Can Nephrotic Syndrome be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment can control symptoms and slow disease progression, but a complete cure may not be achievable in all cases; outcomes depend on the underlying cause, response to treatment, and the management of complications
What is Nephrotic Syndrome?
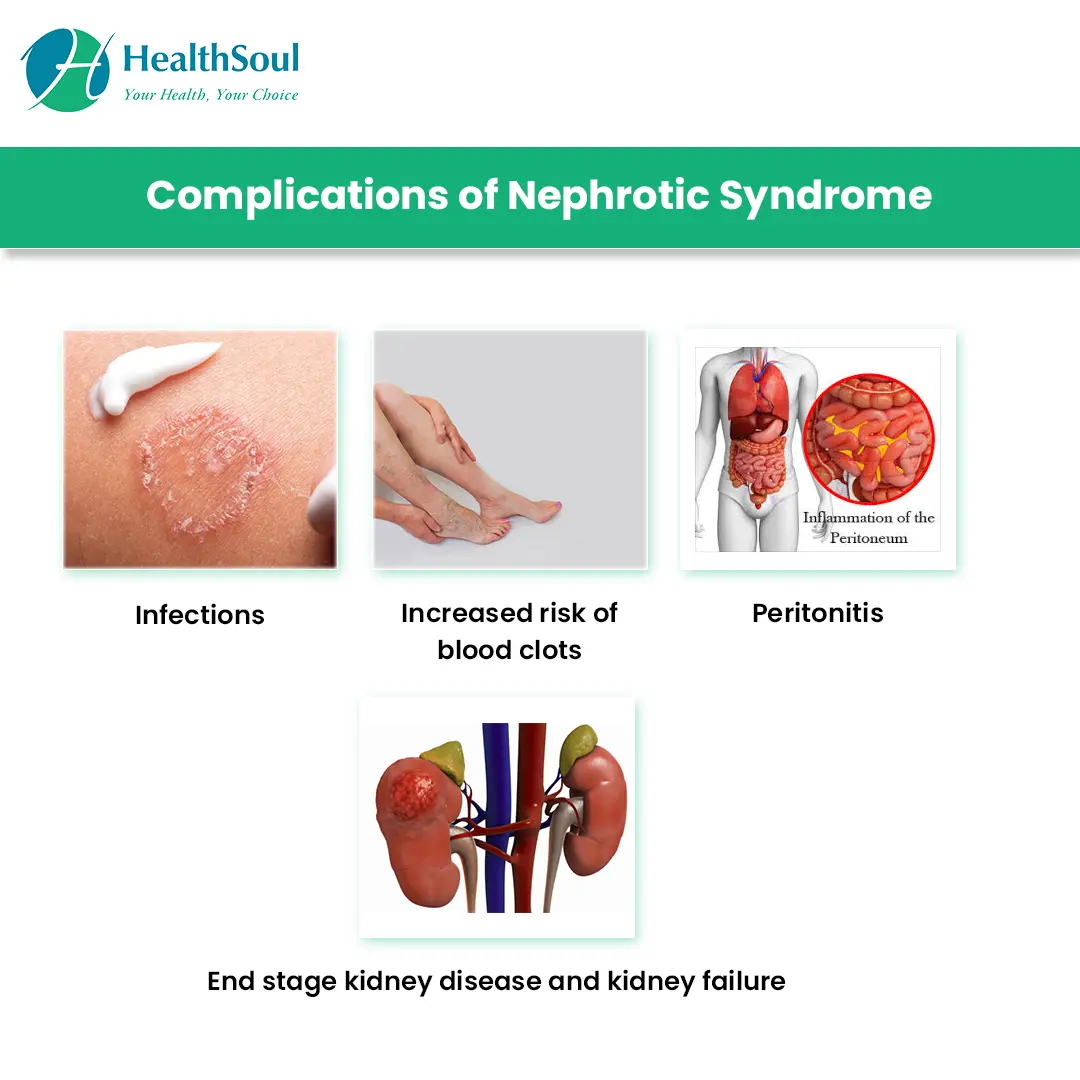
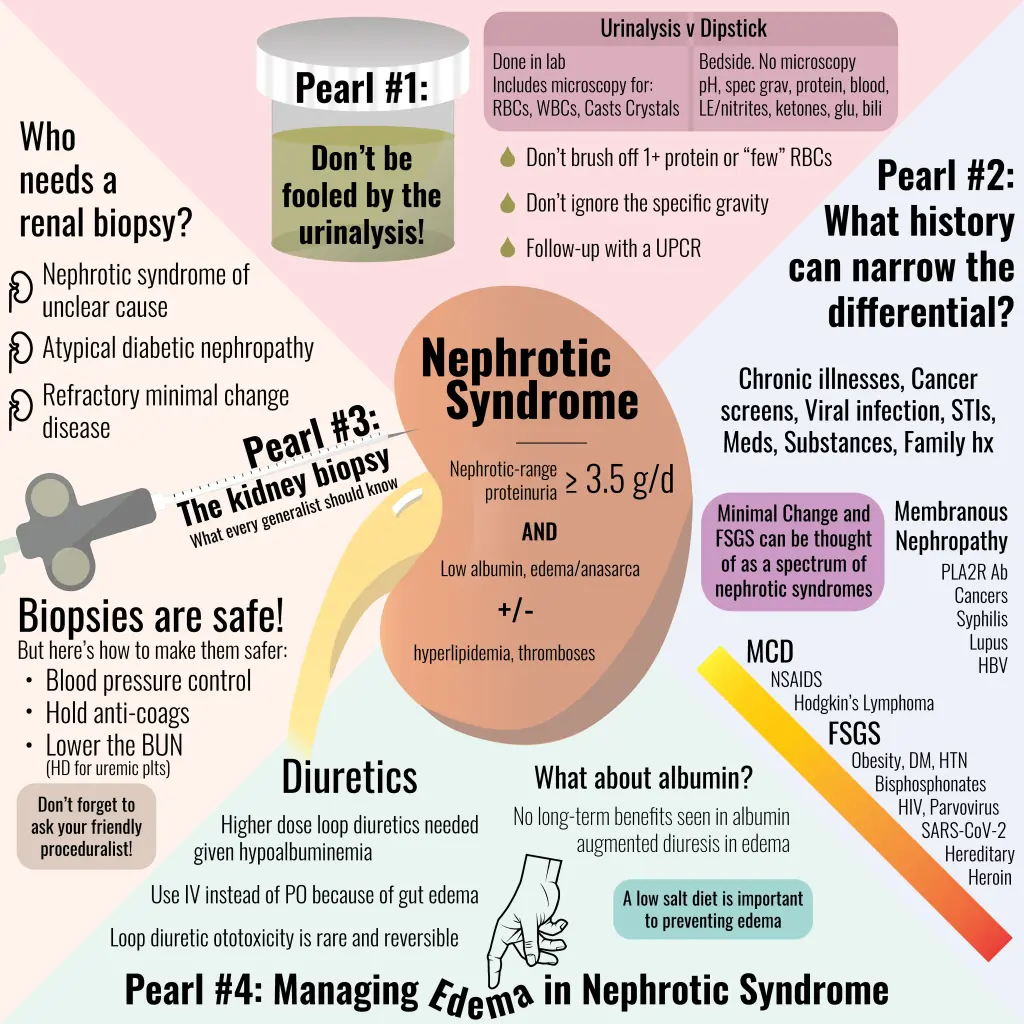
Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder characterized by the presence of protein in the urine, low protein levels in the blood, and swelling. Underlying causes may include glomerulonephritis or systemic diseases. Treatment involves addressing the cause, medications to reduce proteinuria and swelling, and dietary modifications. Ongoing monitoring is important to manage symptoms and prevent complications such as infections and blood clots.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Kidney disorder characterized by excessive protein loss in urine, leading to edema and other complications

Symptoms
Edema (swelling), proteinuria (excess protein in urine), hypoalbuminemia, high cholesterol levels

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, sometimes imaging

Prognosis
Variable, depends on underlying cause

Complications
Impaired function, potential for complications
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Various underlying causes, including glomerular diseases, diabetes, infections, autoimmune conditions, medications

Treatments
Management of underlying cause, medications (diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors), dietary restrictions

Prevention
Management of underlying cause, medications (diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors), dietary restrictions
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common, various causes including trauma

Patient Perspectives
Rehabilitation and management tailored to underlying cause
Please remember that this information is provided for general understanding, and individual cases may vary. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and information.
Share: