Can Beta Thalassemia be Cured?
No
Lifelong management is required; cure may be possible with bone marrow transplant
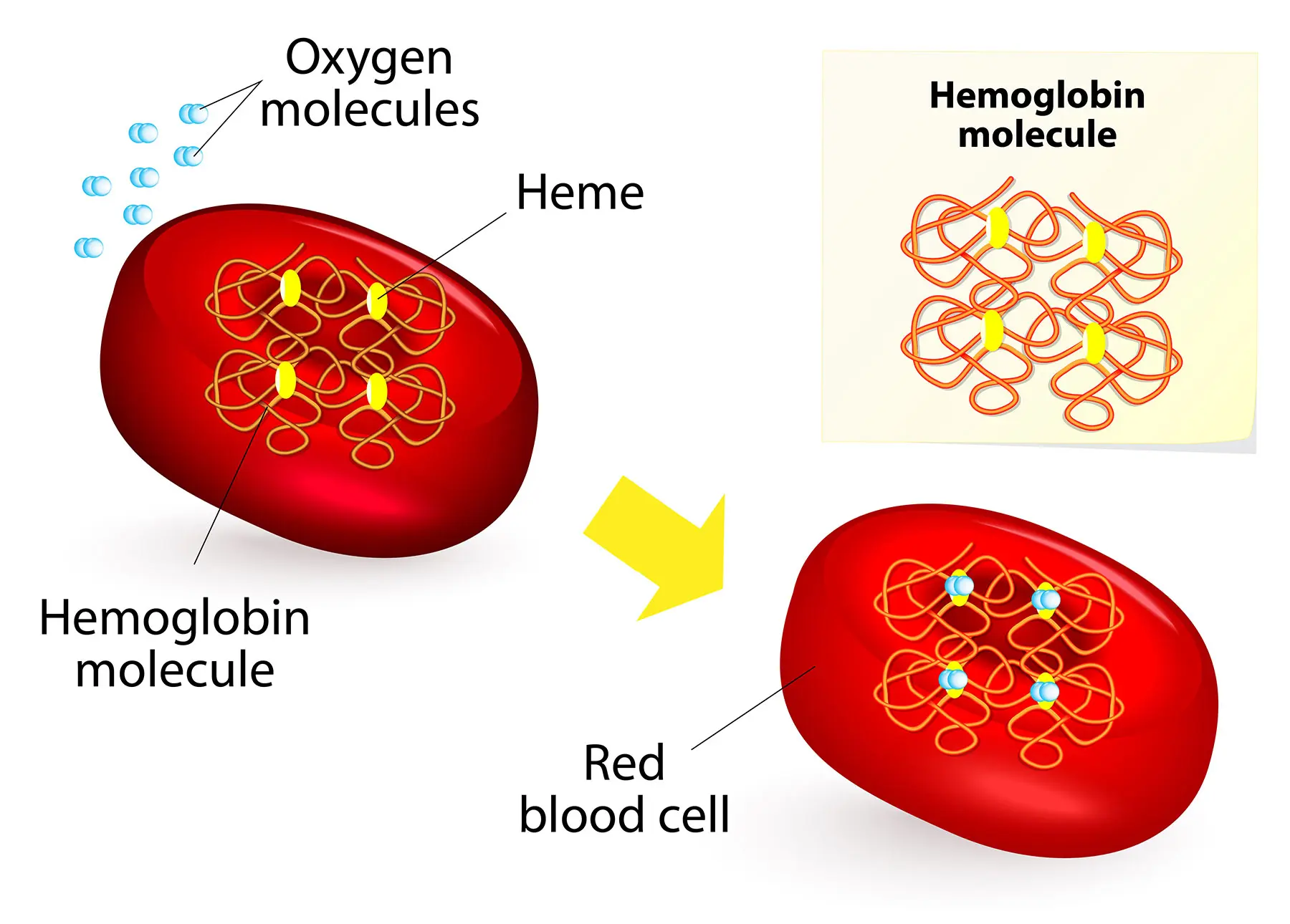
What is Beta Thalassemia?
Beta thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder characterized by reduced or absent production of beta-globin chains, leading to anemia. Treatment may include blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy, and, in severe cases, bone marrow transplantation.
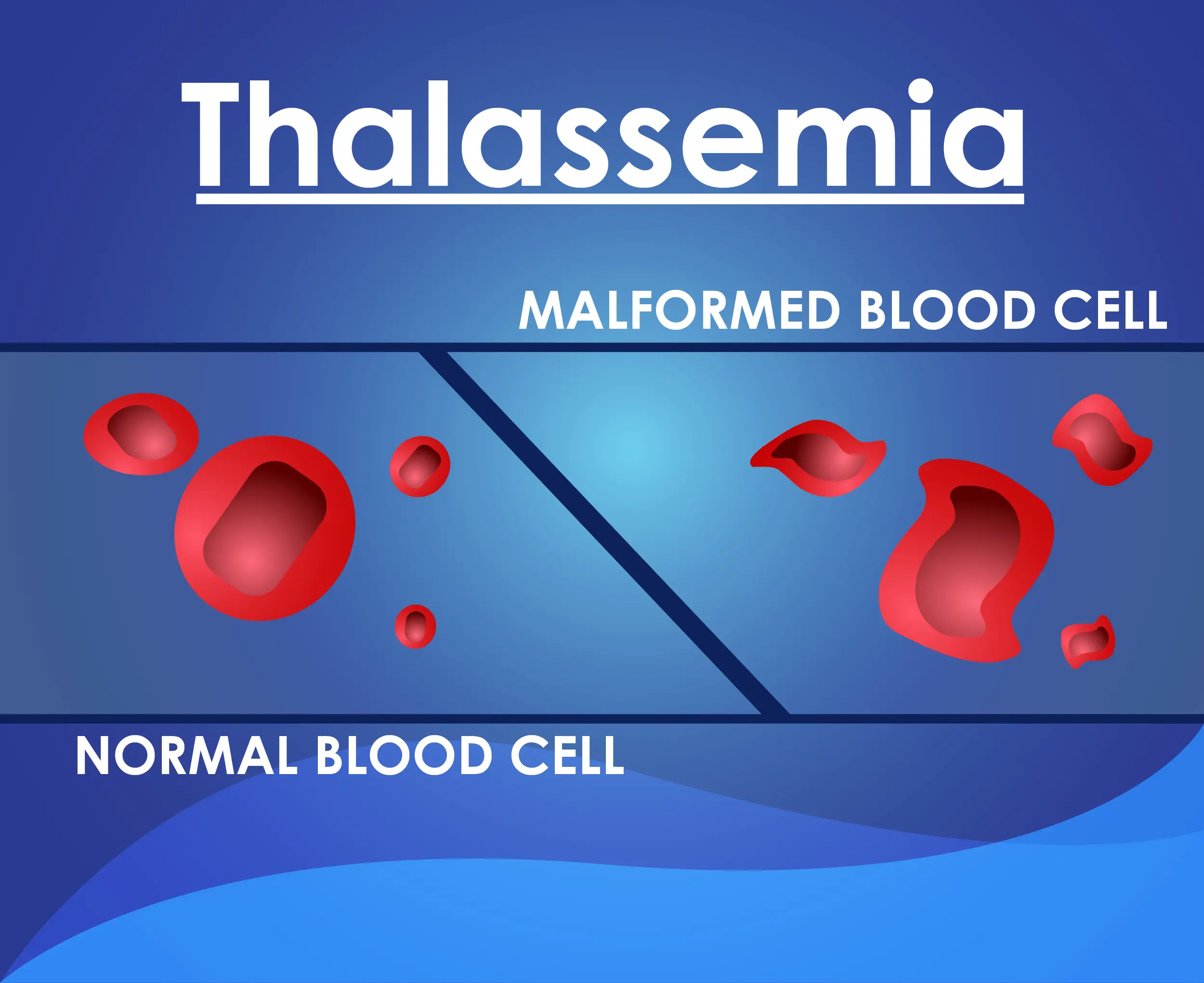
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Inherited blood disorder affecting hemoglobin synthesis

Symptoms
Anemia, fatigue, growth delay

Diagnosis
Genetic testing, blood tests

Prognosis
Variable; depends on the type and severity of thalassemia

Complications
Anemia, complications in severe cases
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic mutations

Treatments
Blood transfusions, iron chelation, bone marrow transplant

Prevention
Blood transfusions, iron chelation, bone marrow transplant
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Genetic disorder affecting hemoglobin production

Patient Perspectives
Individualized care based on the type and severity of thalassemia
Remember, the information provided here is intended for general knowledge purposes and may not apply to every individual case. To ensure you have accurate information relevant to your specific situation, always consult with a healthcare professional.
Share: