Can Pseudogout be Cured?
Sometimes
Pseudogout can be effectively managed, but it is typically a chronic condition; outcomes depend on the individual’s response to treatment and the progression of the disease
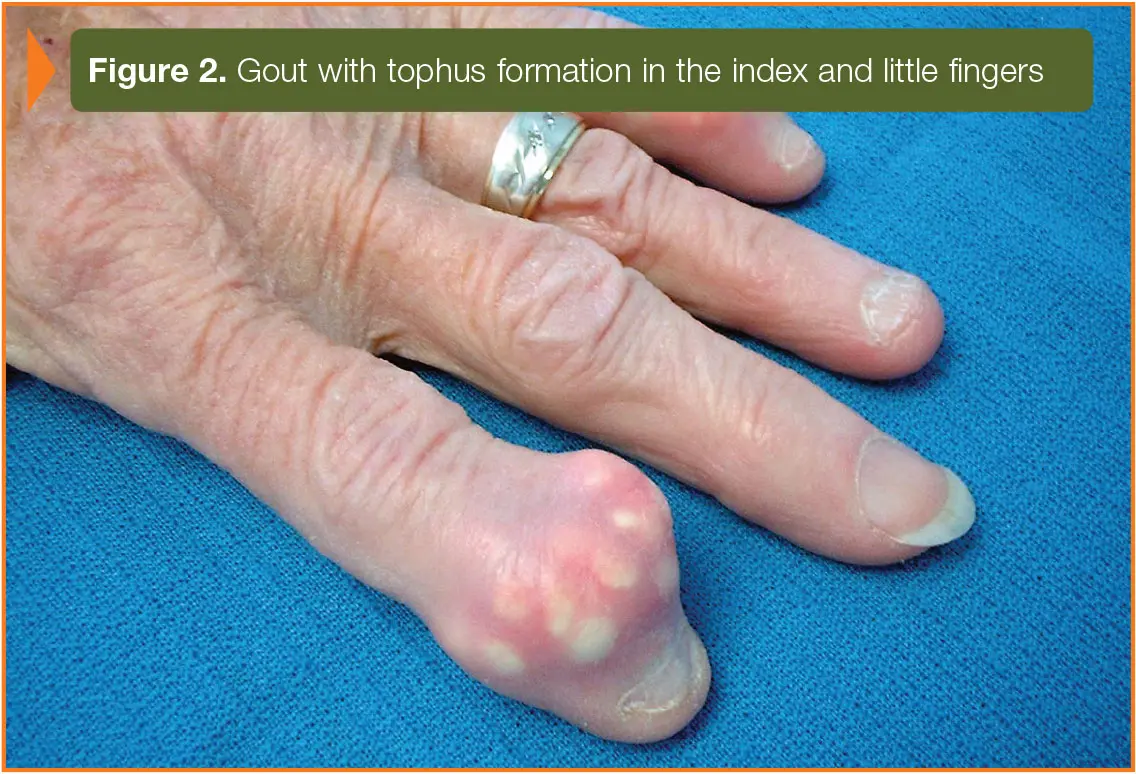
What is Pseudogout?
Pseudogout is a form of arthritis that causes sudden, painful swelling in joints. Treatment involves medications to manage inflammation and pain. Regular monitoring is important for assessing joint health and managing symptoms.
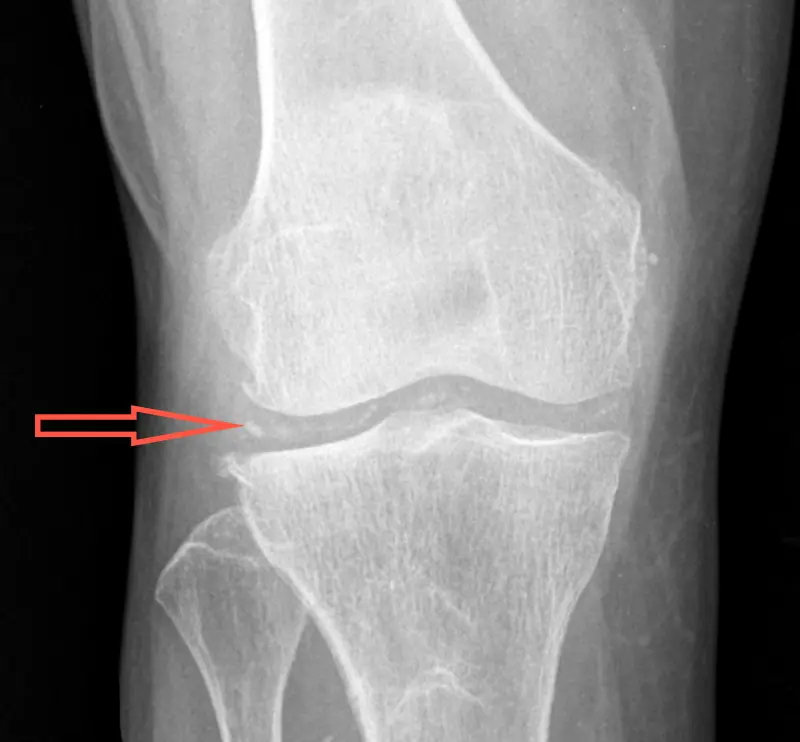
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Form of arthritis caused by the deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in the joints

Symptoms
Joint pain, swelling, redness, stiffness

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, joint fluid analysis

Prognosis
Variable, depends on severity and treatment

Complications
Joint inflammation, potential for complications
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Aging, genetic factors, joint injury, metabolic disorders

Treatments
Medications (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine), joint aspiration

Prevention
Medications (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine), joint aspiration
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common in older adults, associated with crystal deposits

Patient Perspectives
Lifelong management tailored to symptoms
For personalized advice and care, always seek the assistance of healthcare professionals. This information is meant for general understanding and not as a replacement for professional medical advice.
Share: