Can Reactive Arthritis be Cured?
No (manageable)
No cure; management aims to control symptoms, treat underlying infection
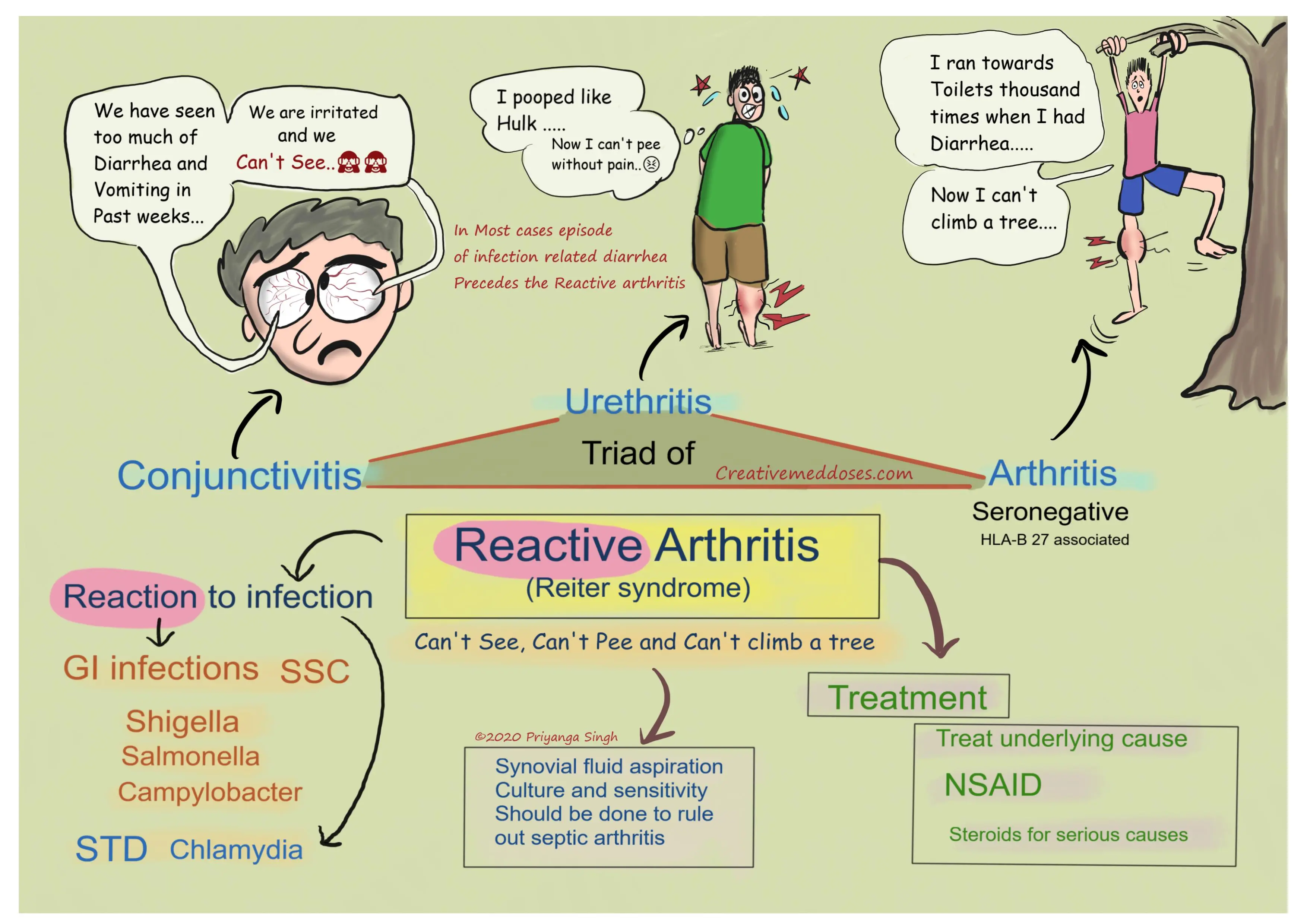
What is Reactive Arthritis?
Reactive arthritis is joint inflammation triggered by an infection in another part of the body. Treatment involves addressing the underlying infection and managing symptoms.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Inflammatory arthritis triggered by infection elsewhere in the body

Symptoms
Joint pain, swelling, eye inflammation

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, sometimes blood tests

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the cause and response to treatment

Complications
Joint damage, complications affecting mobility
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Bacterial or viral infections (often after gastrointestinal or genitourinary infections)

Treatments
Medications (NSAIDs, DMARDs), physical therapy

Prevention
Medications (NSAIDs, DMARDs), physical therapy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Joint inflammation following an infection, often in the genitourinary or gastrointestinal tract

Patient Perspectives
Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy
While the information presented here reflects the current knowledge about these conditions and treatments, it’s important to understand that individual cases may differ. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Share: