Can Hyperthyroidism be Cured?
Sometimes
Management aims to control thyroid hormone levels; outcomes depend on the specific cause and the success of treatment; lifelong management may be necessary, and some cases may require ongoing monitoring and adjustments to treatment
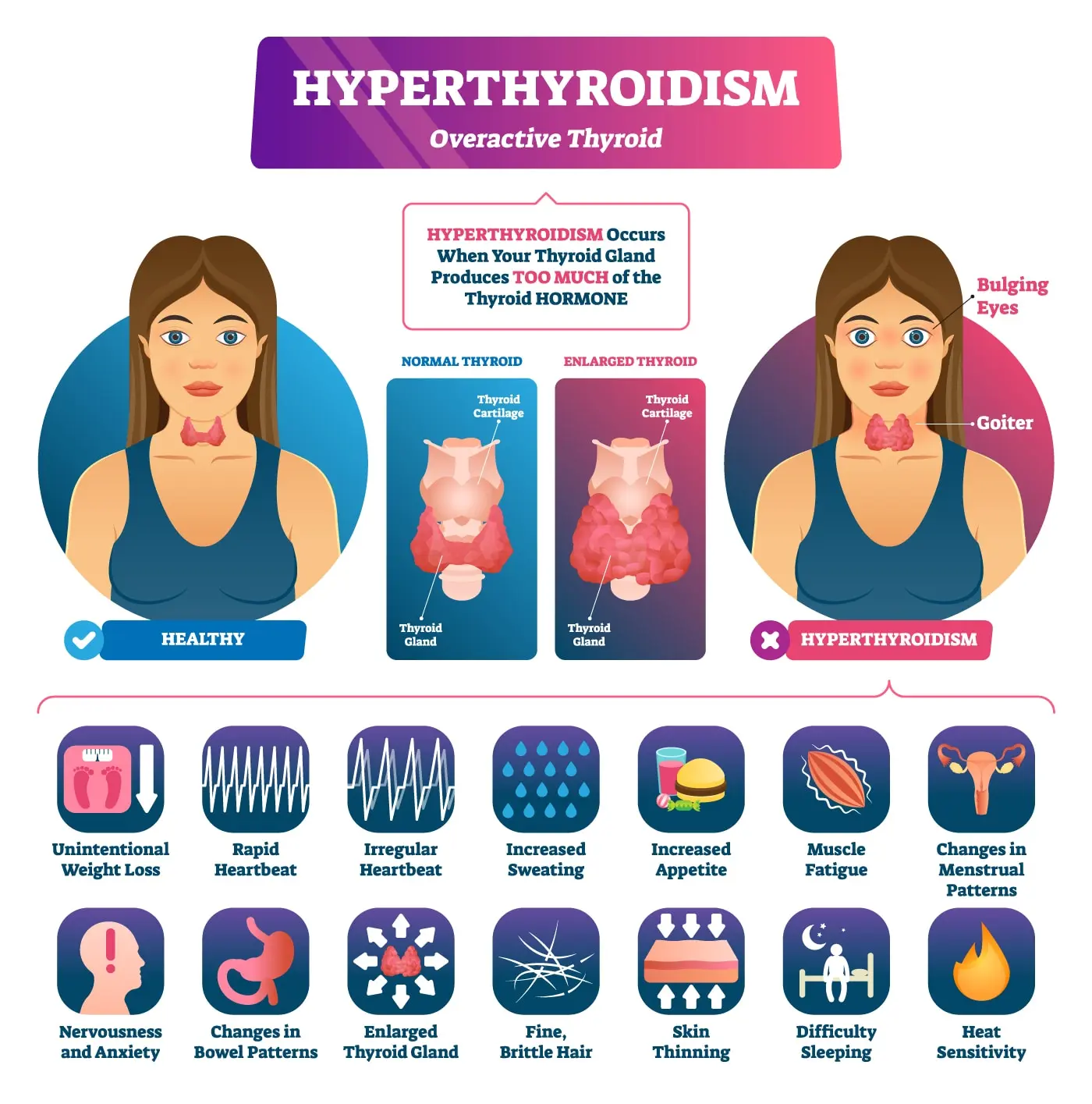
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces excessive thyroid hormones, leading to an overactive metabolism. Symptoms may include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety. Treatment options include medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery to manage thyroid hormone levels.
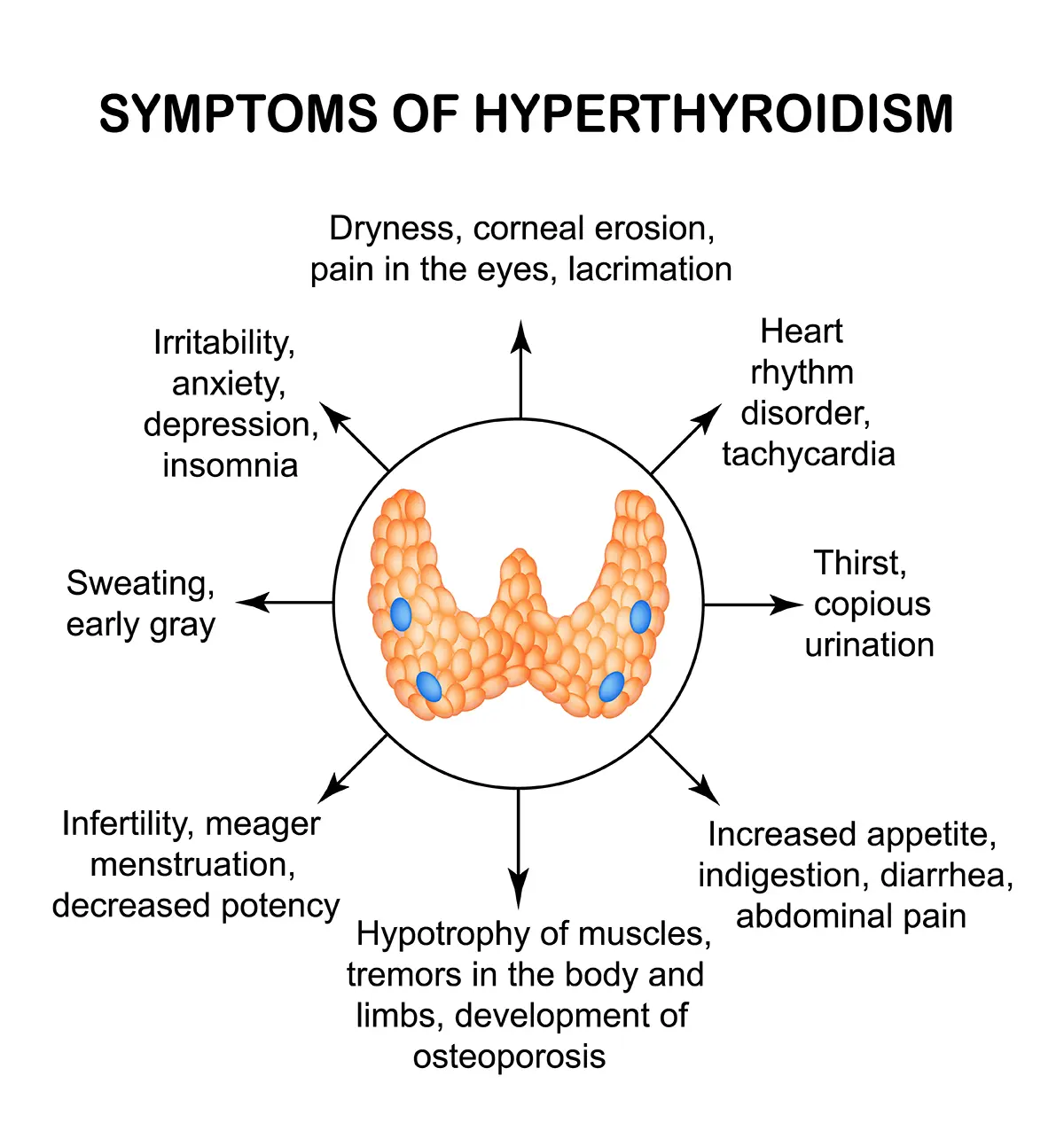
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Overactivity of the thyroid gland, leading to excessive production of thyroid hormones

Symptoms
Weight loss, rapid heartbeat, tremors, heat intolerance, anxiety

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, blood tests, imaging

Prognosis
Variable, depends on treatment and disease control

Complications
Thyroid complications, potential for eye issues
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Graves’ disease, toxic nodular goiter, thyroiditis

Treatments
Medications to block thyroid hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy, surgery to remove the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy)

Prevention
Medications to block thyroid hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy, surgery to remove the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common, more prevalent in females

Patient Perspectives
Lifelong management tailored to symptoms and risks
Remember, the information provided here is intended for general knowledge purposes and may not apply to every individual case. To ensure you have accurate information relevant to your specific situation, always consult with a healthcare professional.
Share: