Can Lipoid Pneumonia be Cured?
Sometimes
Management involves treating symptoms, addressing the underlying cause, and preventing further aspiration; outcomes depend on the severity of lung involvement and the success of treatment
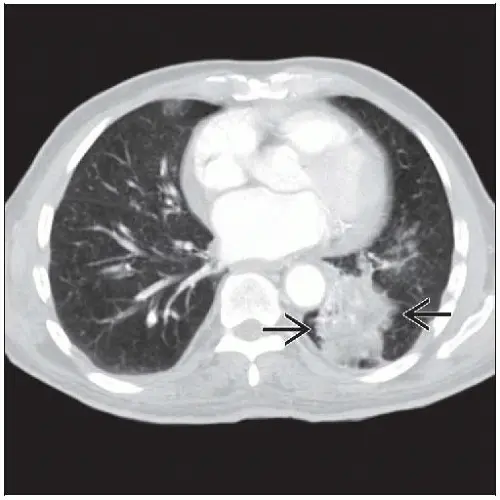
What is Lipoid Pneumonia?
Lipoid pneumonia is a rare type of pneumonia caused by the inhalation or aspiration of lipids or oily substances. Treatment involves identifying and eliminating the source of the lipid exposure and supportive care.
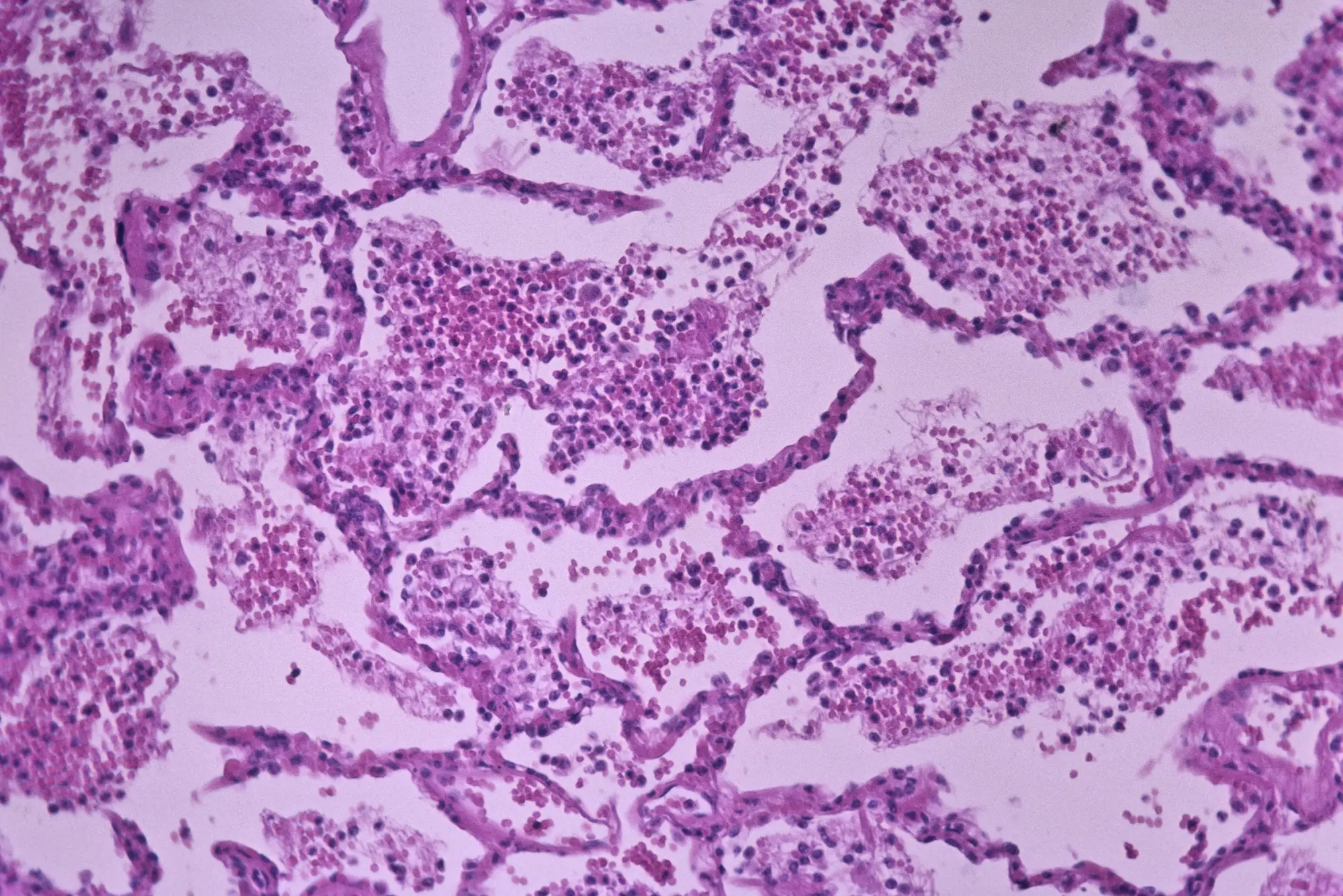
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Inflammatory lung condition caused by the aspiration or inhalation of fatty substances into the lungs

Symptoms
Cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, fever

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, imaging

Prognosis
Variable, depends on severity

Complications
Respiratory distress, potential for complications
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Aspiration or inhalation of oils, fats, or lipids; often associated with conditions like oil-based laxative use, liposuction, or impaired swallowing

Treatments
Supportive care, antibiotics if secondary infection is present, addressing the underlying cause (discontinuing oil-based laxatives, managing swallowing disorders)

Prevention
Supportive care, antibiotics if secondary infection is present, addressing the underlying cause (discontinuing oil-based laxatives, managing swallowing disorders)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common in certain populations, associated with aspiration

Patient Perspectives
Supportive care and addressing underlying cause
Remember, the information provided here is intended for general knowledge purposes and may not apply to every individual case. To ensure you have accurate information relevant to your specific situation, always consult with a healthcare professional.
Share: