Can Hyperuricemia be Cured?
Sometimes
Management involves controlling uric acid levels to prevent complications; outcomes depend on the specific cause and the success of treatment

What is Hyperuricemia?
Hyperuricemia is an elevated level of uric acid in the blood, which can lead to the formation of crystals in joints, causing gout. Lifestyle changes, such as diet modification, and medications to lower uric acid levels are common approaches to managing hyperuricemia and preventing gout attacks.
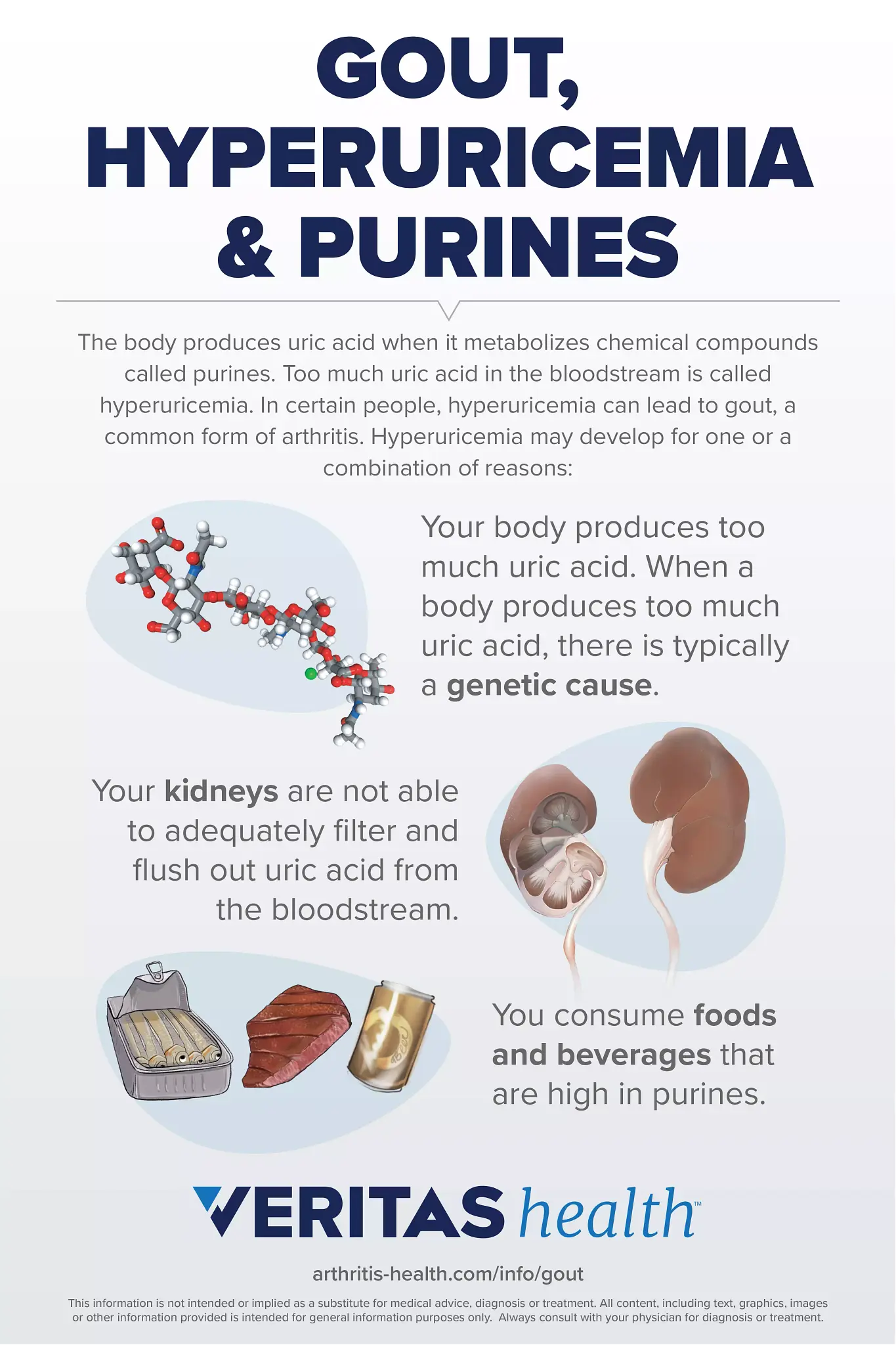
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, which can lead to the formation of urate crystals in joints and tissues

Symptoms
Joint pain, swelling, kidney stones

Diagnosis
Blood tests, imaging

Prognosis
Variable, depends on gout and underlying cause

Complications
Gout, kidney stones
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetics, diet (high-purine foods), certain medical conditions (gout, kidney disease)

Treatments
Lifestyle modifications (dietary changes, hydration), medications to lower uric acid levels

Prevention
Lifestyle modifications (dietary changes, hydration), medications to lower uric acid levels
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common, often associated with gout

Patient Perspectives
Lifelong management and dietary changes
Please remember that this information is provided for general understanding, and individual cases may vary. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and information.
Share: