Can Hyperphosphatemia be Cured?
Sometimes
Management focuses on addressing the underlying cause and controlling phosphate levels; outcomes depend on the specific cause and the success of managing phosphate levels
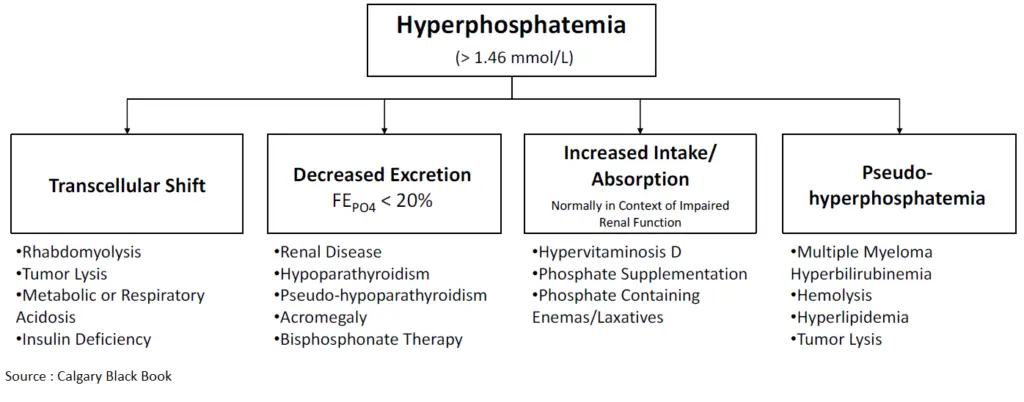
What is Hyperphosphatemia?
Hyperphosphatemia is an elevated level of phosphate in the blood, often associated with kidney dysfunction. It can lead to complications such as bone and cardiovascular issues. Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause, restricting dietary phosphate, and sometimes using phosphate-binding medications.
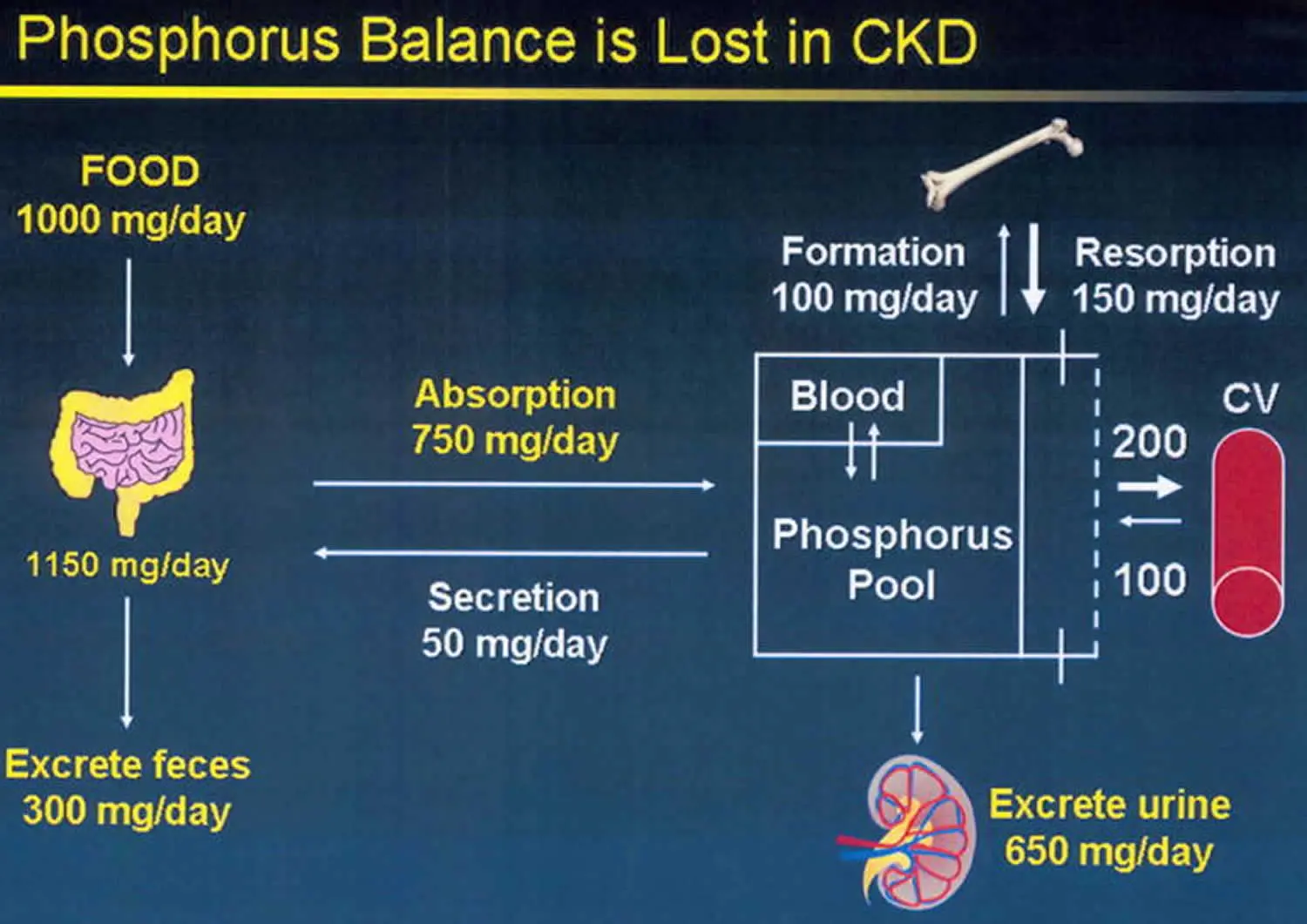
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Elevated levels of phosphate in the blood

Symptoms
Muscle cramps, weakness, joint pain, itching

Diagnosis
Blood tests, imaging

Prognosis
Variable, depends on underlying cause

Complications
Kidney damage, vascular calcification
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Kidney disease, certain medications, excessive intake of phosphate

Treatments
Treatment of the underlying cause, dietary modifications, medications to bind phosphate in the intestines

Prevention
Treatment of the underlying cause, dietary modifications, medications to bind phosphate in the intestines
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common, often associated with kidney disease

Patient Perspectives
Management tailored to underlying cause
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: