Can Neural Tube Defects be Cured?
No
Neural tube defects are structural abnormalities and cannot be reversed; management focuses on preventing complications, providing supportive care, and addressing associated conditions
What is Neural Tube Defects?
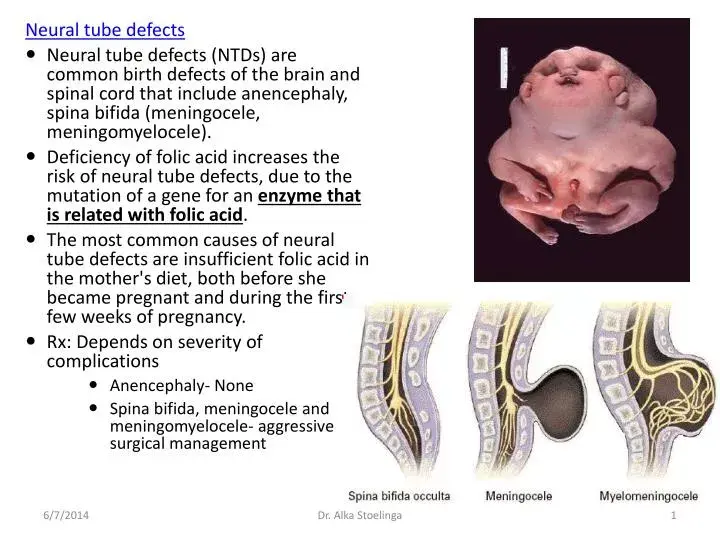
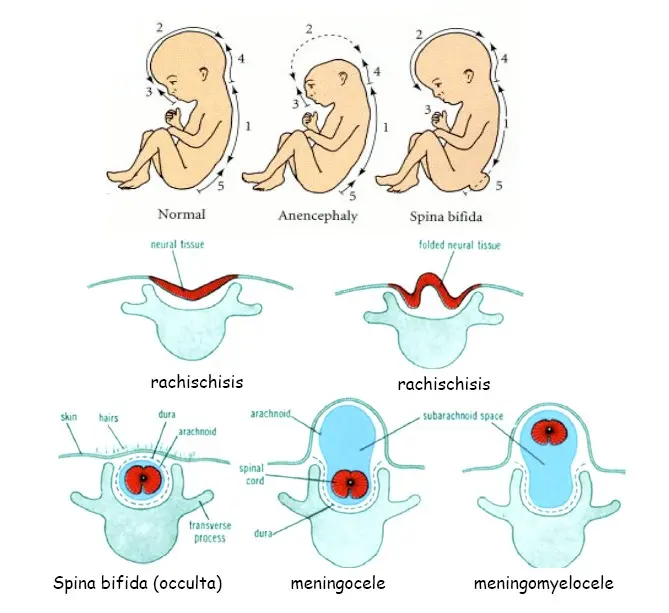
Neural tube defects are congenital abnormalities that result from incomplete closure of the neural tube during fetal development. Examples include spina bifida and anencephaly. Prevention involves folic acid supplementation during pregnancy. Treatment varies based on the specific defect and may include surgery and supportive care. Early detection through prenatal screening is crucial for managing these conditions.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Congenital abnormalities in the formation of the neural tube during embryonic development, leading to malformations of the brain and spinal cord

Symptoms
Varies depending on the type and severity; may include spina bifida, anencephaly, encephalocele

Diagnosis
Imaging studies, biopsy

Prognosis
Variable, depends on stage and treatment response

Complications
Potential for metastasis, complications from treatment
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic factors, folic acid deficiency during pregnancy, certain medications, maternal diabetes

Treatments
Surgical interventions, supportive care, management of associated complications

Prevention
Surgical interventions, supportive care, management of associated complications
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common solid tumor in children

Patient Perspectives
Multidisciplinary care for optimal outcomes
This information is for general understanding and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with healthcare providers for accurate and personalized information related to your health.
Share: