Can Ovarian Cyst be Cured?
Yes
Most ovarian cysts are functional and resolve on their own without treatment; other types may require intervention depending on symptoms and characteristics
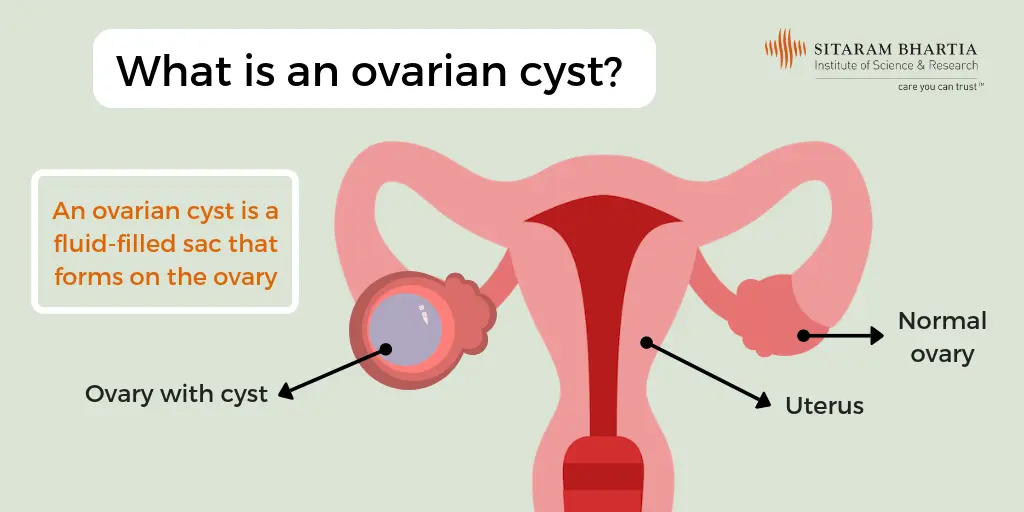
What is Ovarian Cyst?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can form on the ovaries. Most cysts are benign and resolve on their own. Treatment may involve watchful waiting or, in some cases, surgery. Regular monitoring and follow-up are important to assess cyst size, symptoms, and any changes that may require intervention.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Fluid-filled sac that forms on or within the ovaries

Symptoms
Usually no symptoms; may cause pelvic pain, bloating, changes in menstrual cycle

Diagnosis
Ultrasound, clinical examination

Prognosis
Generally good with appropriate management and treatment

Complications
Rupture, complications of untreated ovarian cyst
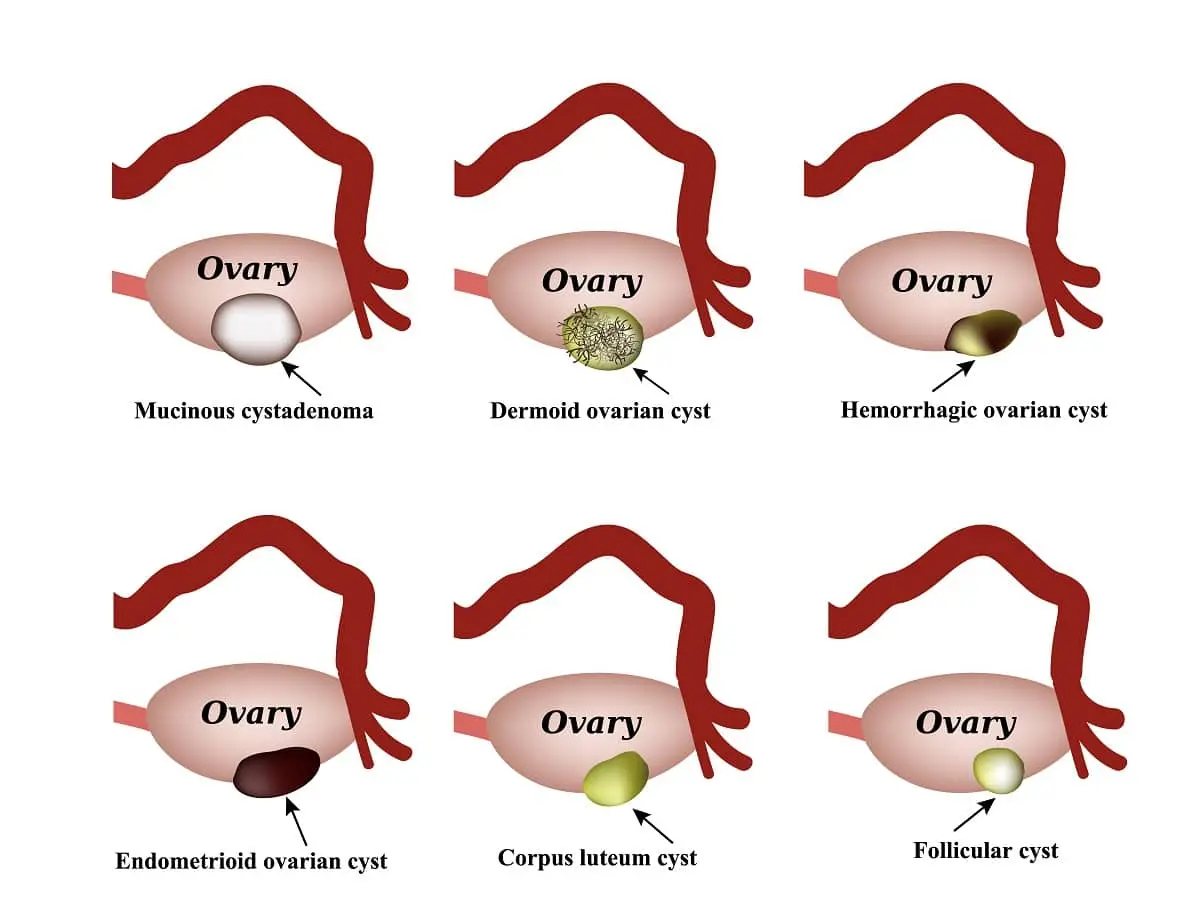
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Follicle cysts (normal part of the menstrual cycle), corpus luteum cysts, endometriomas, dermoid cysts, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)

Treatments
Monitoring for changes, pain management, hormonal contraceptives (to prevent recurrence)

Prevention
Monitoring for changes, pain management, hormonal contraceptives (to prevent recurrence)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Fluid-filled sac on the ovary

Patient Perspectives
Management depends on the size and symptoms of the cyst
While the information presented here reflects the current knowledge about these conditions and treatments, it’s important to understand that individual cases may differ. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Share: