Can Ebola Virus Disease be Cured?
Sometimes
No specific cure; supportive care and treatment of symptoms are crucial; potential vaccines and experimental treatments are being explored
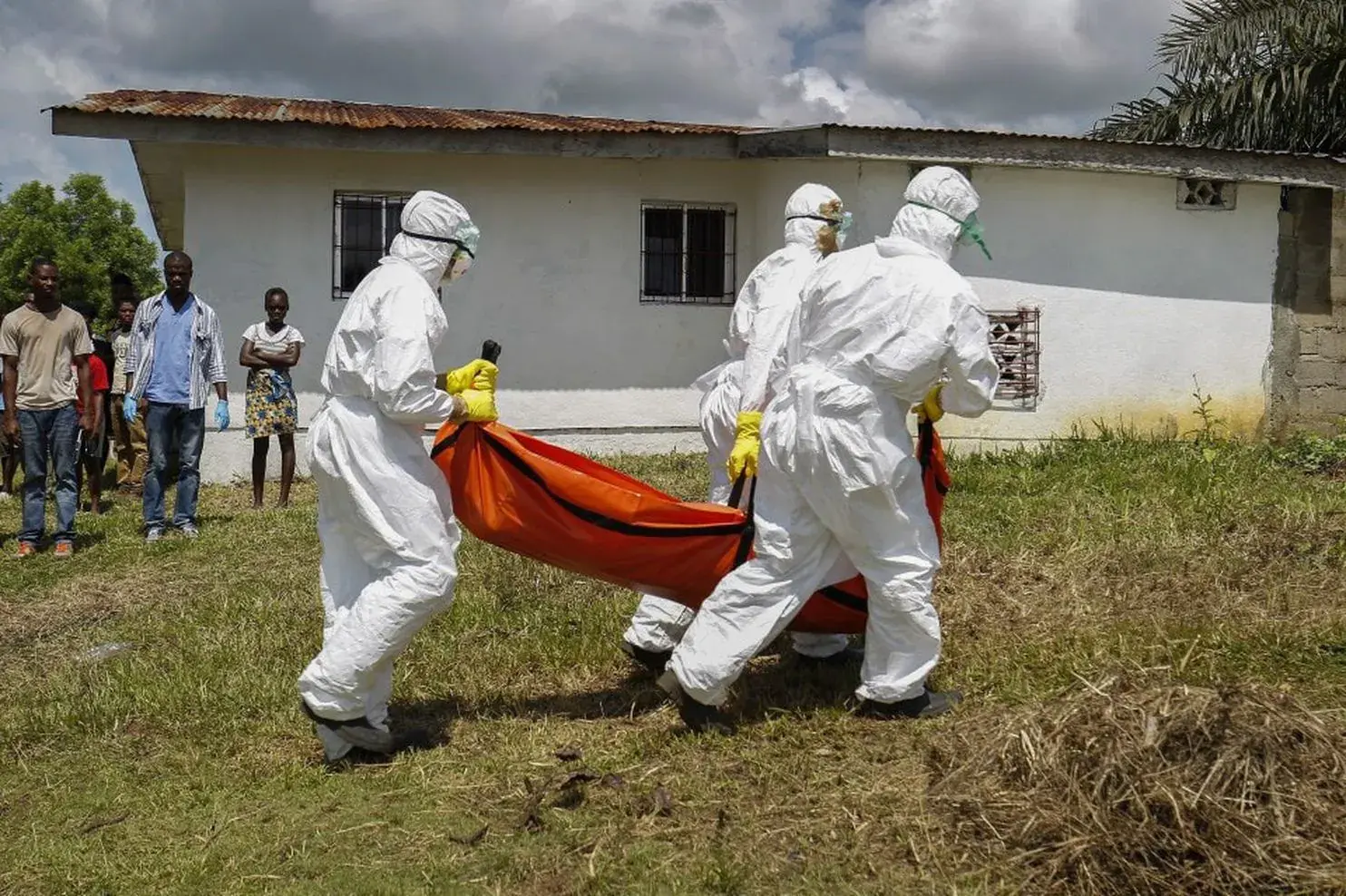

What is Ebola Virus Disease?
Ebola virus disease is a severe and often fatal illness caused by the Ebola virus. It is transmitted through direct contact with the blood or body fluids of an infected person or animal. Prevention involves infection control measures, and treatment focuses on supportive care.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Viral infection caused by the Ebola virus, leading to severe illness and a high mortality rate

Symptoms
Fever, severe headache, muscle pain, fatigue, vomiting, diarrhea, hemorrhagic symptoms

Diagnosis
Laboratory tests, clinical evaluation

Prognosis
Variable; can be severe and life-threatening

Complications
Hemorrhage, organ failure, complications of severe cases
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Zoonotic transmission from animals to humans; human-to-human transmission through contact with infected bodily fluids

Treatments
Supportive care, isolation, treatment of specific symptoms, experimental antiviral medications (in some cases)

Prevention
Supportive care, isolation, treatment of specific symptoms, experimental antiviral medications (in some cases)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Viral infection caused by Ebola virus

Patient Perspectives
Prevention, early detection, and supportive care are crucial
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: