Can Palmar Fasciitis be Cured?
Sometimes
Management can alleviate symptoms and improve hand function, but a complete cure may not always be achievable; outcomes depend on the severity and response to treatment
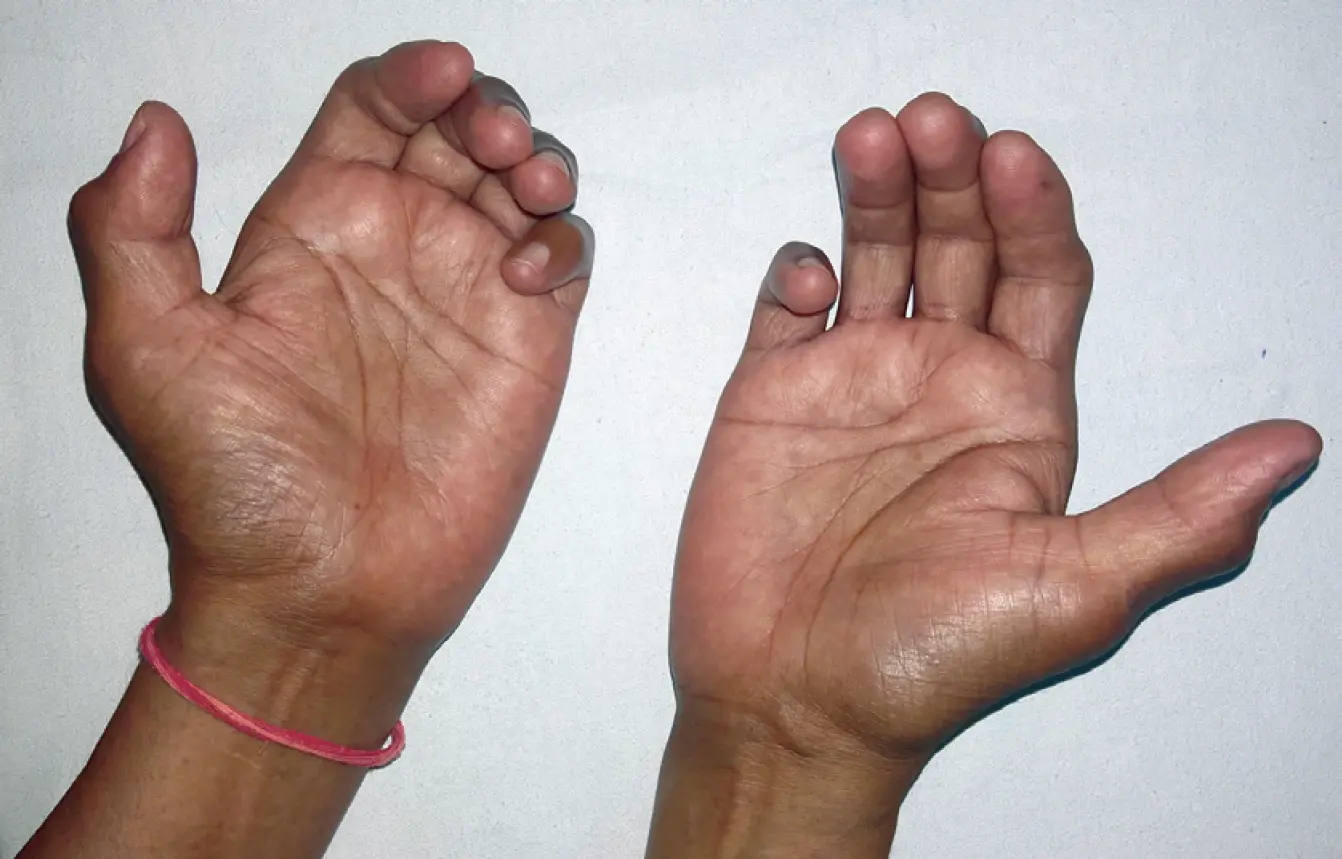
What is Palmar Fasciitis?
Palmar fasciitis is inflammation of the connective tissue in the palm of the hand. Treatment may involve medications and addressing the underlying cause.
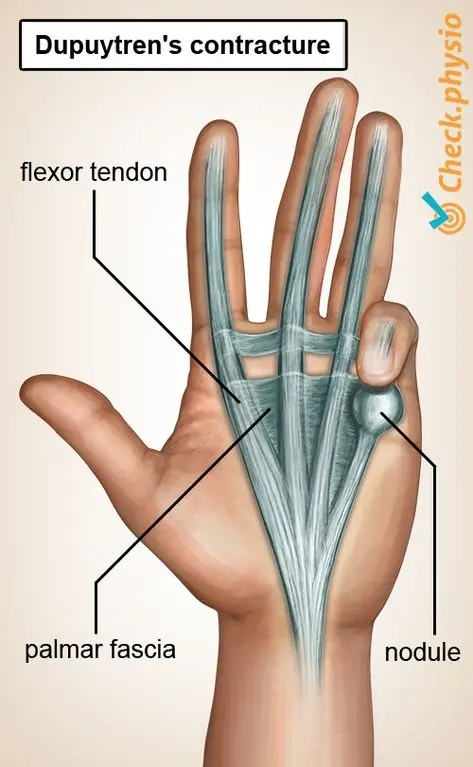
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Inflammation of the palmar fascia in the hand, leading to contracture and finger flexion

Symptoms
Palmar pain, nodules or lumps in the hand, finger contracture

Diagnosis
Clinical examination, sometimes imaging studies

Prognosis
Generally good with appropriate management and treatment

Complications
Hand deformity, complications of untreated palmar fasciitis
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Idiopathic (unknown cause), genetic factors, diabetes, certain medications

Treatments
Physical therapy, splinting, corticosteroid injections, surgery (in advanced cases)

Prevention
Physical therapy, splinting, corticosteroid injections, surgery (in advanced cases)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Inflammation of the tissue in the palm of the hand

Patient Perspectives
Management focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing deformity
This information aims to provide a general understanding of the subject matter, but individual circumstances can vary significantly. Please remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Share: