Can Chagas Disease be Cured?
Sometimes
Treatment can be effective, especially in the acute phase; chronic cases may manage symptoms but not eliminate the infection
What is Chagas Disease?
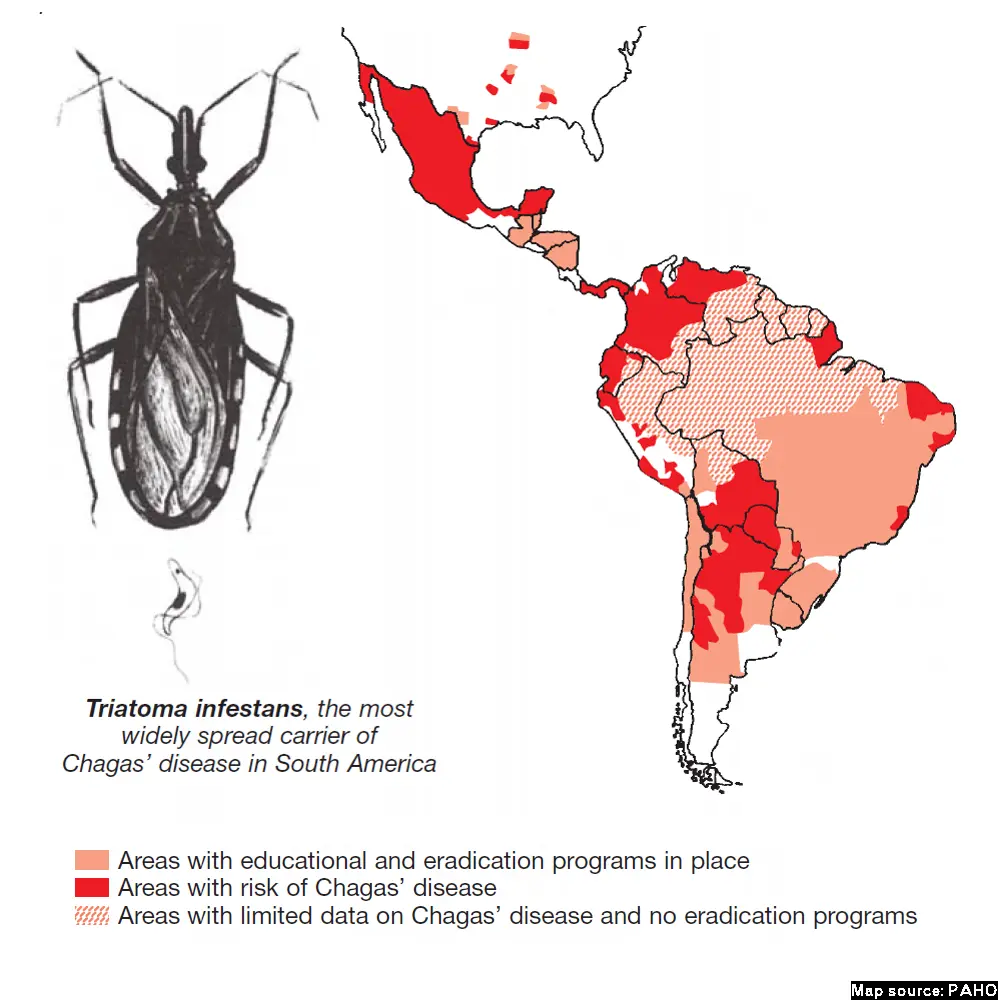
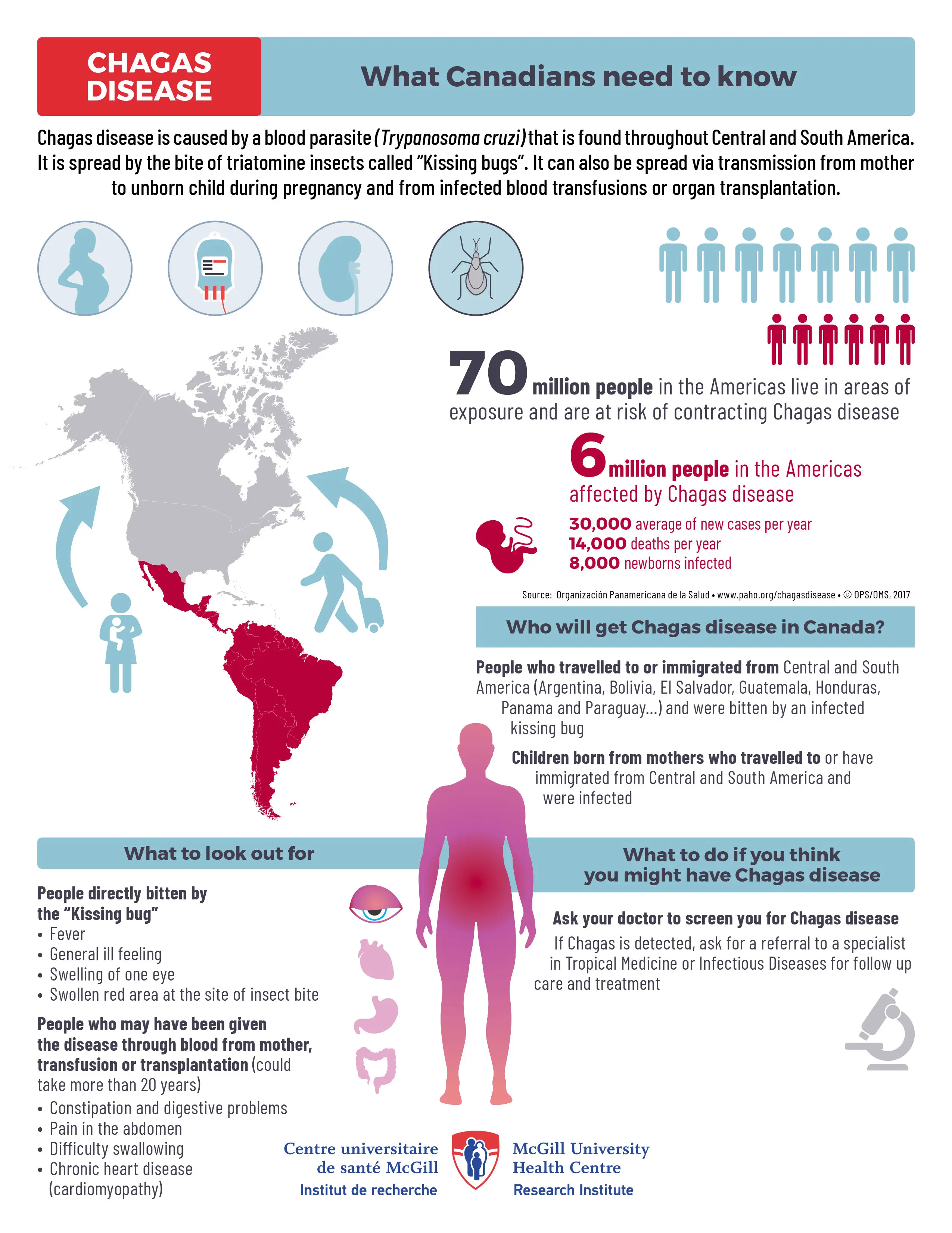
Chagas disease is a tropical parasitic infection caused by the Trypanosoma cruzi parasite. It is transmitted primarily by triatomine bugs. The disease has acute and chronic phases, and treatment involves antiparasitic medications. Early detection and treatment are crucial.
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Tropical parasitic infection caused by the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi

Symptoms
Acute phase: fever, fatigue, body aches; Chronic phase: heart or digestive system complications

Diagnosis
Serological tests, PCR

Prognosis
Variable, acute to chronic progression

Complications
Cardiac and gastrointestinal complications
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Triatomine bug (kissing bug) bites, blood transfusions, organ transplants, or congenital transmission from mother to child

Treatments
Antiparasitic medications (benznidazole or nifurtimox), supportive care

Prevention
Antiparasitic medications (benznidazole or nifurtimox), supportive care
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Endemic in Latin America, emerging globally

Patient Perspectives
Early detection crucial for effective treatment
Please remember that this information is provided for general understanding, and individual cases may vary. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and information.
Share: