Can Respiratory Acidosis be Cured?
Sometimes
Outcomes depend on the severity and underlying cause; effective management can often improve symptoms and blood gas levels
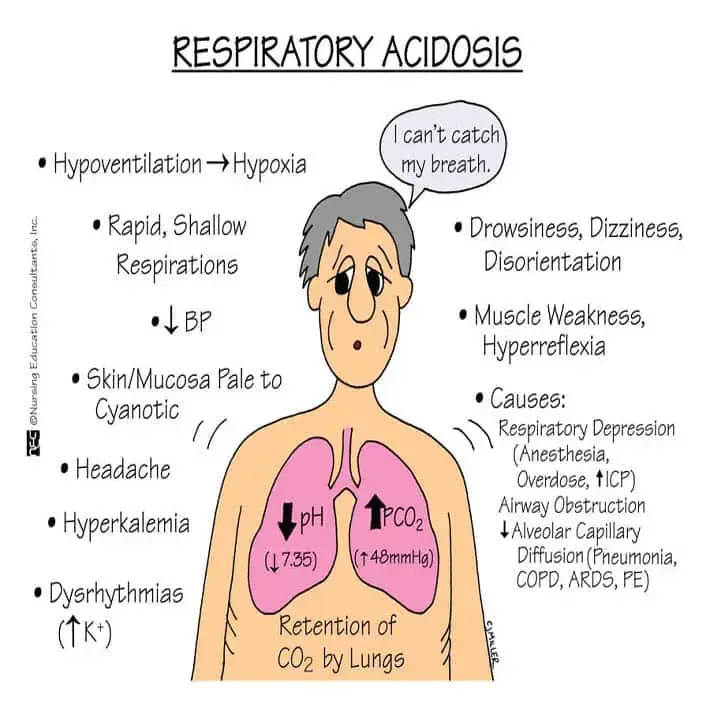
What is Respiratory Acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis is a condition where the lungs cannot remove enough carbon dioxide, leading to an increase in acidity in the body. Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause and may include improving ventilation or using mechanical ventilation. Regular monitoring is crucial for assessing respiratory function and managing acid-base balance.
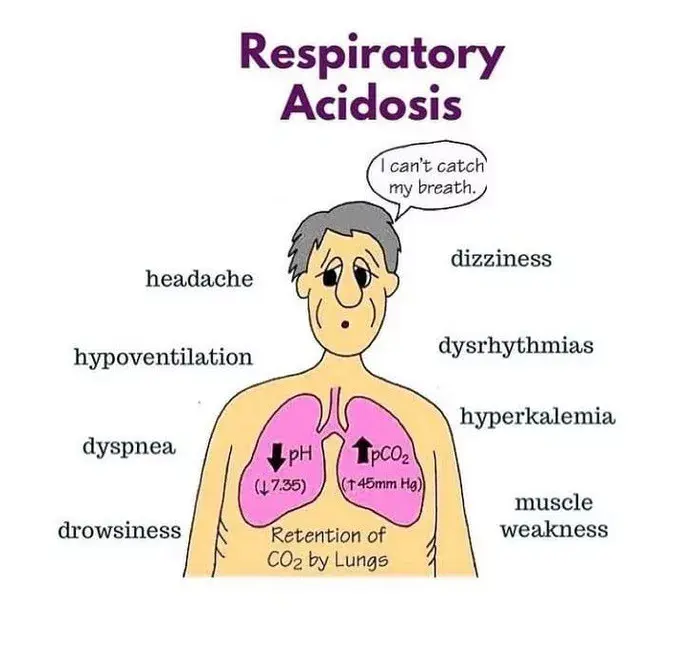
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Condition where the lungs cannot remove enough carbon dioxide, leading to an imbalance in blood acidity

Symptoms
Shortness of breath, confusion, fatigue

Diagnosis
Blood gas analysis, clinical evaluation

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the severity and underlying cause

Complications
Impaired oxygen delivery, complications affecting multiple systems
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Lung diseases (COPD, asthma, pneumonia), chest injuries, medications

Treatments
Treatment of the underlying cause, oxygen therapy

Prevention
Treatment of the underlying cause, oxygen therapy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Excess carbon dioxide in the blood due to respiratory dysfunction

Patient Perspectives
Management of respiratory conditions, supportive care
As always, consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and care.
Share: