Can Calculi be Cured?
Sometimes
Management depends on the type and location of the calculi; some may pass on their own, while others may require intervention
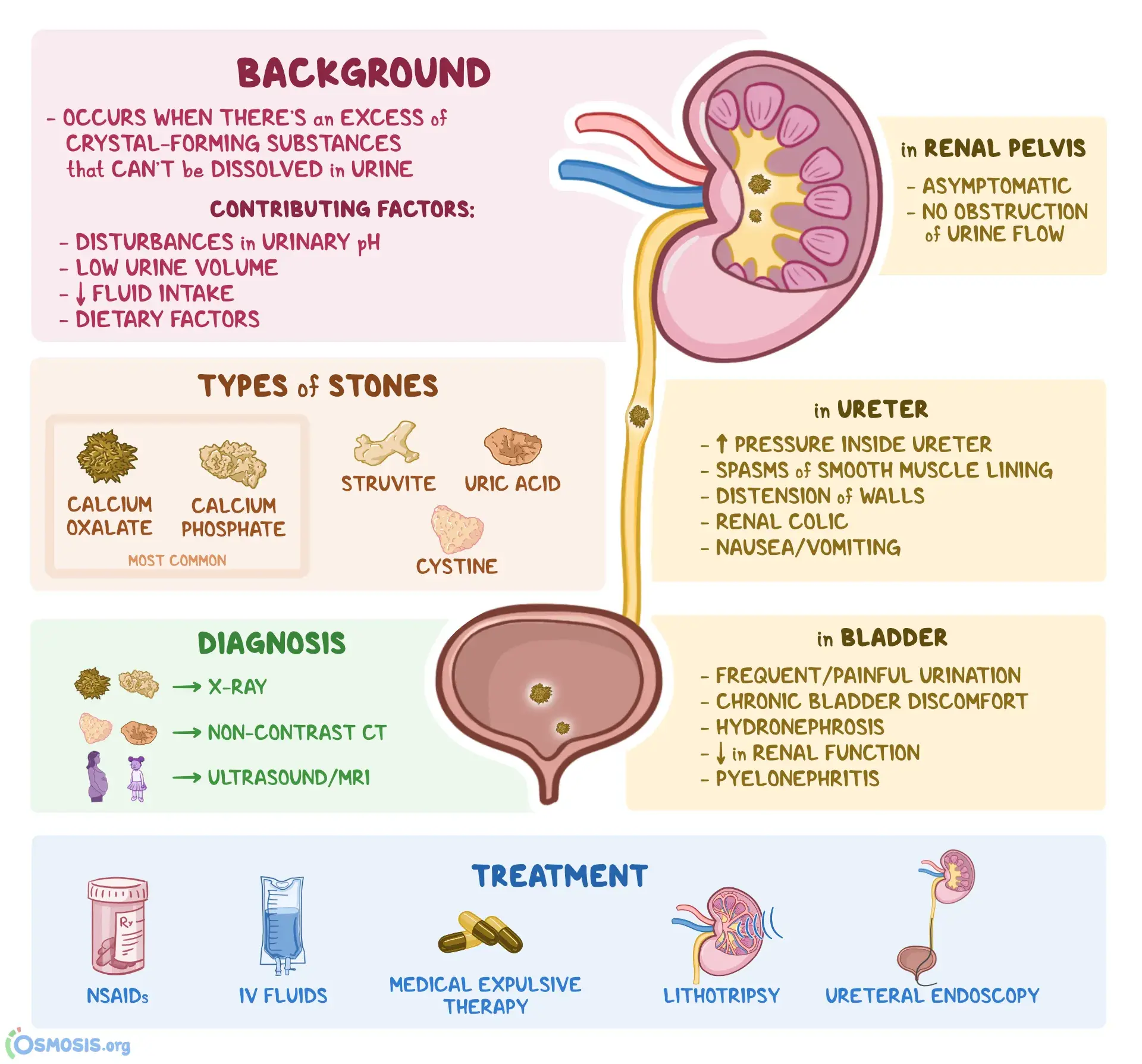
What is Calculi?
Calculi are stones or concretions formed in the body, such as kidney stones (renal calculi) or gallstones (cholelithiasis). Treatment depends on the type and location of the calculi and may involve medications, lifestyle changes, or surgical intervention.

Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Stones or concretions formed in various organs

Symptoms
Pain, urinary symptoms (if in the urinary tract), digestive symptoms (if in the digestive system)

Diagnosis
Imaging studies, laboratory tests

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the type and location of calculi

Complications
Obstruction, organ damage, infections
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Formation of stones in the kidneys, gallbladder, bladder, or other organs

Treatments
Fluid intake, dietary changes, medications, sometimes procedures to remove or break up stones (e.g., lithotripsy)

Prevention
Fluid intake, dietary changes, medications, sometimes procedures to remove or break up stones (e.g., lithotripsy)
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Formation of stones in various organs

Patient Perspectives
Prevention measures and appropriate treatment depend on the type and location of calculi
Please remember that this information is provided for general understanding, and individual cases may vary. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and information.
Share: