Can Hemolytic Anemia be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment aims to control the underlying cause and manage symptoms; outcomes vary depending on the specific type and cause of hemolytic anemia; some cases can be effectively managed, while others may require ongoing interventions
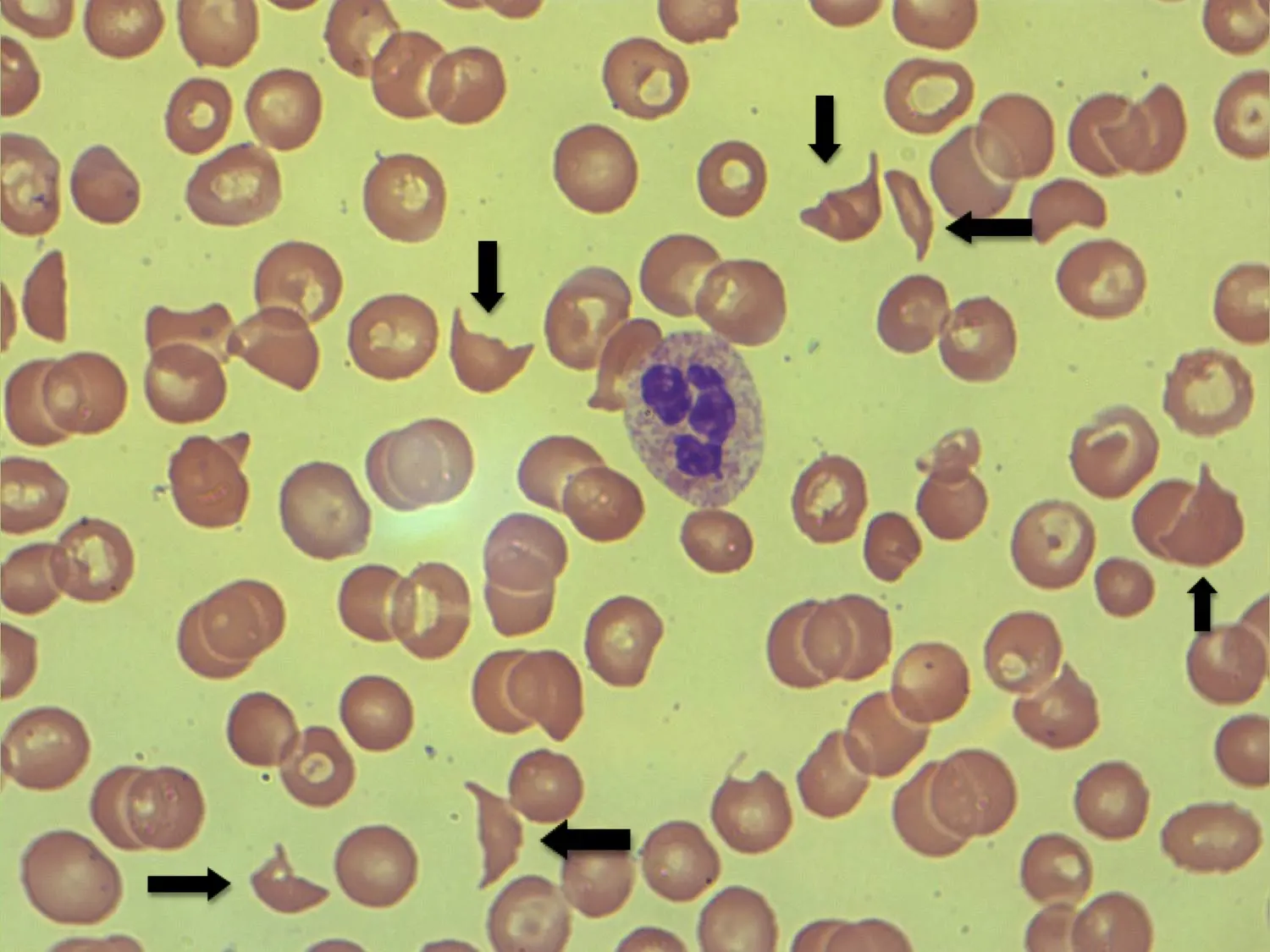
What is Hemolytic Anemia?
Hemolytic anemia occurs when red blood cells are destroyed faster than the body can replace them. Treatment depends on the cause and may involve medications or, in severe cases, blood transfusions.
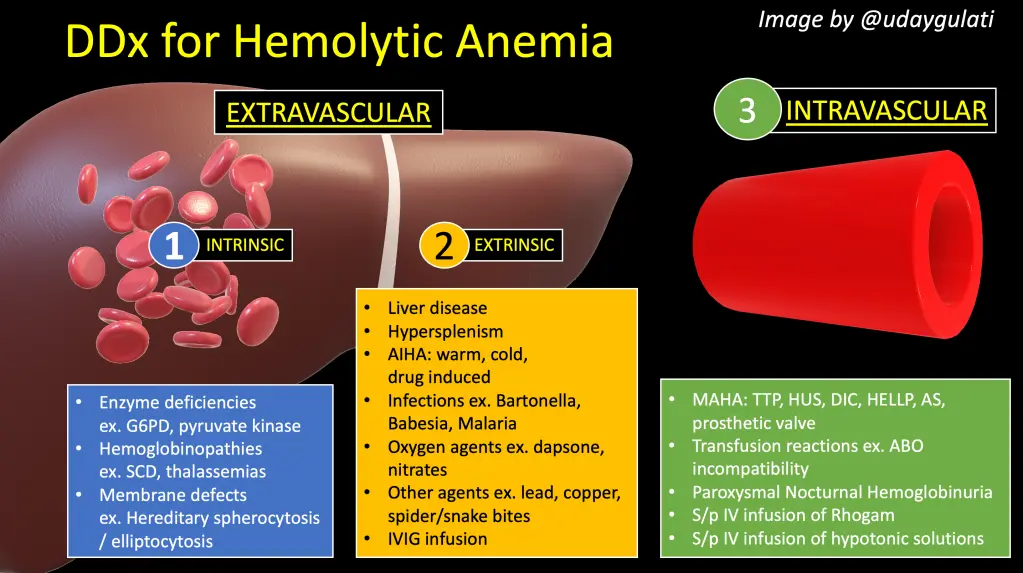
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Group of disorders characterized by the premature destruction of red blood cells

Symptoms
Fatigue, pale skin, jaundice, dark urine, enlarged spleen

Diagnosis
Blood tests, sometimes bone marrow biopsy

Prognosis
Variable, depends on the cause and interventions

Complications
Organ damage, complications affecting multiple systems
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Various causes, including genetic mutations, autoimmune reactions, infections, medications

Treatments
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include medications, blood transfusions, immunosuppressive therapy

Prevention
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include medications, blood transfusions, immunosuppressive therapy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Accelerated destruction of red blood cells

Patient Perspectives
Management of underlying causes, sometimes blood transfusions
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: