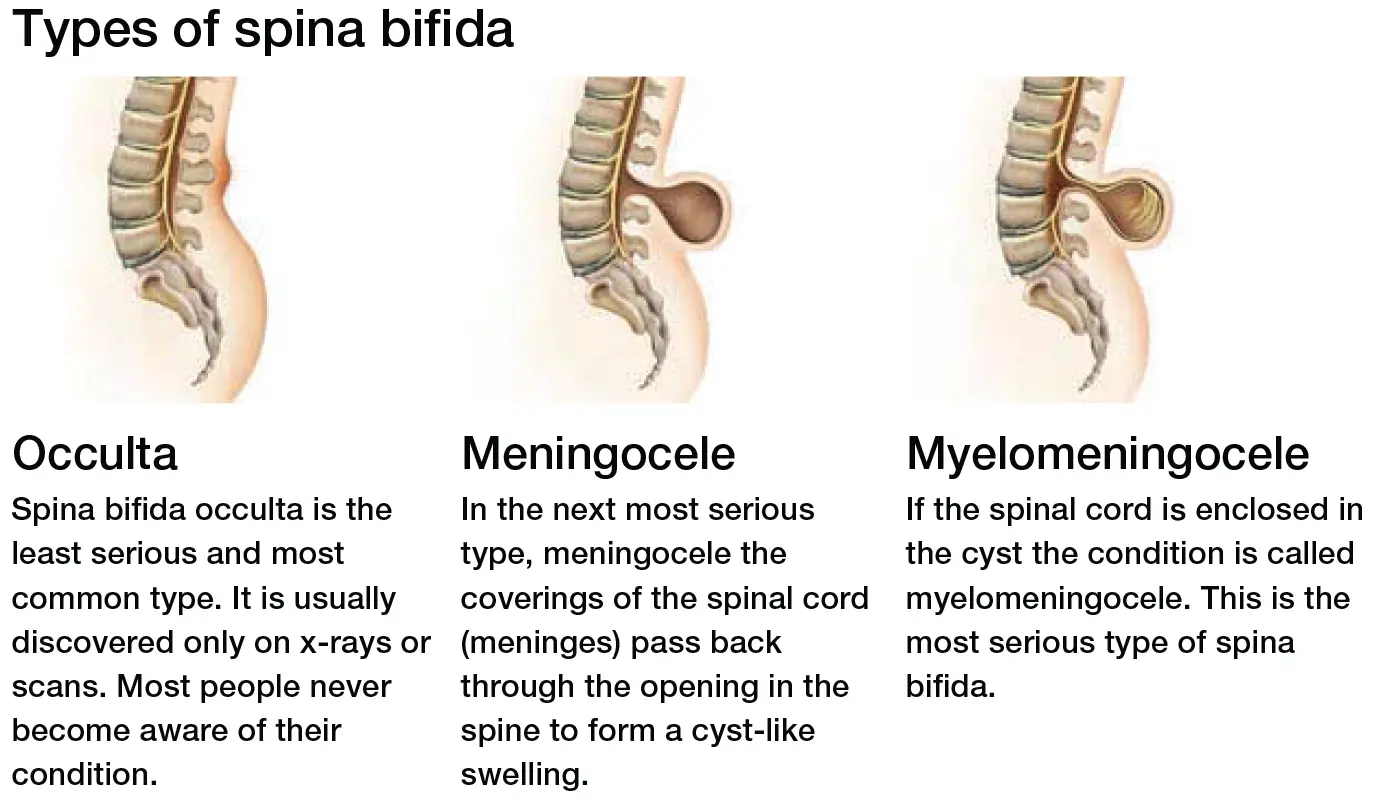
What is Spina Bifida?
Spina bifida is a birth defect where the spinal cord does not develop properly. Treatment may involve surgery, physical therapy, and other interventions to manage symptoms. Regular monitoring is crucial for assessing developmental progress, managing complications, and providing ongoing care.
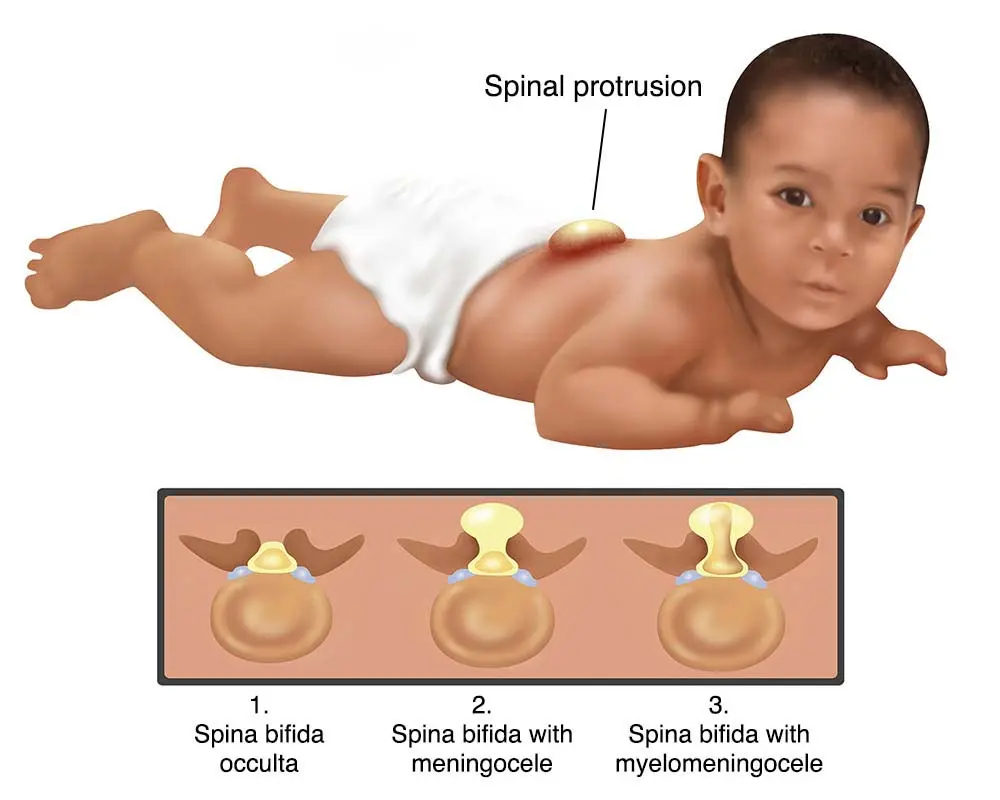
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Neural tube defect affecting spinal cord development

Symptoms
Nerve damage, motor and sensory deficits

Diagnosis
Prenatal ultrasound, sometimes additional tests

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the severity and interventions

Complications
Neurological deficits, complications affecting mobility
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic and environmental factors, folic acid deficiency

Treatments
Surgical repair, supportive care, physical therapy

Prevention
Surgical repair, supportive care, physical therapy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Neural tube defect affecting the spine and spinal cord

Patient Perspectives
Surgical interventions, physical therapy, supportive care
While the information presented here reflects the current knowledge about these conditions and treatments, it’s important to understand that individual cases may differ. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Share: