Can Otitis Externa be Cured?
Yes
Otitis externa is usually curable with appropriate treatment; outcomes depend on early intervention and adherence to recommended care

What is Otitis Externa?
Otitis externa, commonly known as swimmer’s ear, is inflammation of the ear canal. Treatment may involve ear drops, pain management, and addressing underlying causes. Prevention includes keeping the ears dry and avoiding excessive ear cleaning. Regular monitoring is important for assessing treatment response and preventing recurrence.
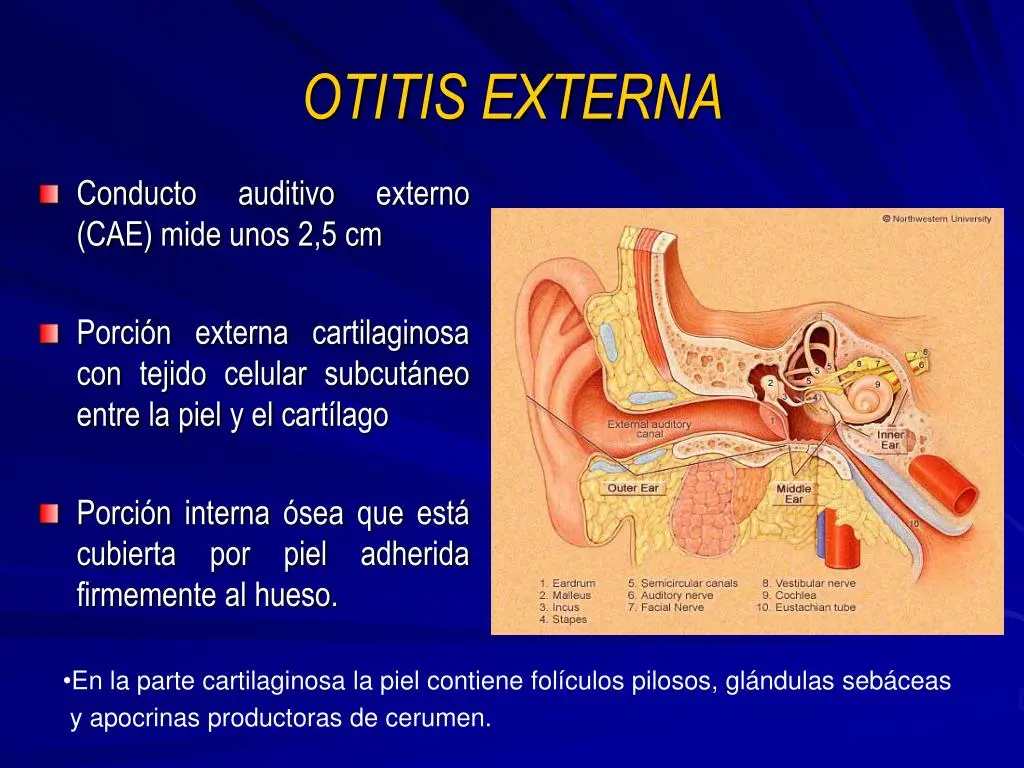
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Infection or inflammation of the external ear canal (swimmer’s ear)

Symptoms
Ear pain, itching, redness, drainage, hearing loss

Diagnosis
Clinical examination

Prognosis
Generally good with appropriate management and treatment

Complications
Hearing loss, complications of severe cases
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Bacterial or fungal infection, moisture in the ear, skin conditions, trauma to the ear canal

Treatments
Ear drops, pain relievers, avoiding water exposure, antibiotics (if bacterial)

Prevention
Ear drops, pain relievers, avoiding water exposure, antibiotics (if bacterial)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Infection of the outer ear canal

Patient Perspectives
Prevention involves ear hygiene and avoiding water exposure
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: