Can Ectopic Pregnancy be Cured?
No
Ectopic pregnancies cannot be relocated to the uterus, and the affected pregnancy must be removed to prevent life-threatening complications
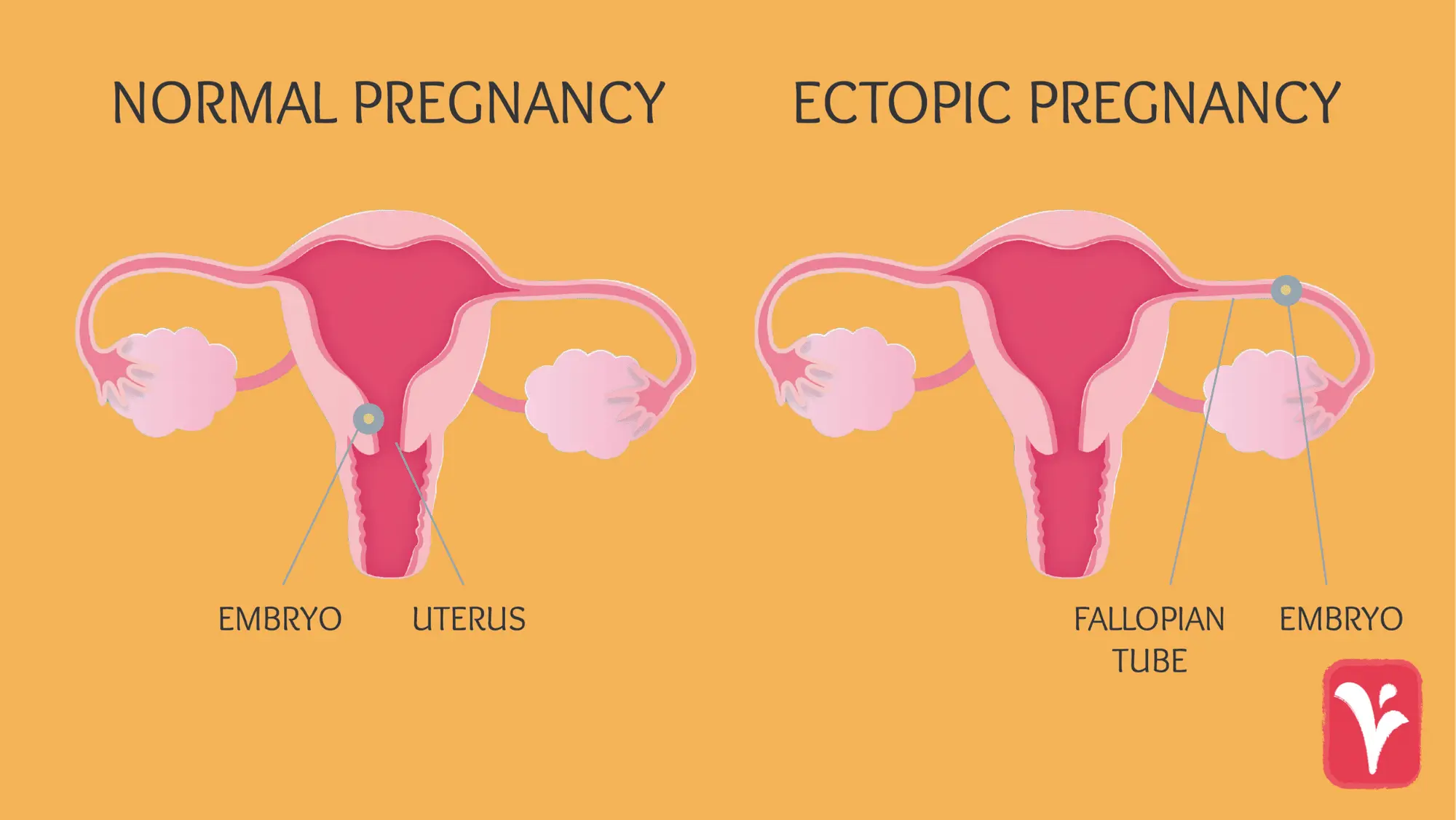
What is Ectopic Pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. It poses a serious health risk and requires medical intervention, often through surgery or medication.
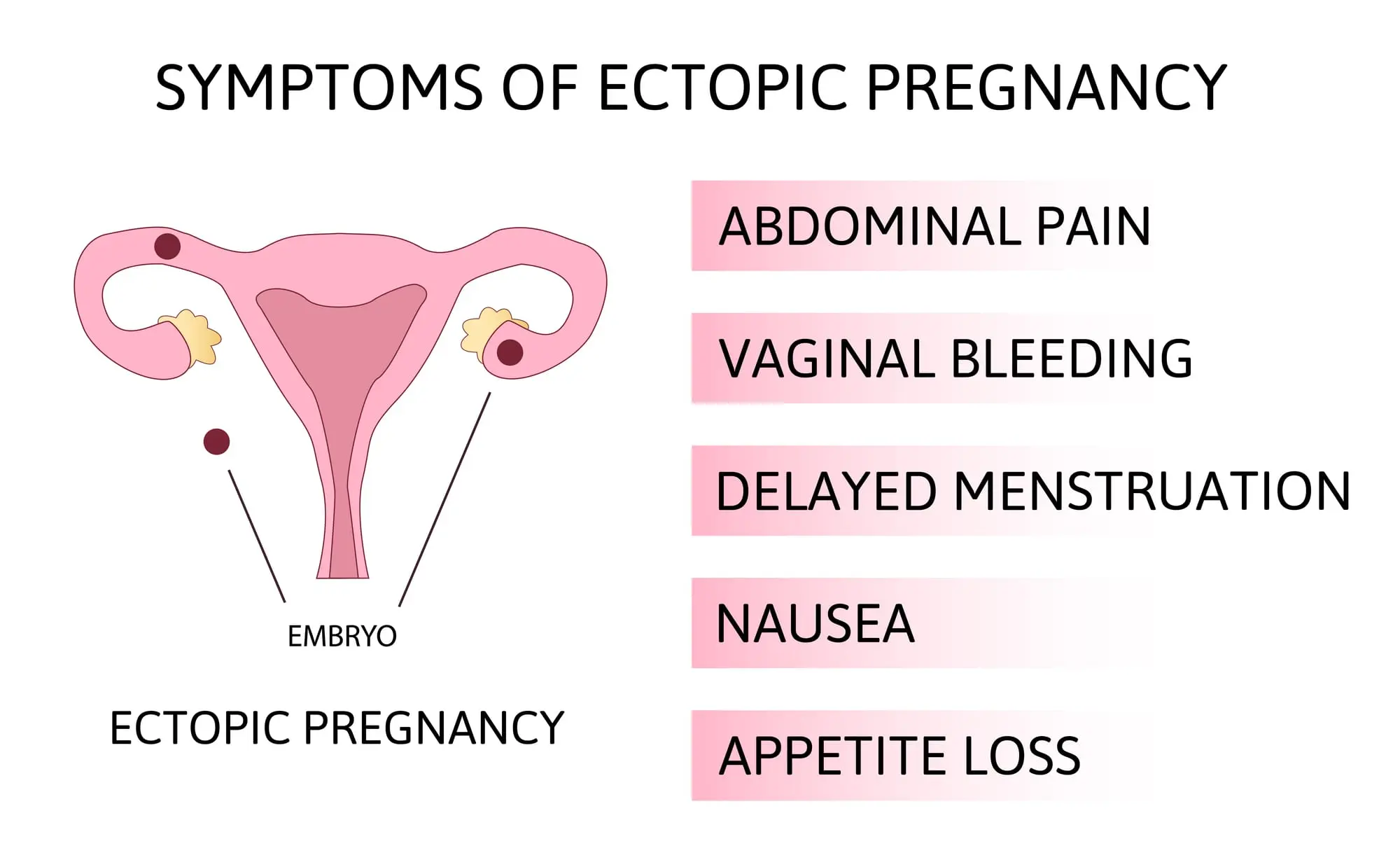
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Implantation of the fertilized egg outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube

Symptoms
Abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, dizziness, shoulder pain (if there is bleeding into the abdomen)

Diagnosis
Clinical examination, ultrasound

Prognosis
Generally good with early detection and appropriate intervention

Complications
Rupture, complications of untreated ectopic pregnancy
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Issues with the fallopian tubes, scarring, inflammation, previous surgeries, hormonal imbalances, use of assisted reproductive technologies

Treatments
Medications to address ectopic tissue, surgery to remove the ectopic pregnancy

Prevention
Medications to address ectopic tissue, surgery to remove the ectopic pregnancy
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Implantation of the embryo outside the uterus

Patient Perspectives
Early detection and intervention are crucial for preventing complications
As always, consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and care.
Share: