Can Emphysema be Cured?
Sometimes
No cure; management focuses on relieving symptoms, slowing disease progression, and improving lung function; smoking cessation is crucial for slowing the progression of emphysema
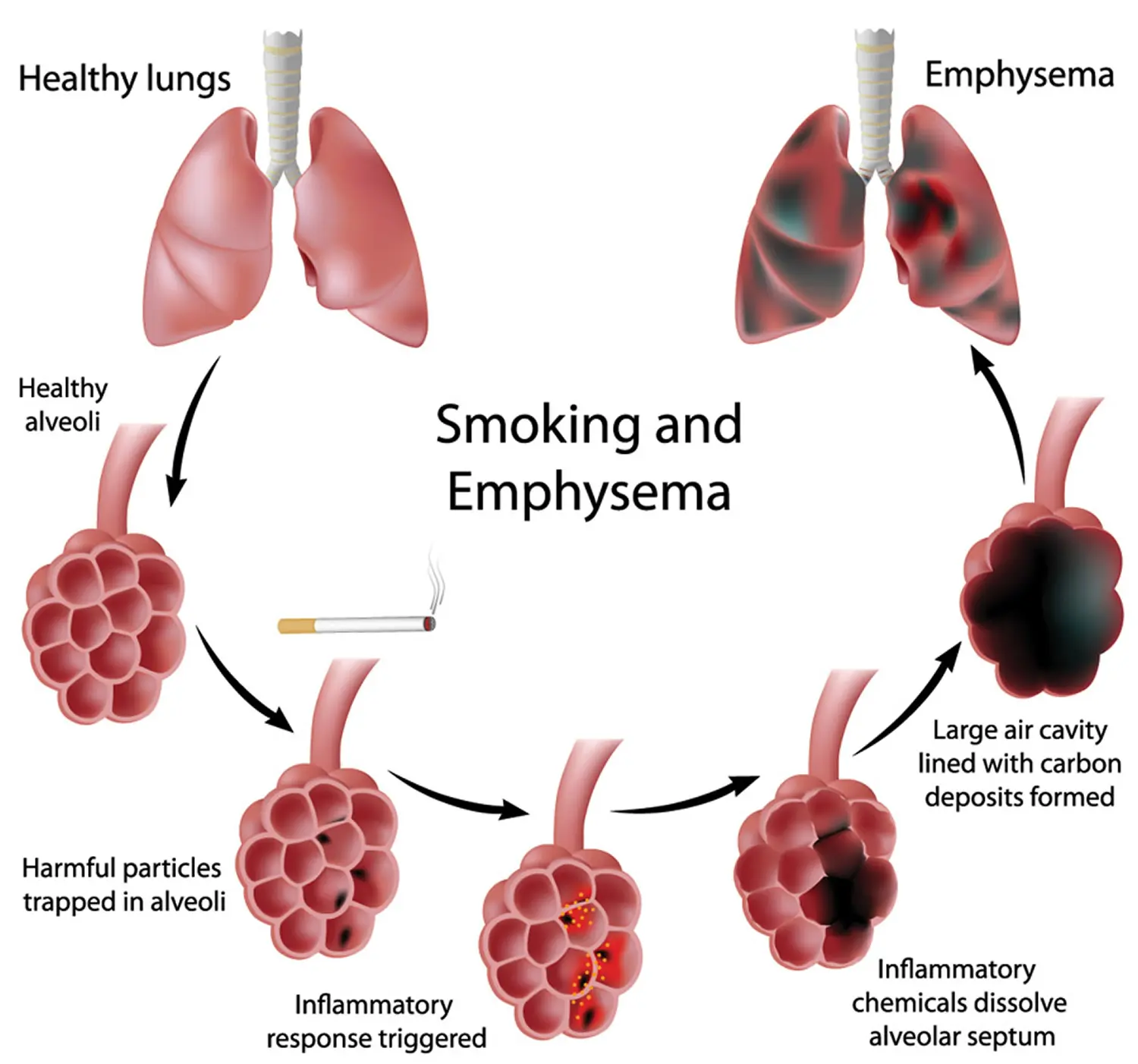
What is Emphysema?
Emphysema is a chronic lung condition characterized by damage to the air sacs in the lungs, leading to difficulty breathing. It is often associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Treatment involves medications, lifestyle changes, and oxygen therapy.
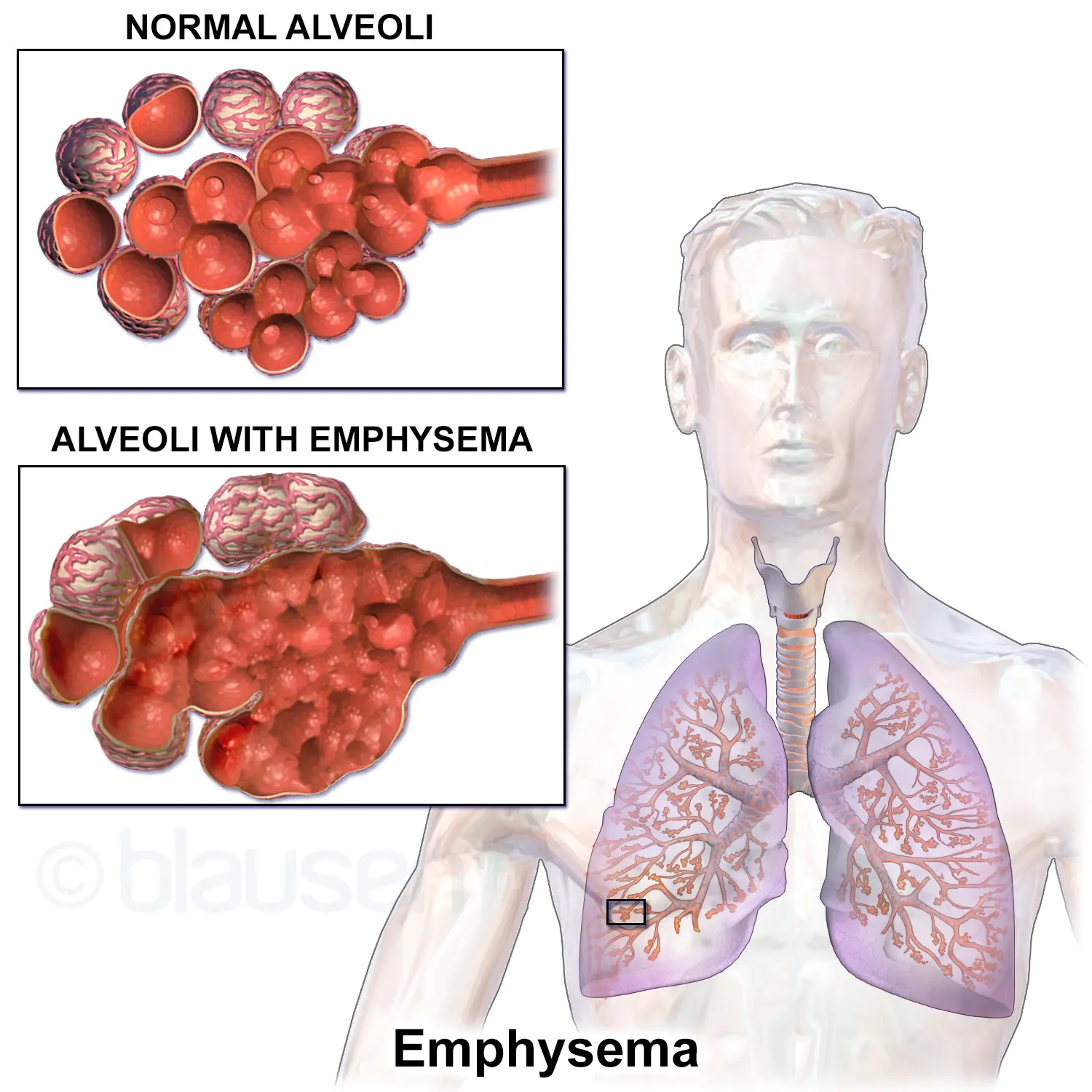
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Chronic lung disease characterized by the destruction of lung tissue, leading to difficulty breathing

Symptoms
Shortness of breath, chronic cough, wheezing

Diagnosis
Pulmonary function tests, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the stage and response to treatment

Complications
Respiratory failure, complications of advanced disease
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Long-term exposure to irritants, primarily cigarette smoke

Treatments
Smoking cessation, bronchodilators, inhaled steroids, oxygen therapy

Prevention
Smoking cessation, bronchodilators, inhaled steroids, oxygen therapy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Chronic lung disease characterized by damaged air sacs

Patient Perspectives
Management involves lifestyle changes, medications, and oxygen therapy
This information serves as a general overview and does not constitute professional medical advice. Always consult with healthcare providers for accurate and personalized insights regarding your health.
Share: