Can Paget’s Disease of Bone be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment can manage symptoms and slow progression, but a complete cure may not be achievable; outcomes depend on the extent of bone involvement and response to therapy
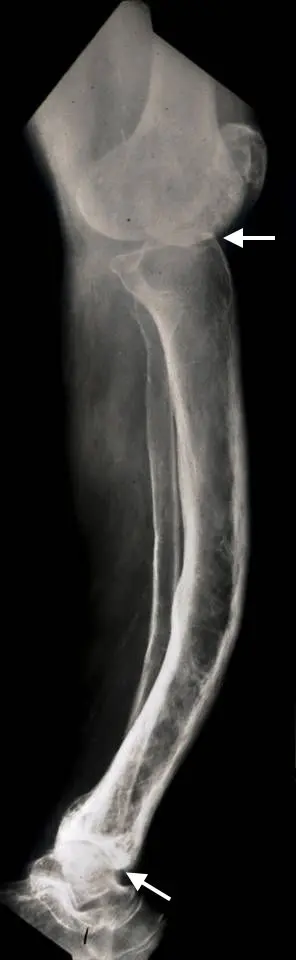
What is Paget’s Disease of Bone?
Paget’s disease of bone is a condition where bone remodeling is abnormal, leading to weakened and deformed bones. Treatment may include medications to regulate bone turnover.
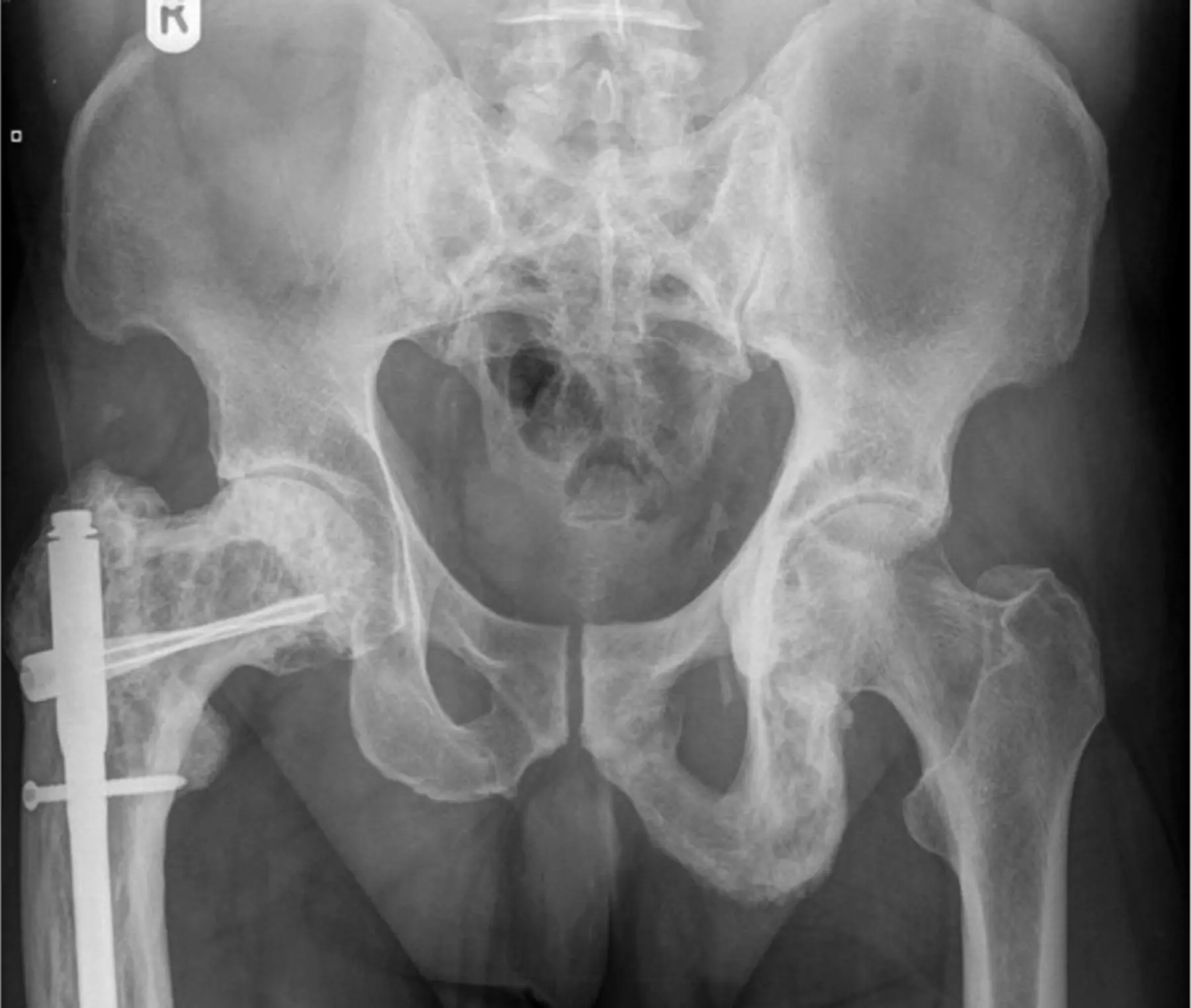
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Abnormal bone remodeling, leading to enlarged and weakened bones

Symptoms
Bone pain, deformities, fractures, hearing loss (if affecting the skull bones)

Diagnosis
Imaging studies, clinical examination

Prognosis
Generally good with appropriate management and treatment

Complications
Fractures, complications of untreated Paget’s disease
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic factors, viral infections (possibly), aging

Treatments
Medications (bisphosphonates, calcitonin), surgery (in severe cases)

Prevention
Medications (bisphosphonates, calcitonin), surgery (in severe cases)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Abnormal bone remodeling, leading to weakened and deformed bones

Patient Perspectives
Management focuses on preventing complications and improving bone health
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: