Can Pulmonary Embolism be Cured?
Yes (with treatment)
Curable with appropriate treatment; prevention involves reducing risk factors
What is Pulmonary Embolism?
Pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage of one or more pulmonary arteries in the lungs, usually caused by blood clots. Treatment may involve anticoagulant medications and, in severe cases, interventions like thrombolytic therapy or surgery.
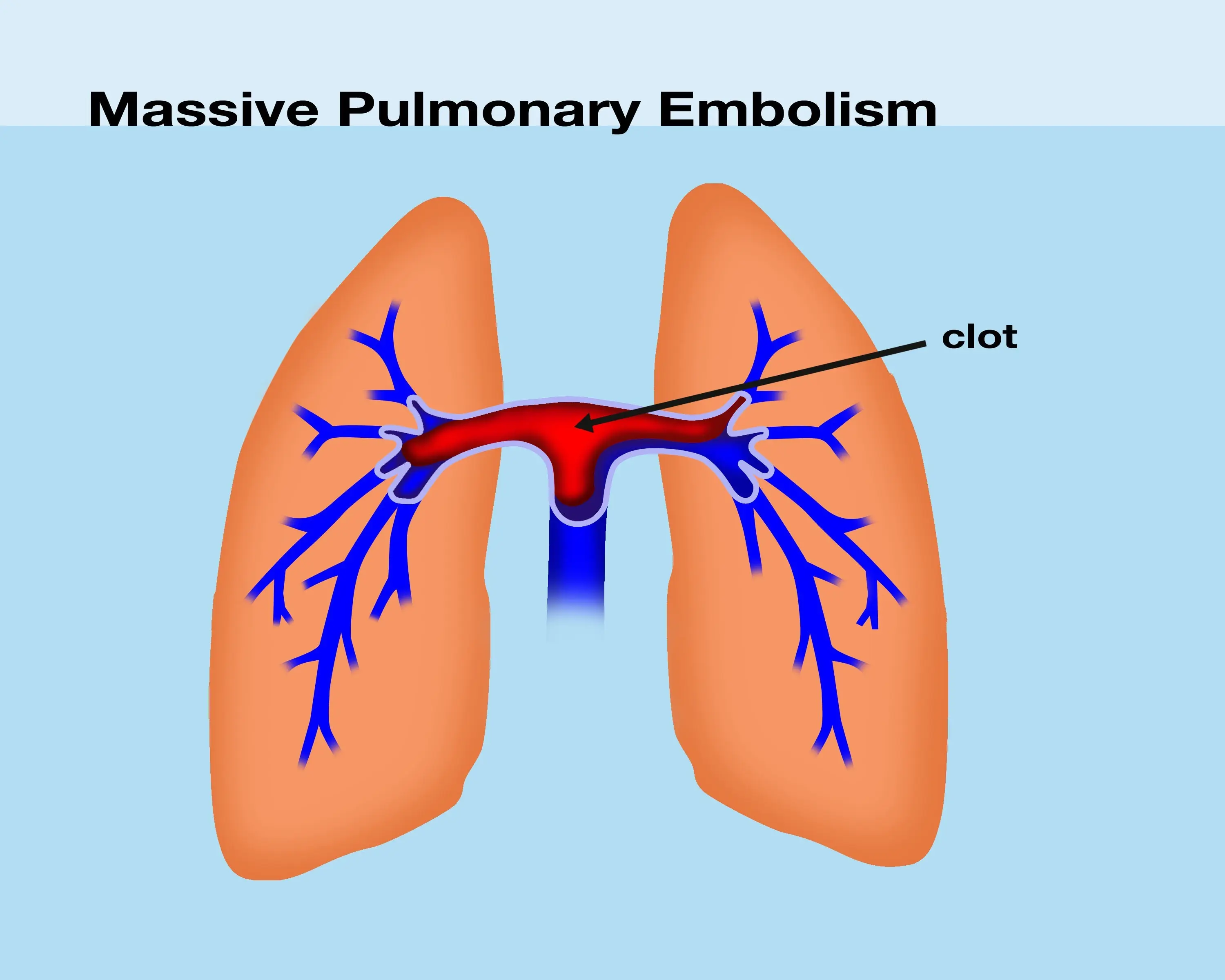
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Blockage of pulmonary arteries by blood clots

Symptoms
Shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid heart rate

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable, depends on size and location of clot

Complications
Impaired lung function, potential for complications
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Deep vein thrombosis, surgery, immobility

Treatments
Anticoagulant medications, oxygen therapy, surgery (in some cases)

Prevention
Anticoagulant medications, oxygen therapy, surgery (in some cases)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common, often associated with deep vein thrombosis

Patient Perspectives
Lifelong management tailored to individual cases
Remember, the information provided here is intended for general knowledge purposes and may not apply to every individual case. To ensure you have accurate information relevant to your specific situation, always consult with a healthcare professional.
Share: