Can Intracranial Aneurysm be Cured?
Depends on size
Management depends on the size and risk of rupture; intervention may be needed in some cases
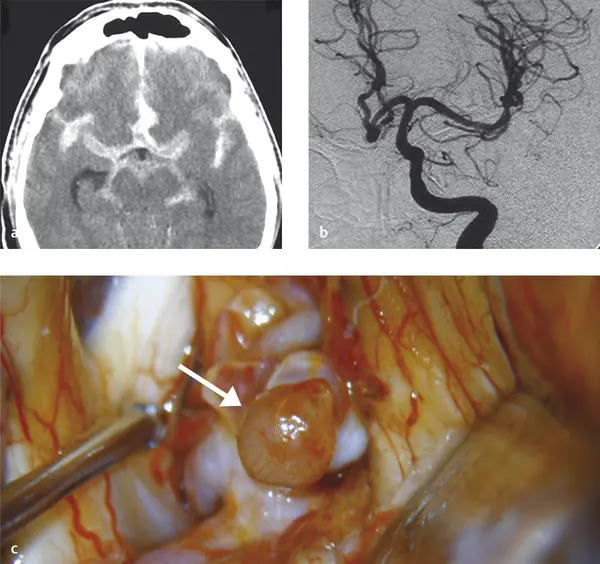
What is Intracranial Aneurysm?
An intracranial aneurysm is a bulging, weakened area in the wall of an artery within the brain. If ruptured, it can lead to a serious condition called subarachnoid hemorrhage. Treatment options include observation, medications to control risk factors, and surgical interventions to prevent rupture in certain cases. Early detection is essential for managing the risk.
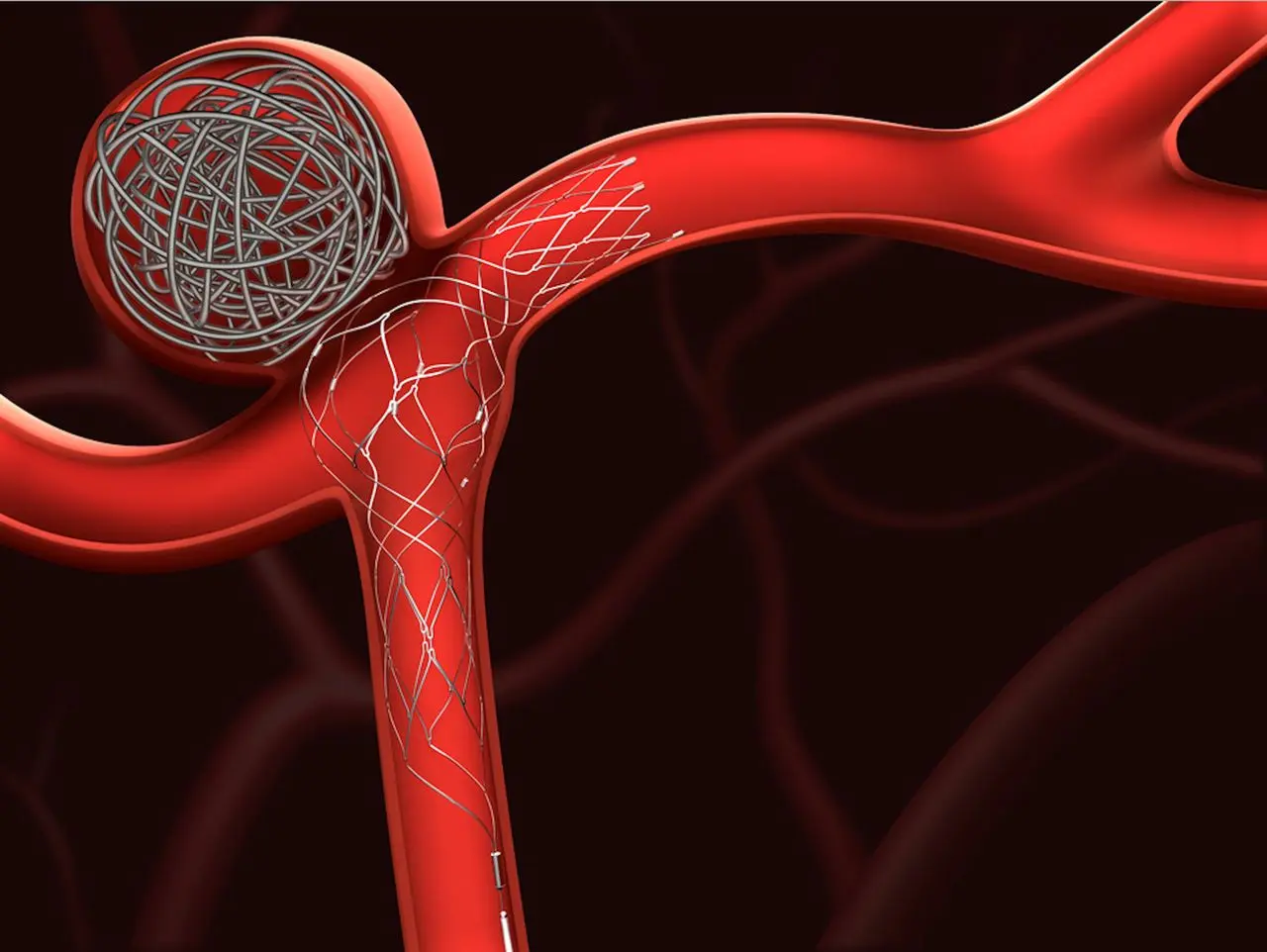
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Ballooning or bulging of a blood vessel in the brain

Symptoms
Headache, visual disturbances

Diagnosis
Imaging studies, sometimes angiography

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the size and location of the aneurysm

Complications
Rupture, complications affecting neurological function
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Weakness in blood vessel walls, genetic factors

Treatments
Monitoring, surgical intervention (if necessary)

Prevention
Monitoring, surgical intervention (if necessary)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Weakness in a blood vessel wall in the brain, leading to ballooning

Patient Perspectives
Monitoring, surgery in certain cases
Please remember that this information is provided for general understanding, and individual cases may vary. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and information.
Share: