Can Asthma be Cured?
No
Manageable with treatment, but no cure; ongoing management focuses on controlling symptoms and preventing exacerbations
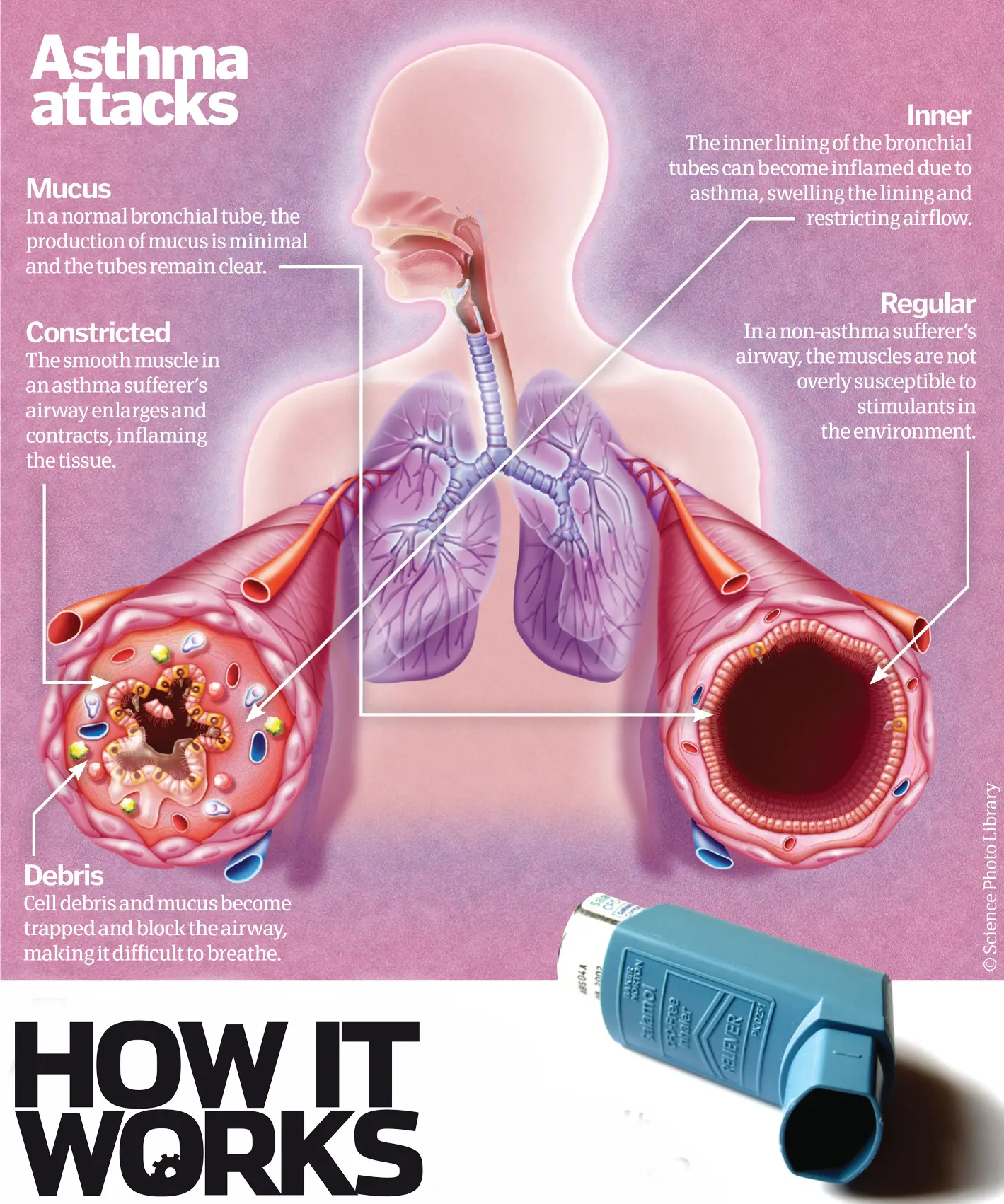
What is Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation of the airways, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. Treatment includes bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory medications, and management of triggers.
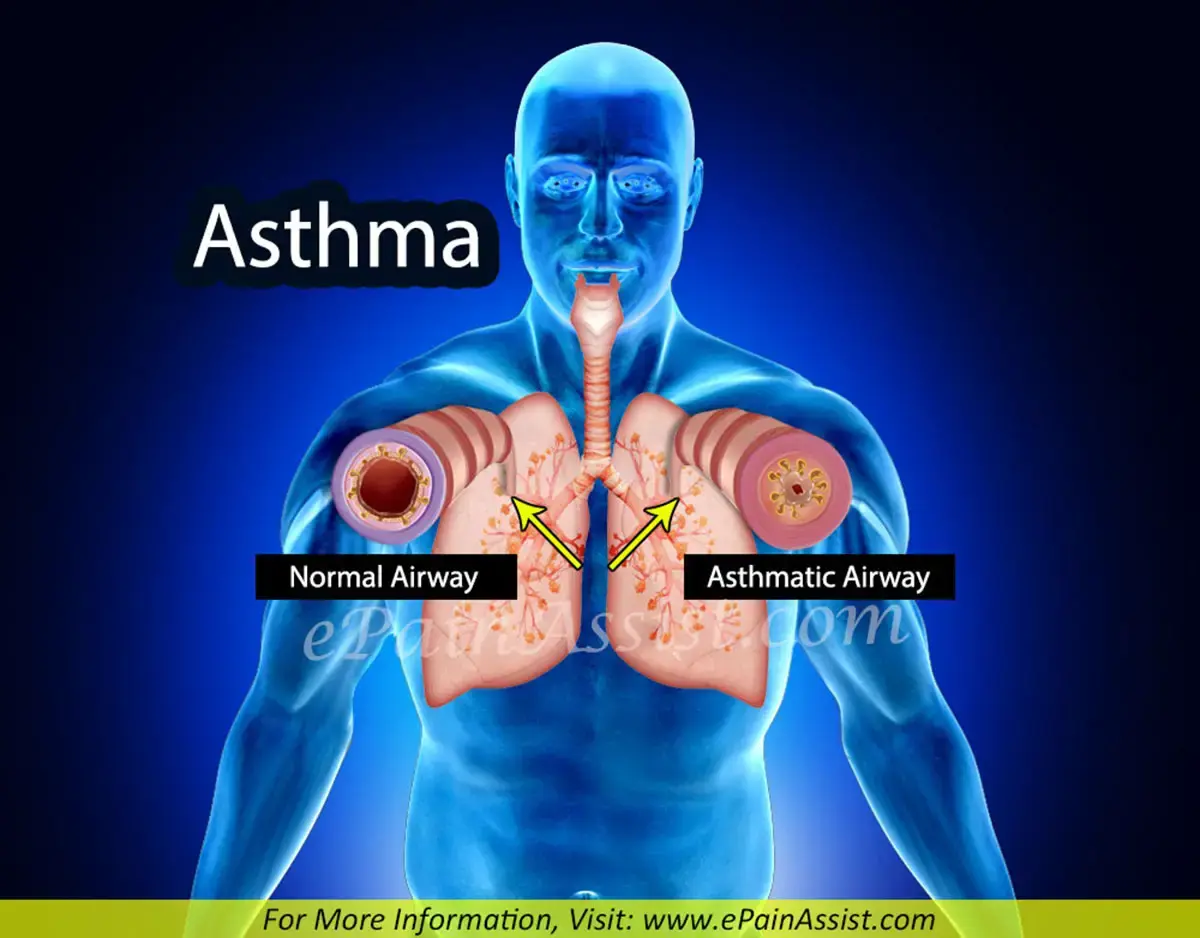
Clinical Aspects

Characteristics
Chronic inflammatory condition of the airways leading to episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing

Symptoms
Wheezing, shortness of breath, coughing, chest tightness

Diagnosis
Lung function tests, clinical evaluation

Prognosis
Variable; can be well-controlled with proper management

Complications
Respiratory distress, impaired quality of life
Etiology and Treatment

Causes
Genetic and environmental factors, including exposure to allergens and irritants

Treatments
Bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, lifestyle management, allergy medications

Prevention
Bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, lifestyle management, allergy medications
Public Health and Patient Perspectives

Epidemiology
Common chronic respiratory condition; often begins in childhood

Patient Perspectives
Long-term management, education, and regular monitoring are key
Please remember that this information is provided for general understanding, and individual cases may vary. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and information.
Share: