Can Eisenmenger Syndrome be Cured?
Sometimes
Management aims to improve symptoms and quality of life; outcomes vary, and advanced cases may require specialized medical interventions
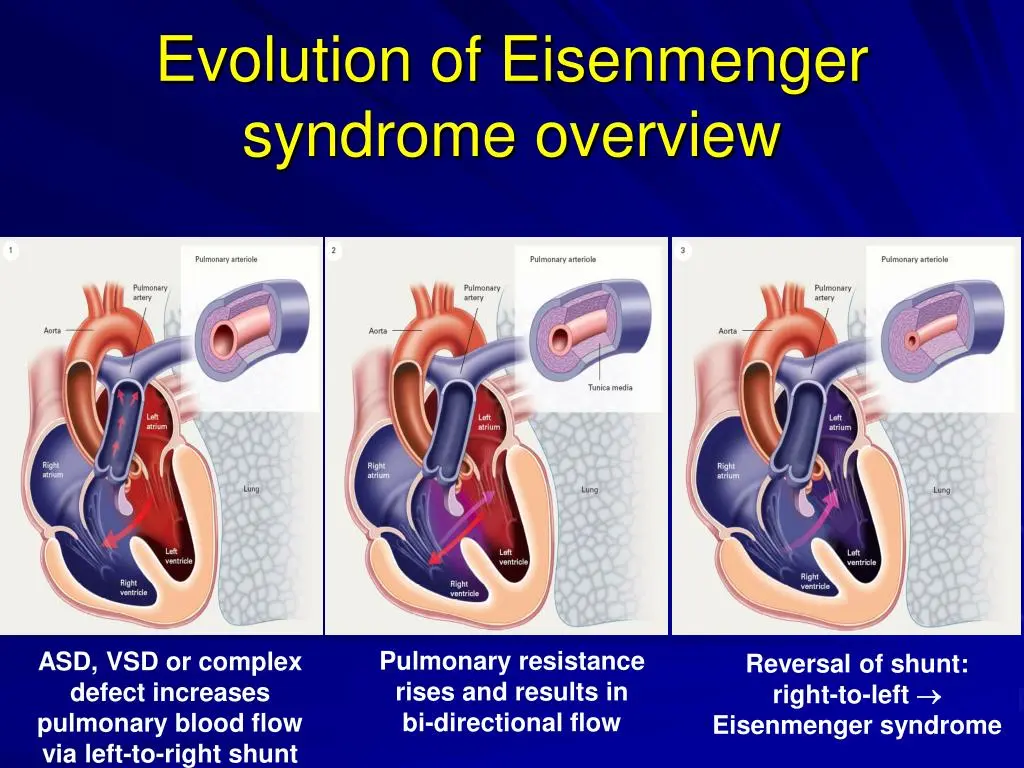
What is Eisenmenger Syndrome?
Eisenmenger syndrome is a condition where a congenital heart defect leads to pulmonary hypertension and reversal of blood flow in the heart. It can result in cyanosis and other complications. Treatment involves managing symptoms and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
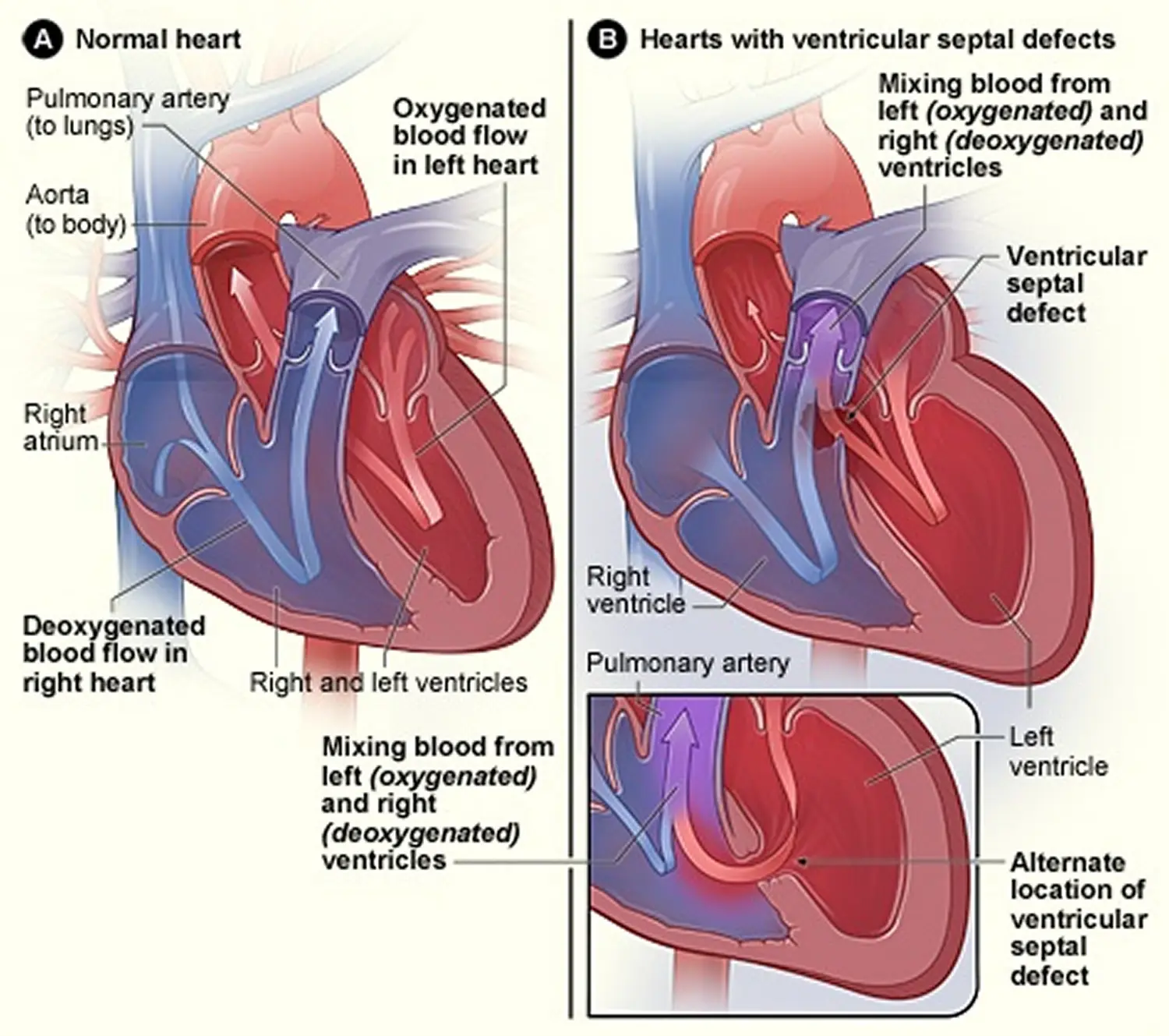
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Complication of certain congenital heart defects, leading to abnormal blood flow and increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries

Symptoms
Shortness of breath, fatigue, cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin), chest pain

Diagnosis
Imaging studies, clinical examination

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the severity and complications

Complications
Heart failure, complications of untreated syndrome
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Congenital heart defects causing a shunt (abnormal blood flow) between the left and right sides of the heart, leading to pulmonary hypertension

Treatments
Medications to manage symptoms, oxygen therapy, heart and lung transplantation in severe cases

Prevention
Medications to manage symptoms, oxygen therapy, heart and lung transplantation in severe cases
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Heart defect leading to increased blood flow in the lungs

Patient Perspectives
Management aims at improving symptoms and preventing complications
For personalized advice and care, always seek the assistance of healthcare professionals. This information is meant for general understanding and not as a replacement for professional medical advice.
Share: