Can Sleep Apnea be Cured?
Sometimes
Management and improvement are possible with treatment, but cure may depend on the underlying cause and severity
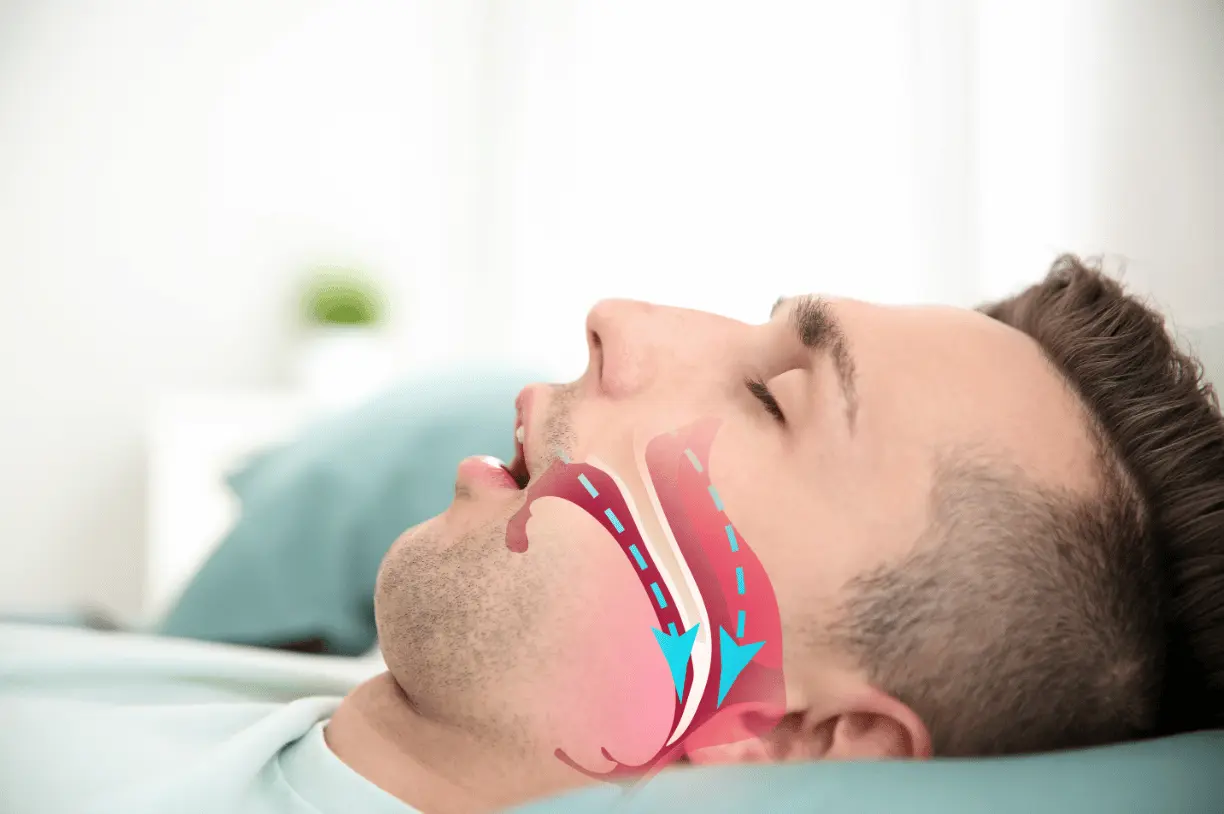
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, and in some cases, surgery.
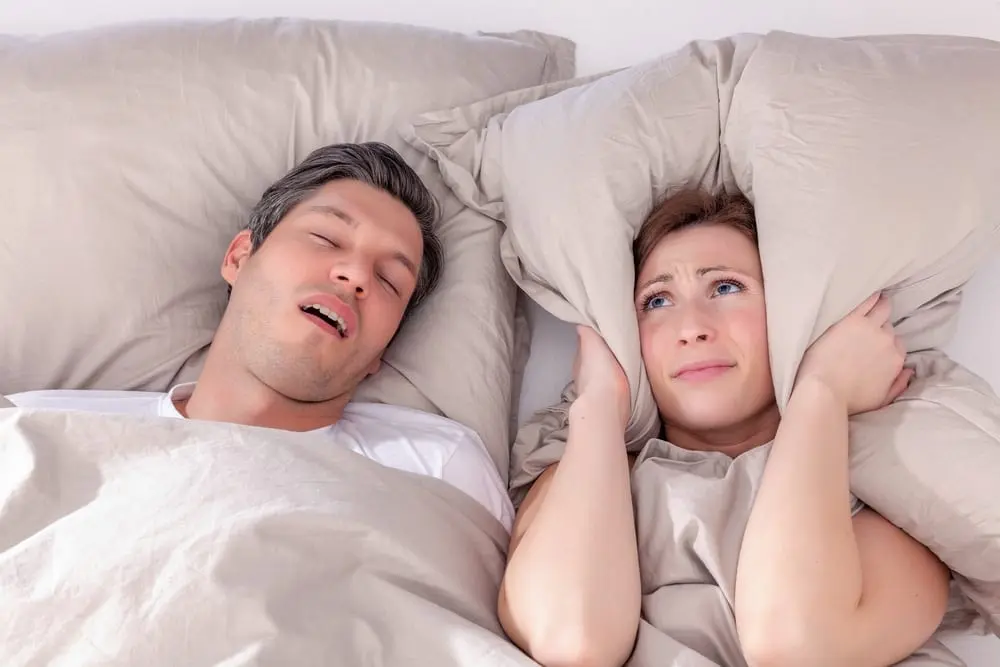

Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Breathing pauses during sleep, often due to the collapse of the airway

Symptoms
Loud snoring, gasping or choking during sleep, daytime sleepiness

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, sleep studies

Prognosis
Variable, depends on severity and treatment

Complications
Impaired sleep, potential for cardiovascular complications
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA): airway blockage; Central sleep apnea: failure of the brain to send proper signals to the muscles controlling breathing

Treatments
Lifestyle changes (weight loss, positional therapy), continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), surgery (in some cases)

Prevention
Lifestyle changes (weight loss, positional therapy), continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), surgery (in some cases)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common, can occur in any age group

Patient Perspectives
Lifelong management tailored to severity
This information aims to provide a general understanding of the subject matter, but individual circumstances can vary significantly. Please remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Share: