Can Osteomyelitis be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment can cure many cases, especially with early diagnosis and appropriate antibiotics; outcomes depend on the severity, underlying cause, and response to treatment
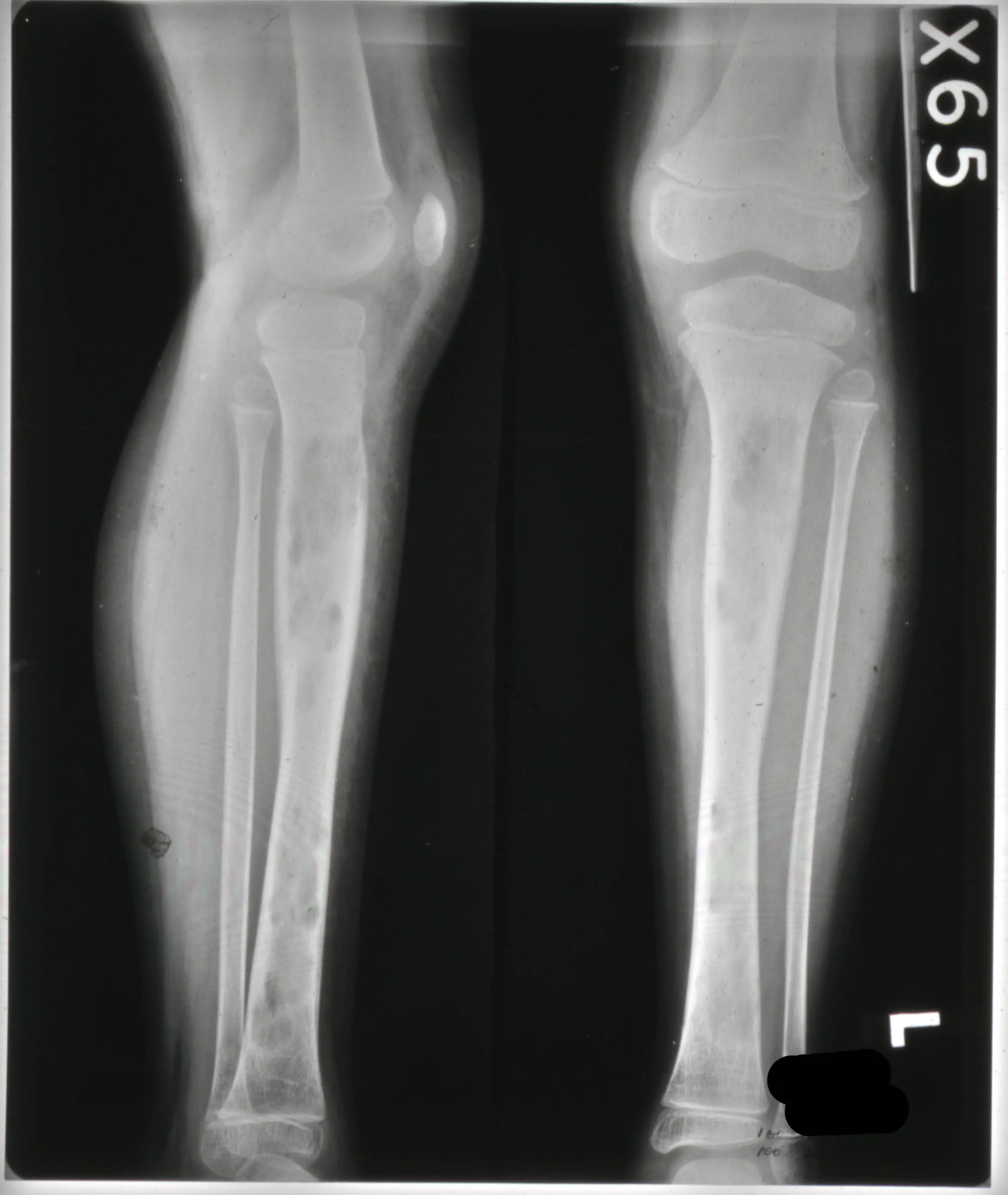
What is Osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone, usually caused by bacteria. Treatment involves antibiotics, and in some cases, surgical intervention to drain abscesses or remove infected tissue. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to prevent the spread of infection and long-term complications.
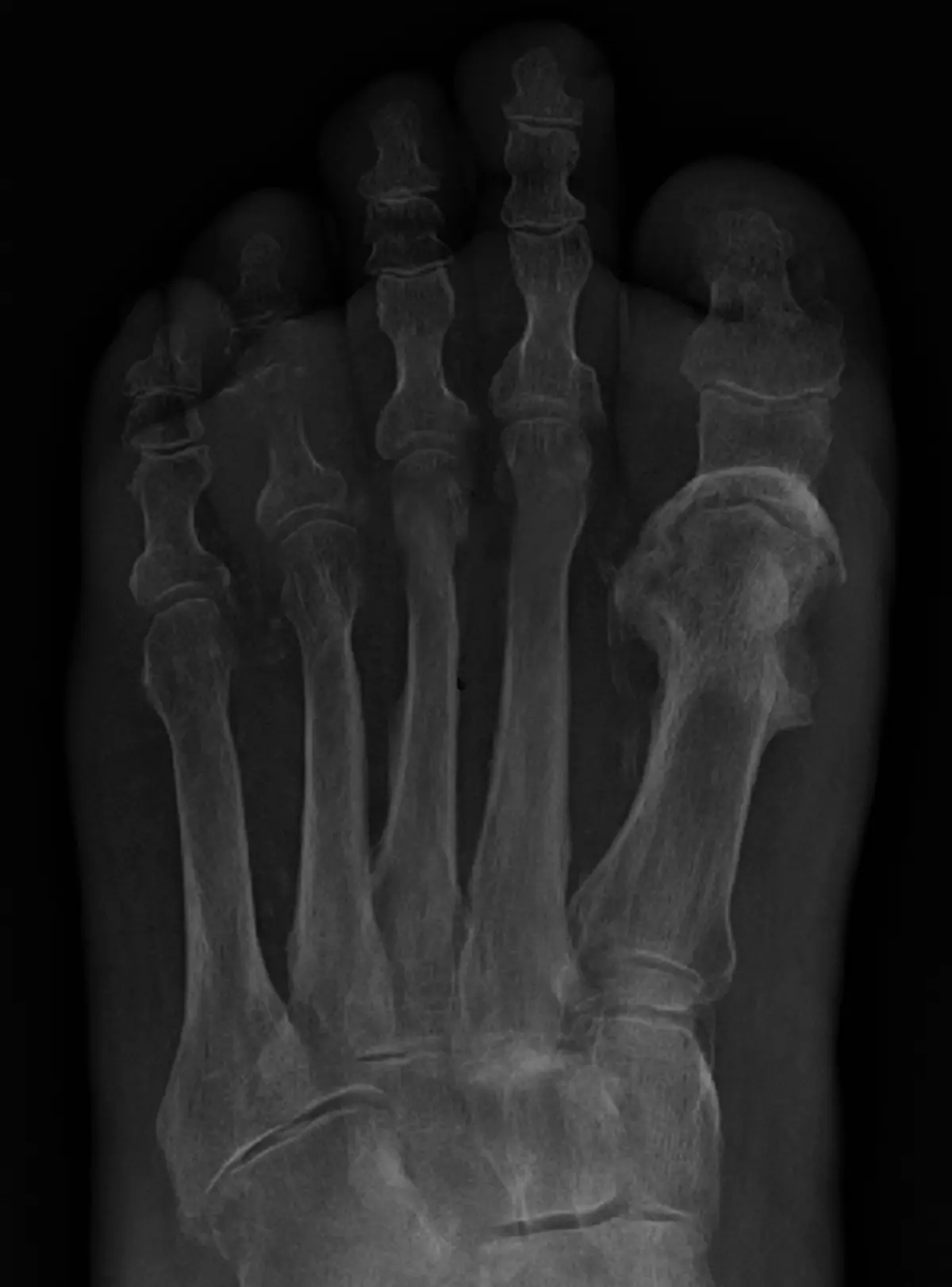
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Infection of the bone, often caused by bacteria

Symptoms
Pain, swelling, redness, fever, difficulty moving the affected limb

Diagnosis
Imaging studies, blood tests

Prognosis
Generally good with appropriate management and treatment

Complications
Bone necrosis, complications of untreated osteomyelitis
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Bacterial infection (commonly Staphylococcus aureus), open fractures, surgical procedures, compromised immune system

Treatments
Antibiotics, surgical drainage or debridement, supportive care

Prevention
Antibiotics, surgical drainage or debridement, supportive care
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Bacterial infection of the bone

Patient Perspectives
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for better outcomes
While the information presented here reflects the current knowledge about these conditions and treatments, it’s important to understand that individual cases may differ. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Share: