Can Endophthalmitis be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment success depends on factors such as the underlying cause, the timeliness of intervention, and the severity of the inflammation; outcomes can vary, and complications may affect vision
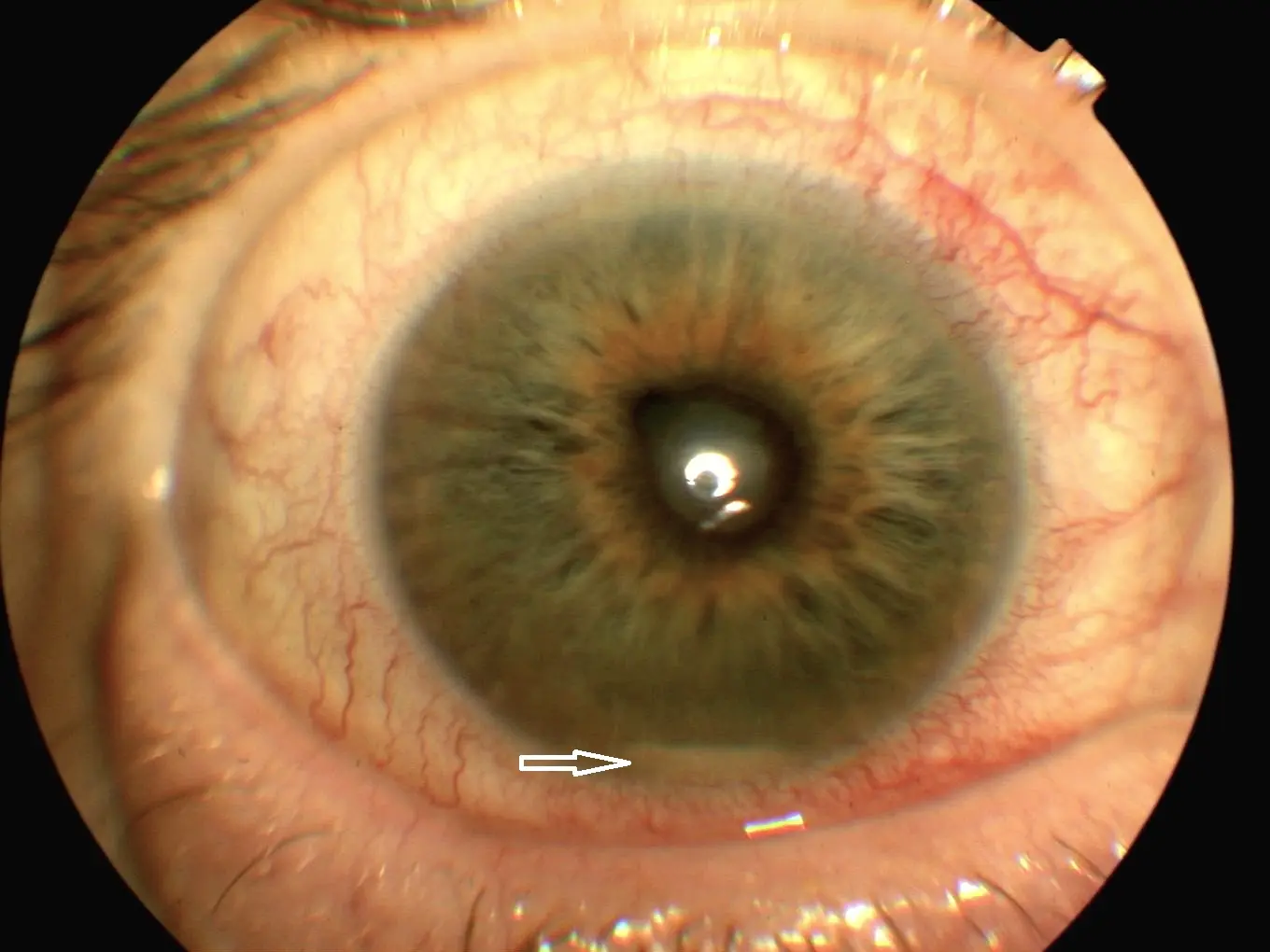
What is Endophthalmitis?
Endophthalmitis is inflammation of the interior of the eye, often caused by infection. It can lead to vision loss if not promptly treated. Treatment involves antibiotics and, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
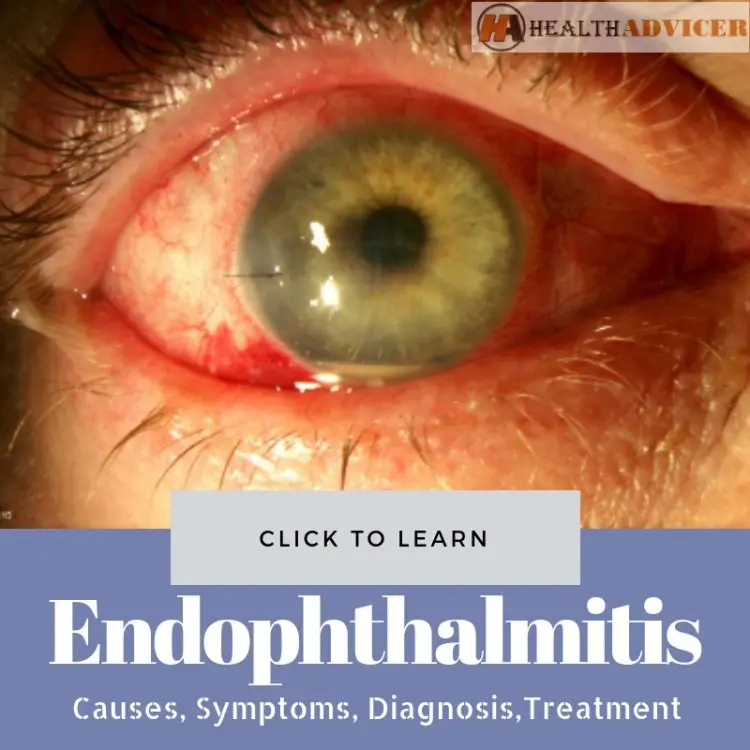
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Inflammation of the interior of the eye, often affecting the uvea (middle layer)

Symptoms
Eye pain, redness, decreased vision

Diagnosis
Clinical examination, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the cause and response to treatment

Complications
Vision loss, complications of untreated endophthalmitis
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Bacterial or fungal infections entering the eye, often following eye surgery, trauma, or other eye conditions

Treatments
Antibiotics or antifungal medications, sometimes surgery to drain infected fluids

Prevention
Antibiotics or antifungal medications, sometimes surgery to drain infected fluids
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Inflammation of the inner eye

Patient Perspectives
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial
This information aims to provide a general understanding of the subject matter, but individual circumstances can vary significantly. Please remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Share: