Can Rhabdomyolysis be Cured?
Sometimes
Outcomes depend on the severity, cause, and prompt treatment; early intervention can improve outcomes, but severe cases may lead to complications
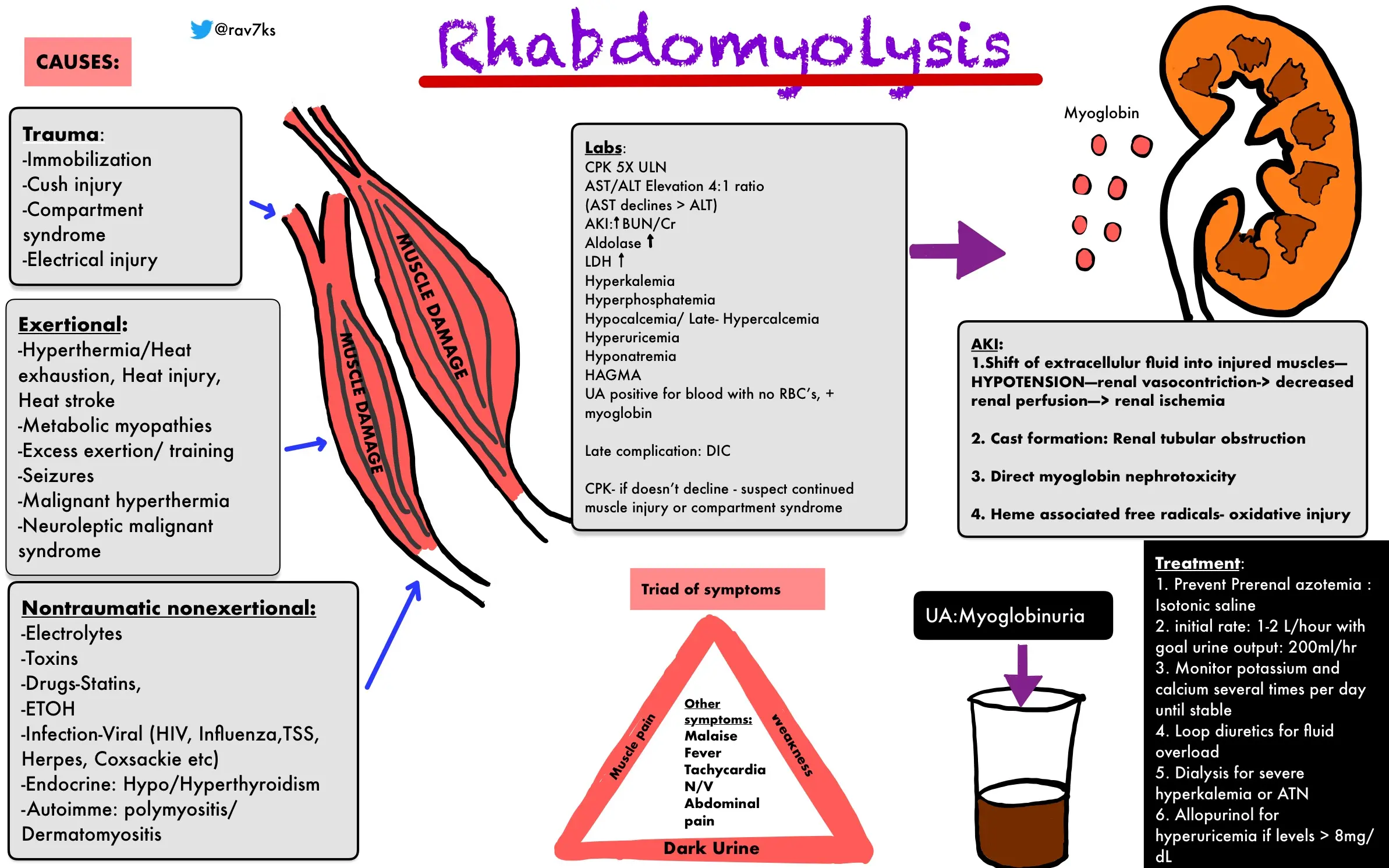
What is Rhabdomyolysis?
Rhabdomyolysis is a condition characterized by the breakdown of muscle tissue, leading to the release of muscle fibers into the bloodstream. Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause, intravenous fluids, and sometimes medications. Regular monitoring is crucial for assessing kidney function and managing complications.
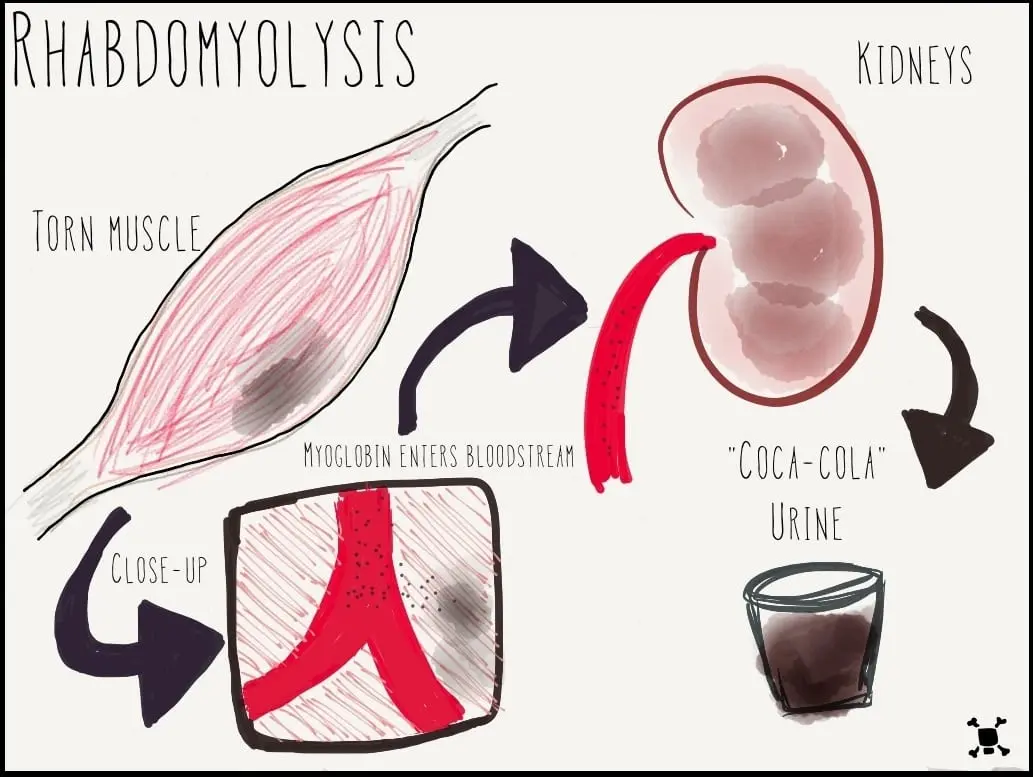
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Serious condition involving the breakdown of muscle tissue, leading to the release of muscle protein into the bloodstream

Symptoms
Muscle pain, weakness, dark urine, kidney problems

Diagnosis
Blood and urine tests, clinical evaluation

Prognosis
Generally good with prompt intervention

Complications
Kidney damage, complications affecting multiple organs
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Trauma, muscle injury, medications, infections, metabolic disorders

Treatments
Intravenous fluids, addressing the underlying cause, supportive care

Prevention
Intravenous fluids, addressing the underlying cause, supportive care
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Breakdown of muscle tissue, releasing myoglobin into the bloodstream

Patient Perspectives
Fluid resuscitation, addressing underlying causes
While the information presented here reflects the current knowledge about these conditions and treatments, it’s important to understand that individual cases may differ. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Share: