Can End-Stage Liver Disease be Cured?
Sometimes
No cure; management focuses on supportive care, addressing complications, and improving quality of life; liver transplantation is a potential option for some individuals
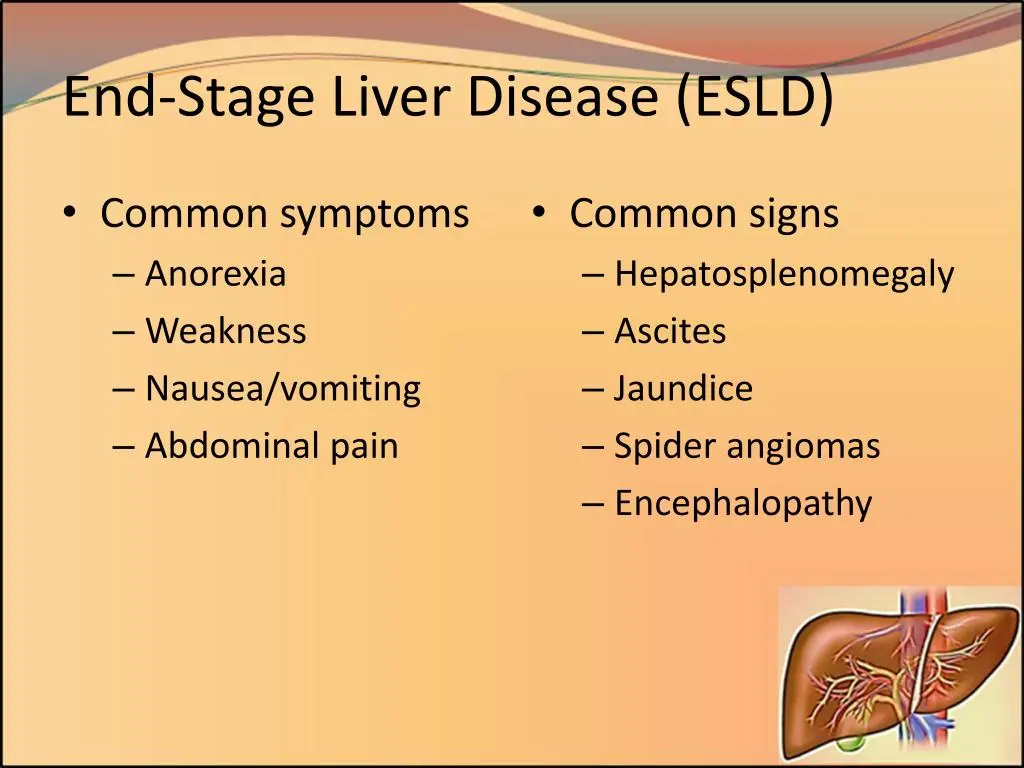
What is End-Stage Liver Disease?
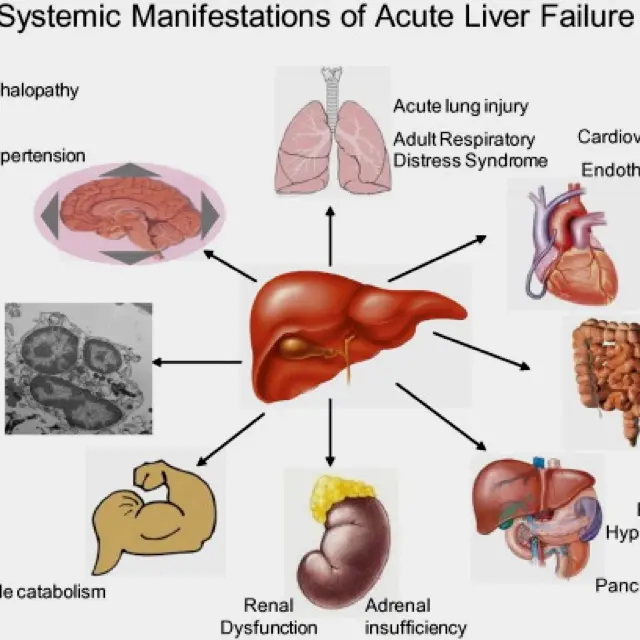
End-stage liver disease refers to advanced liver damage, often caused by chronic liver conditions. Liver transplantation may be considered in severe cases. Management involves addressing symptoms and complications.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Advanced and irreversible damage to the liver, resulting in loss of liver function

Symptoms
Fatigue, abdominal swelling, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)

Diagnosis
Laboratory tests, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the management of complications and treatment

Complications
Hepatic encephalopathy, complications of untreated liver disease
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Chronic liver diseases (e.g., cirrhosis, hepatitis B or C), alcohol-related liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease

Treatments
Liver transplantation, management of complications, lifestyle modifications

Prevention
Liver transplantation, management of complications, lifestyle modifications
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Advanced liver damage with impaired function

Patient Perspectives
Management involves addressing the underlying cause and providing supportive care
Please remember that this information is provided for general understanding, and individual cases may vary. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and information.
Share: