Can Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease be Cured?
No
No cure; management focuses on relieving symptoms, slowing disease progression, and improving quality of life
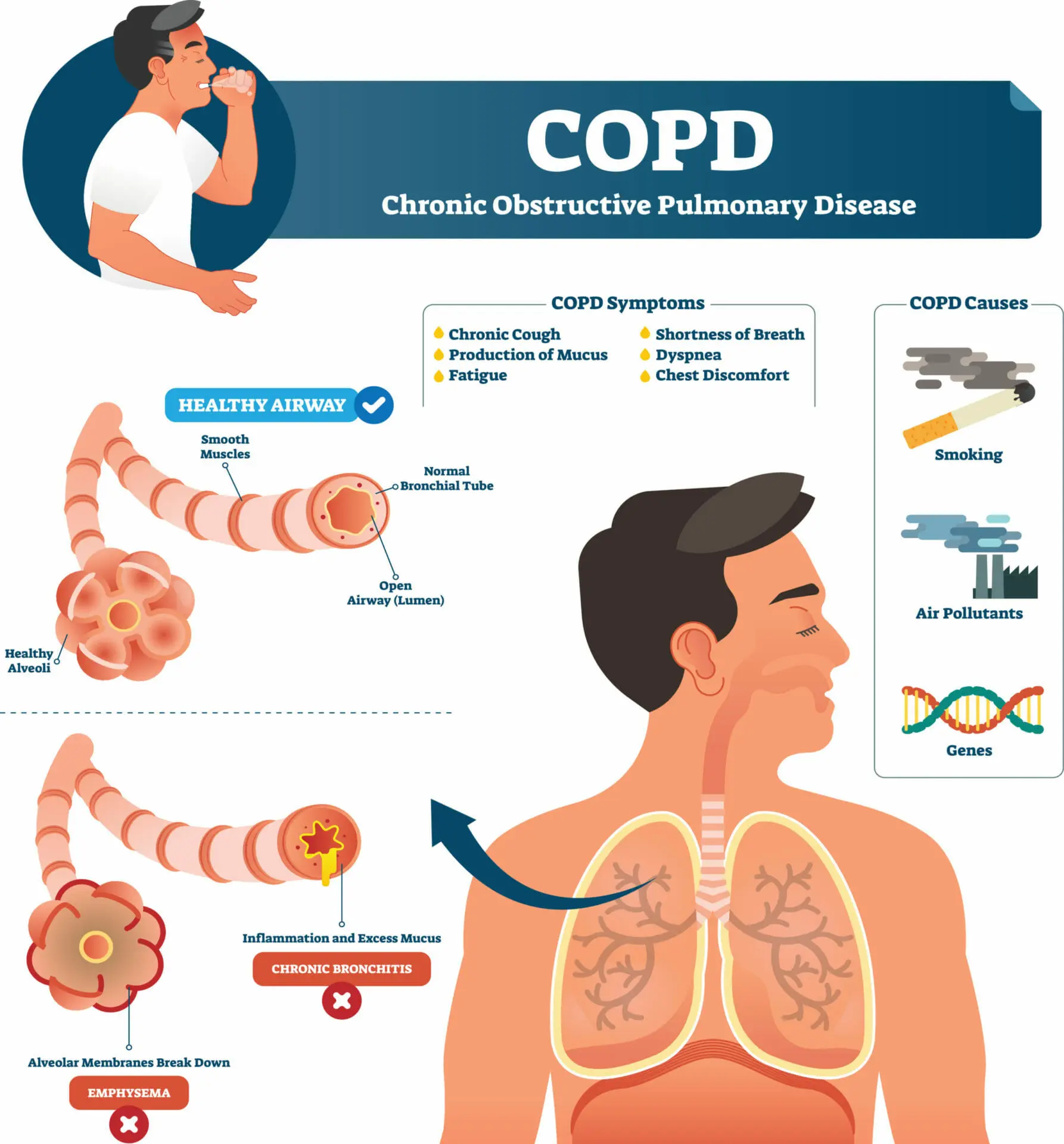
What is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition that includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It is often caused by smoking and leads to breathing difficulties. Management involves smoking cessation, medications, and respiratory therapies.
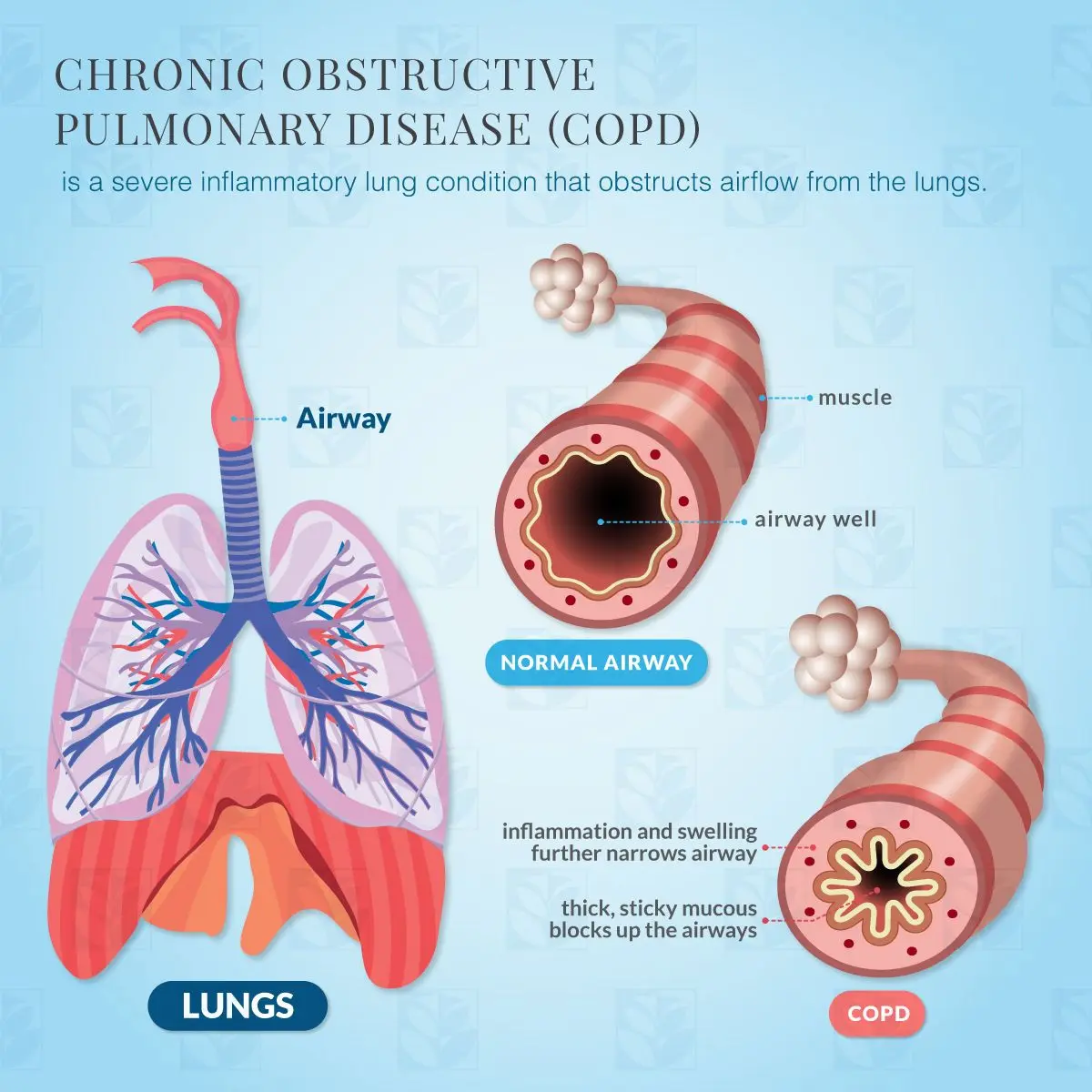
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Progressive lung disease characterized by chronic inflammation, airflow limitation, and difficulty breathing

Symptoms
Chronic cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, frequent respiratory infections

Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation, pulmonary function tests, imaging studies

Prognosis
Variable, may progress over time with appropriate management

Complications
Respiratory failure, complications affecting lung function
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Smoking, exposure to air pollutants, genetic factors

Treatments
Smoking cessation, bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, pulmonary rehabilitation

Prevention
Smoking cessation, bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, pulmonary rehabilitation
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Progressive lung disease characterized by airflow limitation

Patient Perspectives
Smoking cessation, bronchodilators, lifestyle modifications
Please note that the information provided is based on the current understanding of these conditions and treatments may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.
Share: