Can Methemoglobinemia be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment can effectively manage symptoms, but the condition may not be completely cured; outcomes depend on the underlying cause and the success of treatment
What is Methemoglobinemia?
Methemoglobinemia is a condition where there is an abnormal amount of methemoglobin in the blood, reducing its oxygen-carrying capacity. Treatment may involve medications and addressing the underlying cause.

Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Blood disorder where an abnormal amount of methemoglobin is produced, reducing the oxygen-carrying capacity of hemoglobin

Symptoms
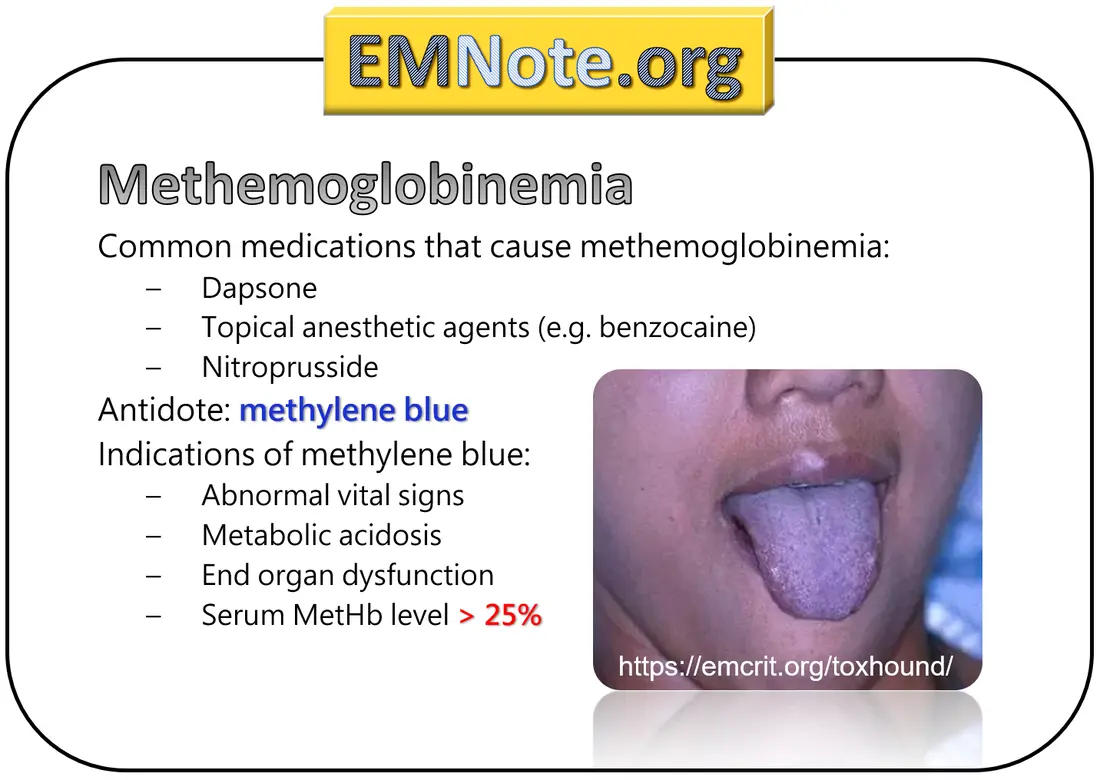
Bluish discoloration of the skin (cyanosis), shortness of breath, fatigue

Diagnosis
Blood tests, clinical evaluation

Prognosis
Generally good with appropriate treatment

Complications
Cyanosis, complications affecting oxygen transport
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Inherited genetic mutations, exposure to certain medications, chemicals, or foods

Treatments
Avoidance of triggering substances, medications (methylene blue, vitamin C), blood transfusion in severe cases

Prevention
Avoidance of triggering substances, medications (methylene blue, vitamin C), blood transfusion in severe cases
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Blood disorder characterized by elevated levels of methemoglobin

Patient Perspectives
Medications, supportive care
While the information presented here reflects the current knowledge about these conditions and treatments, it’s important to understand that individual cases may differ. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Share: